
a) Name the type of current
1. Used in household supply
2. Given by a battery
b) What is an electromagnet?
c) Draw a labelled diagram to show how an electromagnet is made
d) What is the purpose of the soft iron core used in making an electromagnet?
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: An electromagnet can simply be a turn of wire. The voltage across a cell is ideally constant. Currents can be direct or alternating.
Complete step by step solution:
a) Generally, there are two types of current, direct current and alternate current.
Direct current – these are the types of current which are steady and flow in one direction, that is to say they do not change values with time.
Alternate current – this is a type of current which reverses direction constantly and hence changes its value with time.
In household supply, the ac current is used as it can be stepped up and down with a transformer.
A cell gives a direct current since it is dependent on the voltage across its terminals which are ideally constant.
b) An electromagnet, by definition, is simply a type of magnets whose magnetic fields are generated by a physical (macro) electric current. Generally when charges move, they generate a magnetic field, and since current is the time rate of movement of charges, magnetic fields are generated around a current carrying wire.
c)
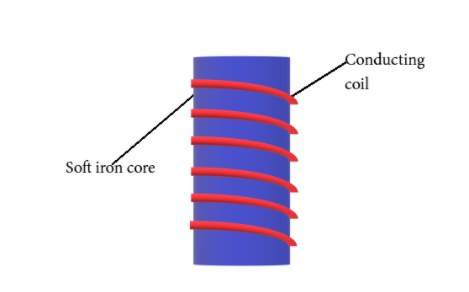
d) The soft iron used in making an electromagnet is simply there for the purpose of increasing the magnetic field of the electromagnet.
Note: To avoid confusions, note that although direct current does not change with time, it can change with position. In a circuit, the current flowing through one branch is not necessarily equal to the current flowing through the other.
The soft iron cores in electromagnets are able to increase the magnetic field because of its higher magnetic permeability. Materials with high permeability amplify the magnetic field that passes through them.
Complete step by step solution:
a) Generally, there are two types of current, direct current and alternate current.
Direct current – these are the types of current which are steady and flow in one direction, that is to say they do not change values with time.
Alternate current – this is a type of current which reverses direction constantly and hence changes its value with time.
In household supply, the ac current is used as it can be stepped up and down with a transformer.
A cell gives a direct current since it is dependent on the voltage across its terminals which are ideally constant.
b) An electromagnet, by definition, is simply a type of magnets whose magnetic fields are generated by a physical (macro) electric current. Generally when charges move, they generate a magnetic field, and since current is the time rate of movement of charges, magnetic fields are generated around a current carrying wire.
c)

d) The soft iron used in making an electromagnet is simply there for the purpose of increasing the magnetic field of the electromagnet.
Note: To avoid confusions, note that although direct current does not change with time, it can change with position. In a circuit, the current flowing through one branch is not necessarily equal to the current flowing through the other.
The soft iron cores in electromagnets are able to increase the magnetic field because of its higher magnetic permeability. Materials with high permeability amplify the magnetic field that passes through them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




