
A mixture is known to contain $N{{O}_{3}}^{-}$ and $N{{O}_{2}}^{-}$. Before performing ring test for $N{{O}_{3}}^{-}$ the aqueous solution should be made free of $N{{O}_{2}}^{-}$. This is done by heating aqueous extract with:
(A) conc. $HN{{O}_{3}}$
(B) dil. $HN{{O}_{3}}$
(C) urea
(D) zinc dust
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: An attempt to this question can be made by determining the difference between the two ions under consideration. Now evaluate the reagents mentioned in the options and their possible reactions with the two ions, $N{{O}_{3}}^{-}$ and $N{{O}_{2}}^{-}$. Based on this you can determine the reagent that will react with just $N{{O}_{2}}^{-}$ and remove it from the solution.
Complete Solution :
We will draw the expanded structure of nitrite ion as well as nitrate ion.
- The oxidation state of nitrogen in nitrite is +3 and +5 in case of nitrate.
Concentrated and dilute $HN{{O}_{3}}$ do not react with either $N{{O}_{3}}^{-}$ or $N{{O}_{2}}^{-}$ ion in the solution.
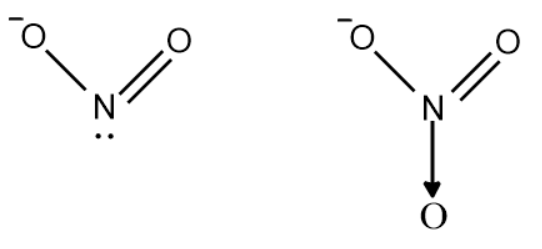
- Urea reacts with $N{{O}_{2}}^{-}$ and reduces nitrogen to its molecular form. Nitrogen along with other gases are released into air separating it from the nitrate solution to perform a ring test.
We will write the reaction below for better understanding.
$CO(N{{H}_{2}})\,+\,HN{{O}_{2}}\,\to \,\,\,2{{N}_{2}}\uparrow \,\,+\,C{{O}_{2}}\,\uparrow \,\,+\,3{{H}_{2}}O$
- In the above reaction we see that the products, nitrogen and carbon dioxide are in gaseous form and thus do not stay in the solution. This reaction is exothermic and thus will occur spontaneously without the supply of any extra energy.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The reason why urea is used to separate nitrite from the mixture is because nitrite ions interfere with nitrate ions during the brown ring test. Nitrite ions too react with the brown ring test reagent and thus needs to be eliminated from the solution before performing the ring test.
Complete Solution :
We will draw the expanded structure of nitrite ion as well as nitrate ion.
- The oxidation state of nitrogen in nitrite is +3 and +5 in case of nitrate.
Concentrated and dilute $HN{{O}_{3}}$ do not react with either $N{{O}_{3}}^{-}$ or $N{{O}_{2}}^{-}$ ion in the solution.

- Urea reacts with $N{{O}_{2}}^{-}$ and reduces nitrogen to its molecular form. Nitrogen along with other gases are released into air separating it from the nitrate solution to perform a ring test.
We will write the reaction below for better understanding.
$CO(N{{H}_{2}})\,+\,HN{{O}_{2}}\,\to \,\,\,2{{N}_{2}}\uparrow \,\,+\,C{{O}_{2}}\,\uparrow \,\,+\,3{{H}_{2}}O$
- In the above reaction we see that the products, nitrogen and carbon dioxide are in gaseous form and thus do not stay in the solution. This reaction is exothermic and thus will occur spontaneously without the supply of any extra energy.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The reason why urea is used to separate nitrite from the mixture is because nitrite ions interfere with nitrate ions during the brown ring test. Nitrite ions too react with the brown ring test reagent and thus needs to be eliminated from the solution before performing the ring test.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




