
A nylon guitar string has a linear density of $7.20g/m$ and is under a tension of $150N$. The fixed supports are distance D$ = 90cm$ apart. The string is oscillating in the standing wave pattern shown in the figure.
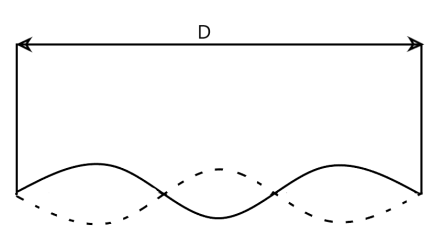
(I) The speed of the travelling waves whose superposition gives this standing wave
(A) $\dfrac{{125}}{{\sqrt 3 }}m/s$
(B) $\dfrac{{500}}{{\sqrt 3 }}m/s$
(C) $\dfrac{{250}}{{\sqrt 3 }}m/s$
(D) $100\sqrt 3 m/s$
(II) The wavelength of the travelling waves whose superposition gives this standing wave
(A) $20cm$
(B) $40.0cm$
(C) $60.0cm$
(D) $80.0cm$
(III) The frequency of the travelling waves whose superposition gives this standing wave
(A) $\dfrac{{1000}}{{3\sqrt 3 }}Hz$
(B) $\dfrac{{1250}}{{3\sqrt 3 }}Hz$
(C)$\dfrac{{1500}}{{3\sqrt 3 }}Hz$
(D) $\dfrac{{1750}}{{3\sqrt 3 }}Hz$

Answer
543.3k+ views
Hint: The speed of the wave has a relation with the linear density$(\mu )$ and tension$(T)$ as speed $v = \sqrt {\dfrac{T}{\mu }} $ . And wavelength is basically the distance between two successive crests or troughs of a wave. The frequency of a wave is the ratio of the speed and the wavelength of the wave.
Complete answer:
The pulling force along the length or the tension is given $150N$ and mass per unit length or linear density is given $7.20g/m$ .
(I) So $T = 150N$ and $\mu = 7.20g/m$ $ = 7.20 \times {10^{ - 3}}kg/m$
Now $v = \sqrt {\dfrac{T}{\mu }} $ $ = \sqrt {\dfrac{{150}}{{7.20 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}} $ $m/s$
$ = \sqrt {\dfrac{{150}}{{720 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}}}} $$m/s$
$ = \sqrt {\dfrac{{150 \times {{10}^5}}}{{720}}} $ $m/s$
$ = \sqrt {\dfrac{{62500}}{3}} m/s$
$ = \dfrac{{250}}{{\sqrt 3 }}m/s$
So, the speed of the travelling waves whose superposition gives this standing wave is $\dfrac{{250}}{{\sqrt 3 }}m/s$.
The correct answer is option (C)
(II) Wavelength is the distance between two successive crests or troughs. So we can draw the wavelength for this wave like
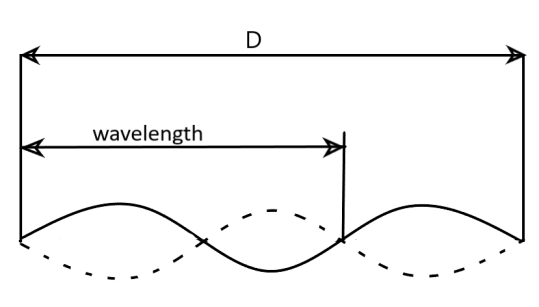
Two half cycles complete a wavelength$(\lambda )$. So one half cycle means $\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ . Here $3$ half cycles are present in between distance $D$$ = 90cm$
Hence, $3 \times \dfrac{\lambda }{2} = 90$
$ \Rightarrow \lambda = 30 \times 2$
$ \Rightarrow \lambda = 60$
So, the wavelength of the travelling waves whose superposition gives this standing wave is $60.0cm$.
The correct answer is option (C)
(III) The ratio of the speed of speed and wavelength of the wave is its frequency. Frequency describes the number of waves that pass a particular place in a particular time.
So, frequency $ = \dfrac{v}{\lambda }$ [ where $v$ is the speed and $\lambda $ is the wavelength of that wave]
Now $v = \dfrac{{250}}{{\sqrt 3 }}m/s$ and $\lambda = 60cm = .6m$
Frequency $ = $ $\dfrac{{250}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \div 0.6$$Hz$
$ = \dfrac{{2500}}{{6\sqrt 3 }}$$Hz$
$ = \dfrac{{1250}}{{3\sqrt 3 }}$$Hz$
So, the frequency of the travelling waves whose superposition gives this standing wave is $\dfrac{{1250}}{{3\sqrt 3 }}Hz$
The correct answer is option (B).
Note:
A guitar string has a number of frequencies at which it vibrates naturally. These natural frequencies are called the harmonics of the guitar strings. And the natural frequency and wavelength depend upon the tension, linear density and the tension of the string. Solving this problem with making a meaningful diagram makes this problem a lot easier to solve.
Complete answer:
The pulling force along the length or the tension is given $150N$ and mass per unit length or linear density is given $7.20g/m$ .
(I) So $T = 150N$ and $\mu = 7.20g/m$ $ = 7.20 \times {10^{ - 3}}kg/m$
Now $v = \sqrt {\dfrac{T}{\mu }} $ $ = \sqrt {\dfrac{{150}}{{7.20 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}} $ $m/s$
$ = \sqrt {\dfrac{{150}}{{720 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}}}} $$m/s$
$ = \sqrt {\dfrac{{150 \times {{10}^5}}}{{720}}} $ $m/s$
$ = \sqrt {\dfrac{{62500}}{3}} m/s$
$ = \dfrac{{250}}{{\sqrt 3 }}m/s$
So, the speed of the travelling waves whose superposition gives this standing wave is $\dfrac{{250}}{{\sqrt 3 }}m/s$.
The correct answer is option (C)
(II) Wavelength is the distance between two successive crests or troughs. So we can draw the wavelength for this wave like

Two half cycles complete a wavelength$(\lambda )$. So one half cycle means $\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ . Here $3$ half cycles are present in between distance $D$$ = 90cm$
Hence, $3 \times \dfrac{\lambda }{2} = 90$
$ \Rightarrow \lambda = 30 \times 2$
$ \Rightarrow \lambda = 60$
So, the wavelength of the travelling waves whose superposition gives this standing wave is $60.0cm$.
The correct answer is option (C)
(III) The ratio of the speed of speed and wavelength of the wave is its frequency. Frequency describes the number of waves that pass a particular place in a particular time.
So, frequency $ = \dfrac{v}{\lambda }$ [ where $v$ is the speed and $\lambda $ is the wavelength of that wave]
Now $v = \dfrac{{250}}{{\sqrt 3 }}m/s$ and $\lambda = 60cm = .6m$
Frequency $ = $ $\dfrac{{250}}{{\sqrt 3 }} \div 0.6$$Hz$
$ = \dfrac{{2500}}{{6\sqrt 3 }}$$Hz$
$ = \dfrac{{1250}}{{3\sqrt 3 }}$$Hz$
So, the frequency of the travelling waves whose superposition gives this standing wave is $\dfrac{{1250}}{{3\sqrt 3 }}Hz$
The correct answer is option (B).
Note:
A guitar string has a number of frequencies at which it vibrates naturally. These natural frequencies are called the harmonics of the guitar strings. And the natural frequency and wavelength depend upon the tension, linear density and the tension of the string. Solving this problem with making a meaningful diagram makes this problem a lot easier to solve.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




