
(a) Mention the functional components of the ecosystem.
(b) What is the trophic level?
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: An ecosystem is defined as the functional unit of nature in which living organisms live and interact within themselves as well as the abiotic factors of their environment. Trophic level is associated with energy flow between producers, consumers, decomposers, etc.
Complete Answer:
The functional components of the ecosystem work together to function as a unit and are as follows:
- Productivity: Productivity is defined as the rate of the amount of biomass or organic matter produced by living organisms over a period of time. It is divided further into primary productivity (the amount of biomass produced by plants i.e. producers by trapping the energy from sunlight) and secondary productivity (the amount of biomass produced by consumers after eating producers) .
- Decomposition: Decomposition is carried out by decomposers that break the dead and decaying organic matter into inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide, water, and nutrients. The dead matter such as leaves, barks, flowers, and remains of animals are known as detritus which is decomposed by decomposers such as fungi and other microbes.
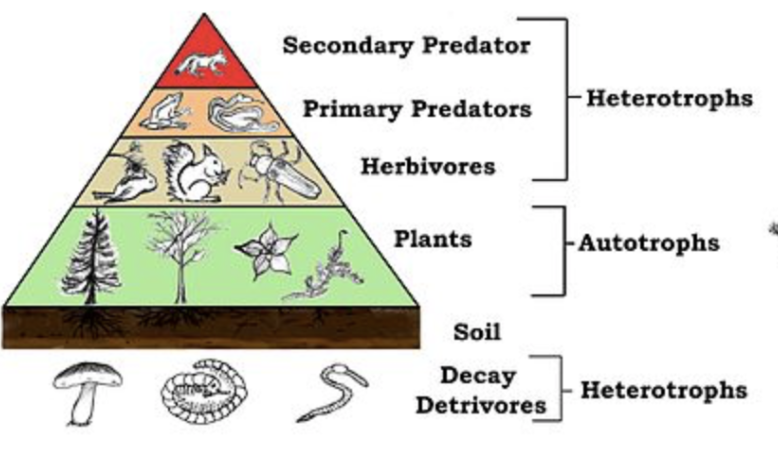
- Energy flow: It is the unidirectional flow of energy from sunlight to producers and then consumers after which it is finally lost to the environment. Sun is the source of energy for all ecosystems except deep- sea hydrothermal vents.
- Nutrient cycling: Nutrients are never lost from the ecosystems but instead they are recycled again and again indefinitely. This cycling of nutrients is divided into two types gaseous and sedimentary on the basis of the nutrient cycle.
- Trophic level: Organisms in an ecosystem exist in a feeding relationship with other organisms. Based on the source of their nutrition, organisms are placed in a specific place in the food chain known as the trophic level. Plants are producers and they are placed in the first trophic level whereas herbivores that eat plants are placed in the second trophic level.
Note:
- Primary productivity is also divided into gross primary productivity and net primary productivity.
- Decomposition is divided into many steps known as fragmentation, leaching, catabolism, humification, and mineralization.
- Nutrient cycling is also known as biogeochemical cycling as it is the bio cycling of minerals found in rocks.
Complete Answer:
The functional components of the ecosystem work together to function as a unit and are as follows:
- Productivity: Productivity is defined as the rate of the amount of biomass or organic matter produced by living organisms over a period of time. It is divided further into primary productivity (the amount of biomass produced by plants i.e. producers by trapping the energy from sunlight) and secondary productivity (the amount of biomass produced by consumers after eating producers) .
- Decomposition: Decomposition is carried out by decomposers that break the dead and decaying organic matter into inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide, water, and nutrients. The dead matter such as leaves, barks, flowers, and remains of animals are known as detritus which is decomposed by decomposers such as fungi and other microbes.

- Energy flow: It is the unidirectional flow of energy from sunlight to producers and then consumers after which it is finally lost to the environment. Sun is the source of energy for all ecosystems except deep- sea hydrothermal vents.
- Nutrient cycling: Nutrients are never lost from the ecosystems but instead they are recycled again and again indefinitely. This cycling of nutrients is divided into two types gaseous and sedimentary on the basis of the nutrient cycle.
- Trophic level: Organisms in an ecosystem exist in a feeding relationship with other organisms. Based on the source of their nutrition, organisms are placed in a specific place in the food chain known as the trophic level. Plants are producers and they are placed in the first trophic level whereas herbivores that eat plants are placed in the second trophic level.
Note:
- Primary productivity is also divided into gross primary productivity and net primary productivity.
- Decomposition is divided into many steps known as fragmentation, leaching, catabolism, humification, and mineralization.
- Nutrient cycling is also known as biogeochemical cycling as it is the bio cycling of minerals found in rocks.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




