
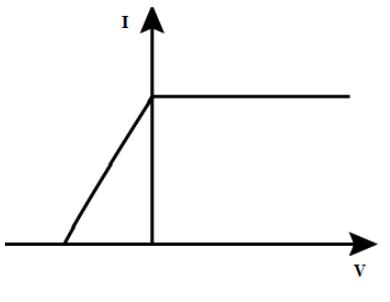
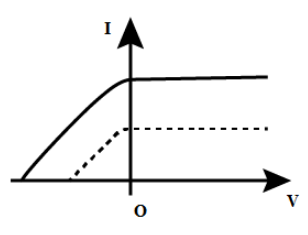
A metal surface is an evacuated tube illuminated with monochromatic light causing the emission of photoelectrons which are collected at an adjacent electrode. For a given intensity of light, the way in which the photocurrent I depends on the potential difference V between the electrodes is shown by an approximate graph in figure. If the experiment were repeated with light of twice the intensity but the same wavelength, which of the graphs below would best represent the new relation between I and V? (In this graph, the result of the original experiment is indicated by a broken line.)
(A)
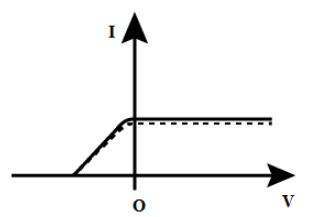
(B)
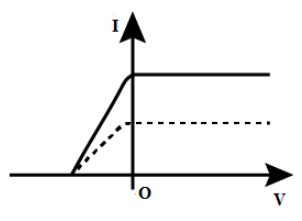
(C)
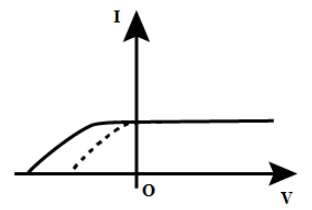
(D)





Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint:We know that if the wavelength of the light is the same, then the frequency of light also remains constant. If the accelerating potential and frequency of the radiation is kept constant, the photo current I increase linearly with the intensity of light. We know that stopping potential or retarding potential depends upon the frequency of radiation.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that when an ultraviolet light incident on a metal electrode, a high voltage pulse generates across the electrode. We can measure the potential difference V if we place a voltmeter across an emitter and collector. When the ultraviolet radiation falls on the emitter plate, the current is recorded. We know that the current I is the function of intensity of ultraviolet light.
We have given that the same light is used for the next case when the intensity of light is doubled. We know that if the wavelength of the light is the same, then the frequency of light also remains constant.
We know from the I-V characteristics of the photoelectric effect, if the accelerating potential and frequency of the radiation is kept constant, the photo current I increase linearly with the intensity of light. Therefore, we have given that the intensity of light is doubled. So, we can say that the photo current also gets doubled.
We know that stopping potential or retarding potential depends upon the frequency of radiation. Since the frequency of radiation does not change, the stopping potential of both the curves will be the same.Therefore, we can say, on doubling the intensity, the photo current gets doubled.
So, the correct curve for the second case is option (B).
Note:To answer this type of questions, students should know the terms accelerating potential, retarding potential and intensity of light. You should know the frequency of light does not change even when the wavelength of light changes.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that when an ultraviolet light incident on a metal electrode, a high voltage pulse generates across the electrode. We can measure the potential difference V if we place a voltmeter across an emitter and collector. When the ultraviolet radiation falls on the emitter plate, the current is recorded. We know that the current I is the function of intensity of ultraviolet light.
We have given that the same light is used for the next case when the intensity of light is doubled. We know that if the wavelength of the light is the same, then the frequency of light also remains constant.
We know from the I-V characteristics of the photoelectric effect, if the accelerating potential and frequency of the radiation is kept constant, the photo current I increase linearly with the intensity of light. Therefore, we have given that the intensity of light is doubled. So, we can say that the photo current also gets doubled.
We know that stopping potential or retarding potential depends upon the frequency of radiation. Since the frequency of radiation does not change, the stopping potential of both the curves will be the same.Therefore, we can say, on doubling the intensity, the photo current gets doubled.
So, the correct curve for the second case is option (B).
Note:To answer this type of questions, students should know the terms accelerating potential, retarding potential and intensity of light. You should know the frequency of light does not change even when the wavelength of light changes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




