
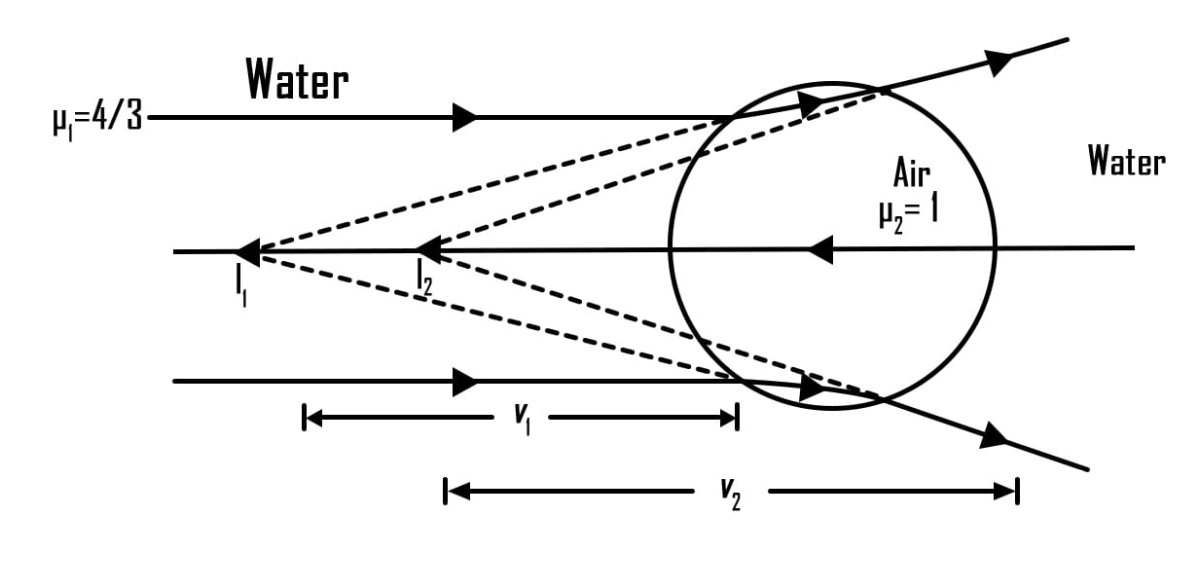
A parallel beam of light travelling in water (Refractive index$\dfrac{4}{3}$) is refracted by a spherical air bubble of radius 2mm situated in water. Assuming the light ray to be paraxial, Find out the distance between a final image from the centre of the bubble in mm.
Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint: Recall the equations of refraction through spherical surfaces. Use that equation for the two cases as given in the question.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\mu {}_2}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{\mu {}_2 - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Where u = object distance, v= Image distance, R=radius of curvature
$\mu {}_2$and$\mu {}_1$ is the refractive index of the two media.
Complete step by step answer:
Step1:
Use the relation of refraction at spherical surfaces for the case 1.
We have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\mu {}_2}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{\mu {}_2 - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Where u = object distance=$\infty $,
v= Image distance,
R=radius of curvature=2mm,
And ${\mu _1} = \dfrac{4}{3}$ & ${\mu _2} = 1$are the refractive indices at object and image side respectively.
Substitute all the values in above r=equation for case 1
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v_1}}} - \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)}}{\infty } = \dfrac{{1 - \left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v_1}}} - 0 = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{3}} \right)}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v_1}}} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{6}$
$ \Rightarrow {v_1} = - 6mm$
Step2:
Now again use the same equation for the second case.
For the second case the object distance =6+4=10 mm
Using sign conventions u=-10mm
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\mu {}_2}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{\mu {}_2 - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Again substituting all values in the equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)}}{{{v_2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{( - 10)}} = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right) - 1}}{2}$
Now simplifying the above equation to calculate the final image distance,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{{3{v_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{10}} = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}} \right)}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow {v_2} = - 5mm$
This is the required image distance.
Additional information:
The focal length of a lens depends on the refractive index of the lens and the radii of curvature. The lens maker’s equation is another formula used for lenses that give us a relationship between the focal length, refractive index, and radii of curvature of the two spheres used in lenses.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right]$
Where f=focal length, $\mu $=refractive index, ${R_1}$ and ${R_2}$are the radii of the two surfaces of the lens.
Note: For the second case in this question, the object distance is taken as the image distance of the first case because for the second case the object is the image in the first case. Use the sign conventions carefully, always consider signs accordingly.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\mu {}_2}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{\mu {}_2 - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Where u = object distance, v= Image distance, R=radius of curvature
$\mu {}_2$and$\mu {}_1$ is the refractive index of the two media.
Complete step by step answer:
Step1:
Use the relation of refraction at spherical surfaces for the case 1.
We have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\mu {}_2}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{\mu {}_2 - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Where u = object distance=$\infty $,
v= Image distance,
R=radius of curvature=2mm,
And ${\mu _1} = \dfrac{4}{3}$ & ${\mu _2} = 1$are the refractive indices at object and image side respectively.
Substitute all the values in above r=equation for case 1
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v_1}}} - \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)}}{\infty } = \dfrac{{1 - \left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v_1}}} - 0 = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{3}} \right)}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v_1}}} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{6}$
$ \Rightarrow {v_1} = - 6mm$

Step2:
Now again use the same equation for the second case.
For the second case the object distance =6+4=10 mm
Using sign conventions u=-10mm
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\mu {}_2}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{\mu {}_2 - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Again substituting all values in the equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)}}{{{v_2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{( - 10)}} = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right) - 1}}{2}$
Now simplifying the above equation to calculate the final image distance,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{{3{v_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{10}} = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}} \right)}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow {v_2} = - 5mm$
This is the required image distance.
Additional information:
The focal length of a lens depends on the refractive index of the lens and the radii of curvature. The lens maker’s equation is another formula used for lenses that give us a relationship between the focal length, refractive index, and radii of curvature of the two spheres used in lenses.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right]$
Where f=focal length, $\mu $=refractive index, ${R_1}$ and ${R_2}$are the radii of the two surfaces of the lens.
Note: For the second case in this question, the object distance is taken as the image distance of the first case because for the second case the object is the image in the first case. Use the sign conventions carefully, always consider signs accordingly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




