
A metal crystallizes in bcc lattice. The percent fraction of edge length not covered by atom is-
A \[10.4{\text{ }}\% \]
B \[13.4{\text{ }}\% \]
C \[12.4{\text{ }}\% \]
D \[11.4{\text{ }}\% \]
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: A Body-centered cubic lattice (bcc) unit cell has atoms at each corner of the cube and an atom at the centre of the structure. The atom at the body centre wholly belongs to the unit cell in which it is present.
Complete Step by step answer: In Body-centered cubic lattice (bcc) unit cell every corner has atoms has a open structure and we have - 8 corners × 1/8 per corner atom = \[8{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}1/8{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1\] atom
1 body centre atom = \[1{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}1{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1\] atom
Therefore, the total number of atoms present per unit cell =\[2{\text{ }}atoms\;\] .
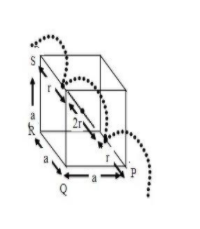
In body centered cubic lattice, the atom at the body centre touches the spheres at the corners .The body diagonal has a length that is four times the radius of the atom\[\;r\]
Body diagonal \[PS{\text{ }} = 4r\;\],
Face diagonal \[PR = \sqrt {P{Q^2} + Q{R^2}} = \sqrt {2a} \]
Body diagonal \[ = PS = \sqrt {P{R^2} + R{S^{2}}} = \sqrt {2{a^2} + {a^{2}}} = \sqrt {3a} \]
radius of atom\[\left( r \right)\] , \[
4r = \sqrt {3a} \\
\Rightarrow 2r = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}a \\
\]
(divide both the sides by 2)
Edge length of bcc is \[ \to \]\[\;a\]
Length of two atoms \[ \to \] \[2r\;\;\;\;\;\]
\[\therefore \] Edge length not covered by atom =\[a - 2r\] = \[a{\text{ }} - \;\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\;a\]=\[\;a\dfrac{{\left( {2 - \sqrt 3 } \right)}}{2}\]
\[\therefore \% \;\] fraction not covered = \[a\dfrac{{\dfrac{{\left( {2 - \sqrt 3 } \right)}}{2}}}{a} \times 100 = \dfrac{{2 - 1.732}}{2} \times 100\] = \[13.4\% \]
so the option (B) is correct.
Note: In Body-centered cubic lattice (bcc) unit cell vectors a = b = c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°, There are 23 metals that have the bcc lattice like it include iron, chromium, tungsten, tantalum, and molybdenum. etc.
Complete Step by step answer: In Body-centered cubic lattice (bcc) unit cell every corner has atoms has a open structure and we have - 8 corners × 1/8 per corner atom = \[8{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}1/8{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1\] atom
1 body centre atom = \[1{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}1{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1\] atom

Therefore, the total number of atoms present per unit cell =\[2{\text{ }}atoms\;\] .
In body centered cubic lattice, the atom at the body centre touches the spheres at the corners .The body diagonal has a length that is four times the radius of the atom\[\;r\]
Body diagonal \[PS{\text{ }} = 4r\;\],
Face diagonal \[PR = \sqrt {P{Q^2} + Q{R^2}} = \sqrt {2a} \]
Body diagonal \[ = PS = \sqrt {P{R^2} + R{S^{2}}} = \sqrt {2{a^2} + {a^{2}}} = \sqrt {3a} \]
radius of atom\[\left( r \right)\] , \[
4r = \sqrt {3a} \\
\Rightarrow 2r = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}a \\
\]
(divide both the sides by 2)
Edge length of bcc is \[ \to \]\[\;a\]
Length of two atoms \[ \to \] \[2r\;\;\;\;\;\]
\[\therefore \] Edge length not covered by atom =\[a - 2r\] = \[a{\text{ }} - \;\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\;a\]=\[\;a\dfrac{{\left( {2 - \sqrt 3 } \right)}}{2}\]
\[\therefore \% \;\] fraction not covered = \[a\dfrac{{\dfrac{{\left( {2 - \sqrt 3 } \right)}}{2}}}{a} \times 100 = \dfrac{{2 - 1.732}}{2} \times 100\] = \[13.4\% \]
so the option (B) is correct.
Note: In Body-centered cubic lattice (bcc) unit cell vectors a = b = c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°, There are 23 metals that have the bcc lattice like it include iron, chromium, tungsten, tantalum, and molybdenum. etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




