
A n – p – n transistor conducts in active mode when
A) Both collector and emitter are positive with respect to the base
B) Collector is positive and the emitter is negative with respect to the base
C) Collector is positive and emitter is at the same potential as the base
D) Both collector and emitter are negative with respect to the base
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint:
From the setup of the n – p – n transistor, we can observe the conditions for it to be in active mode.
In n we have negatively charged electrons and in p we have positively charged protons.
When n is connected to the negative terminal or p is connected to the positive terminal of a cell/battery it is called forward biasing and when n is connected to positive terminal or p is connected to the negative terminal of a cell/battery it is called reverse biasing.
Complete step by step answer:
The setup of a n – p – n transistor is:
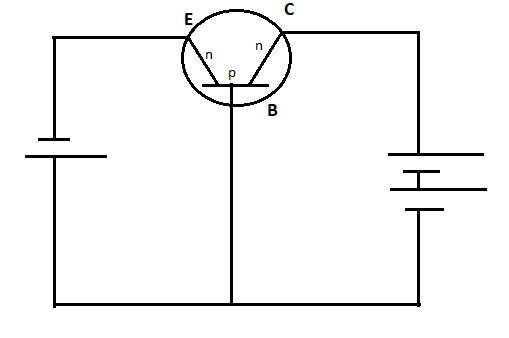
Here,
E = Emitter
B = Base
C = Collector
We can see that,
The emitter is forward biased (n is connected to the negative terminal of cell)
The collector is reverse biased (n is connected to the positive terminal of cell)
🡪 This is when the transistor is in active mode
Relationship of emitter and collector with respect to the base:
The emitter is negative. [Connected to negative terminal]
The collector is positive. [Connected to positive terminal]
Therefore, among the options, option B) stating that the collector is positive and the emitter is negative with respect to the base is correct.
Note:Doping levels of the layer of transitions:
Emitter: Thick layer, heavily doped
Base: Thin layer, lightly doped
Collector: Thick layer, moderately doped
🡪Here doping refers to the number of protons or electrons present in these layers
From the setup of the n – p – n transistor, we can observe the conditions for it to be in active mode.
In n we have negatively charged electrons and in p we have positively charged protons.
When n is connected to the negative terminal or p is connected to the positive terminal of a cell/battery it is called forward biasing and when n is connected to positive terminal or p is connected to the negative terminal of a cell/battery it is called reverse biasing.
Complete step by step answer:
The setup of a n – p – n transistor is:

Here,
E = Emitter
B = Base
C = Collector
We can see that,
The emitter is forward biased (n is connected to the negative terminal of cell)
The collector is reverse biased (n is connected to the positive terminal of cell)
🡪 This is when the transistor is in active mode
Relationship of emitter and collector with respect to the base:
The emitter is negative. [Connected to negative terminal]
The collector is positive. [Connected to positive terminal]
Therefore, among the options, option B) stating that the collector is positive and the emitter is negative with respect to the base is correct.
Note:Doping levels of the layer of transitions:
Emitter: Thick layer, heavily doped
Base: Thin layer, lightly doped
Collector: Thick layer, moderately doped
🡪Here doping refers to the number of protons or electrons present in these layers
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




