
A particle is executing SHM with time period $T$. Starting from mean position, time taken by it to complete $\dfrac{5}{8}$ oscillations, is
A. $\dfrac{T}{{12}}$
B. $\dfrac{T}{6}$
C. $\dfrac{{5T}}{{12}}$
D. $\dfrac{{7T}}{{12}}$
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: To solve the given question we will use the concept of phasor diagram. A phasor diagram is used to represent two or more stationary sinusoidal quantities at any instant of time. The projection of phasor onto an axis at a specific time gives the value of the quantity at that time.
Formula used:
$Y = A\sin \omega t$
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to phasor diagram concept, we know that
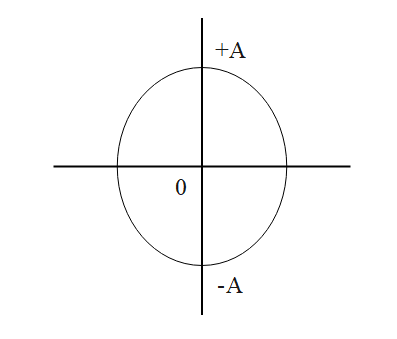
So, Total distance covered by a particle in one oscillation $ = 4A$
we will divide this whole path in $8$ intervals,
Then, each interval would be of measurement $\dfrac{A}{2}$
So, $\dfrac{5}{8}$ oscillations mean, it has already completed $\dfrac{1}{2}$ oscillations
i.e. total distance $ = 2A$ and is halfway to the other side which is $\dfrac{A}{2}$.
Equation of SHM is given by, $Y = A\sin \omega t$; where $A = $ amplitude and $\omega = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{T}$
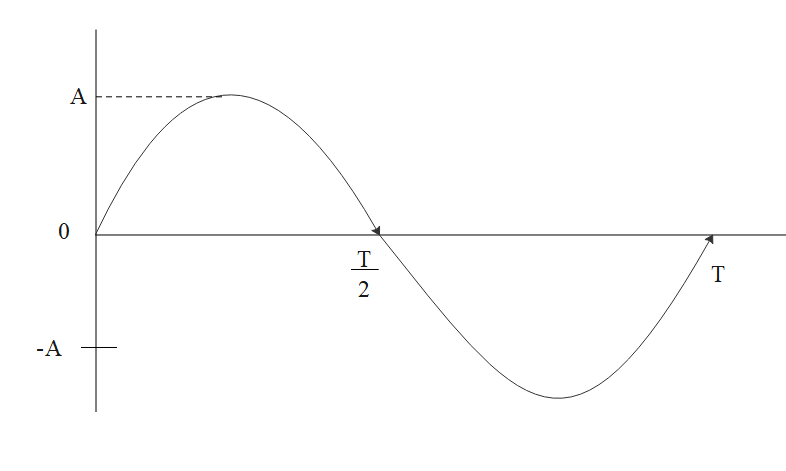
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{A}{2} = A\sin \dfrac{{2\pi }}{T} \times t$
$t = \dfrac{T}{{12}}$
Now, substituting $t = \dfrac{T}{{12}}$
Total time taken = time to complete previous $\dfrac{1}{2}$ oscillations + time taken to complete $\dfrac{A}{2}$
$ = \dfrac{t}{2} + \dfrac{t}{{12}} = \dfrac{{7T}}{{12}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information: Phasor diagrams are used in simple harmonic motion and RLC circuits which have elements that are out of phase with one another and thus difficult to work with in configuration space.
When the motion of a particle performing uniform circular motion is projected onto its diameter, the projection undergoes simple harmonic motion. The circular motion is the representation of SHM in the phase diagram or phasor, and the angular velocity of this circular motion is the frequency of the SHM.
Note: The equation of SHM explicitly represents a sinusoidal function, i.e. it represents a function which varies periodically with time. Amplitude is defined as the maximum displacement. The shortest time taken to complete one oscillation is defined as the time period.
Formula used:
$Y = A\sin \omega t$
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to phasor diagram concept, we know that

So, Total distance covered by a particle in one oscillation $ = 4A$
we will divide this whole path in $8$ intervals,
Then, each interval would be of measurement $\dfrac{A}{2}$
So, $\dfrac{5}{8}$ oscillations mean, it has already completed $\dfrac{1}{2}$ oscillations
i.e. total distance $ = 2A$ and is halfway to the other side which is $\dfrac{A}{2}$.
Equation of SHM is given by, $Y = A\sin \omega t$; where $A = $ amplitude and $\omega = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{T}$

$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{A}{2} = A\sin \dfrac{{2\pi }}{T} \times t$
$t = \dfrac{T}{{12}}$
Now, substituting $t = \dfrac{T}{{12}}$
Total time taken = time to complete previous $\dfrac{1}{2}$ oscillations + time taken to complete $\dfrac{A}{2}$
$ = \dfrac{t}{2} + \dfrac{t}{{12}} = \dfrac{{7T}}{{12}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information: Phasor diagrams are used in simple harmonic motion and RLC circuits which have elements that are out of phase with one another and thus difficult to work with in configuration space.
When the motion of a particle performing uniform circular motion is projected onto its diameter, the projection undergoes simple harmonic motion. The circular motion is the representation of SHM in the phase diagram or phasor, and the angular velocity of this circular motion is the frequency of the SHM.
Note: The equation of SHM explicitly represents a sinusoidal function, i.e. it represents a function which varies periodically with time. Amplitude is defined as the maximum displacement. The shortest time taken to complete one oscillation is defined as the time period.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




