
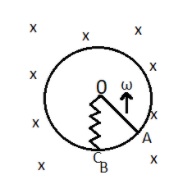
A metallic rod of ′L′ length is rotated with angular frequency of \[\omega \] with one end hinged at the center and the other end at the circumference of a circular metallic ring of radius L about an axis passing through the center and perpendicular to the plane of the ring. A constant and uniform magnetic field B parallel to the axis is present everywhere. Deduce the expression for the emf between the center and the metallic ring.

Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint:Calculate the induced emf in the rod as it moves through a magnetic field. Assume that the rod is moving with a velocity \[v=\omega L\] . Consider an emf on some length \[dl\] of the rod and then integrate this length to the total length of the rod. The radius of the ring is equal to L.
Complete step by step solution:
Since all the points on the rod are moving in the direction perpendicular to the magnetic field as a result, a small amount of emf will be induced in the rod.
This induced emf will be:
\[\varepsilon =B vL\]
Where \[\varepsilon \] is the induced emf
\[B \] is the uniform magnetic field
\[v\] is the linear velocity of the rod
\[L\] is the length of the rod
Consider a small length \[dl\] on the rod at some distance from the center,
The emf induced on this small portion will be given as:
\[d\varepsilon =B vdl\]
Where \[d\varepsilon \] is the emf induced on length \[dl\]
Now we know that, \[v=\omega l\]
\[\Rightarrow d\varepsilon =B\omega ldl\]
Since the length of rod is L, therefore the total emf will be given as:
\[\Rightarrow \varepsilon =\int\limits_{0}^{L}{B\omega ldl}\]
\[\Rightarrow \varepsilon =\dfrac{B\omega {{L}^{2}}}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow \varepsilon =\dfrac{B\omega {{L}^{2}}}{2}\] is the emf between the center and the metallic ring.
Note: Any rod moving with a certain velocity in some magnetic field perpendicular to the velocity of the rod will always experience an induced emf which results due to its motion. Thus, any rod moving parallel to Earth’s surface and is vertical with respect to the Earth’s surface experiences an induced due to the magnetic field of Earth and the velocity of rod. Though this velocity is very small it can be detected.
Complete step by step solution:
Since all the points on the rod are moving in the direction perpendicular to the magnetic field as a result, a small amount of emf will be induced in the rod.
This induced emf will be:
\[\varepsilon =B vL\]
Where \[\varepsilon \] is the induced emf
\[B \] is the uniform magnetic field
\[v\] is the linear velocity of the rod
\[L\] is the length of the rod
Consider a small length \[dl\] on the rod at some distance from the center,
The emf induced on this small portion will be given as:
\[d\varepsilon =B vdl\]
Where \[d\varepsilon \] is the emf induced on length \[dl\]
Now we know that, \[v=\omega l\]
\[\Rightarrow d\varepsilon =B\omega ldl\]
Since the length of rod is L, therefore the total emf will be given as:
\[\Rightarrow \varepsilon =\int\limits_{0}^{L}{B\omega ldl}\]
\[\Rightarrow \varepsilon =\dfrac{B\omega {{L}^{2}}}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow \varepsilon =\dfrac{B\omega {{L}^{2}}}{2}\] is the emf between the center and the metallic ring.
Note: Any rod moving with a certain velocity in some magnetic field perpendicular to the velocity of the rod will always experience an induced emf which results due to its motion. Thus, any rod moving parallel to Earth’s surface and is vertical with respect to the Earth’s surface experiences an induced due to the magnetic field of Earth and the velocity of rod. Though this velocity is very small it can be detected.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




