
A mixture of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$, ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$ and ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ is bubbled through alkaline solution of copper (I) chloride, contained in Woulf’s bottle. The gas coming out is:
A.Original mixture
B.${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$
C.${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ and ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$ mixture
D.${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$ and ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint:Alkynes react with copper (I) chloride and form a red-brown coloured precipitate. Alkenes and alkanes do not react with copper (I) chloride.
Complete step by step answer:
When a mixture of ethyne $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$, ethene $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}} \right)$ and ethane $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}} \right)$ is bubbled through an alkaline solution of copper (I) chloride:
Ethyne $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$ reacts with the alkaline solution of copper (I) chloride.
Ethene $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}} \right)$ and ethane $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}} \right)$ do not react with the alkaline solution of copper chloride and come out as gas.
Thus, the gas coming out is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ and ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$ mixture.
Thus, the correct option is option (C).
Additional Information:
Ethane and ethene do not react with the alkaline solution of copper (I) chloride as they do not have acidic hydrogen.
Note: The reaction of ethyne $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$ with an alkaline solution of copper (I) chloride is as follows:
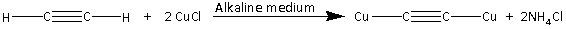
Copper (I) acetylide is produced in the reaction. Copper (I) acetylide is a brown colored precipitate.
Complete step by step answer:
When a mixture of ethyne $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$, ethene $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}} \right)$ and ethane $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}} \right)$ is bubbled through an alkaline solution of copper (I) chloride:
Ethyne $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$ reacts with the alkaline solution of copper (I) chloride.
Ethene $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}} \right)$ and ethane $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}} \right)$ do not react with the alkaline solution of copper chloride and come out as gas.
Thus, the gas coming out is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ and ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$ mixture.
Thus, the correct option is option (C).
Additional Information:
Ethane and ethene do not react with the alkaline solution of copper (I) chloride as they do not have acidic hydrogen.
Note: The reaction of ethyne $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$ with an alkaline solution of copper (I) chloride is as follows:
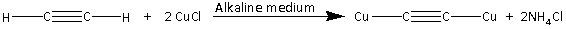
Copper (I) acetylide is produced in the reaction. Copper (I) acetylide is a brown colored precipitate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




