
A man wearing glasses of power $+2D$, can read a book clearly placed at a distance of $40\;cm$ from the eye. The power of the lens required, so that he can read at $25\;cm$ from the eye is?
A. $+4.5D$
B. $+4.0D$
C. $+3.5D$
D.$+3.0D$
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: Power of a lens is the ability or the extent to which the given lens can bend the light ray. According to the nature of the lens, the power either converges or diverges the incident ray. It is measured in $m^{-1}$ or $D$.
Formula used:
$P=\dfrac{1}{f}$ and $\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Since power is the ability to bend or focus the incident light to a given point of interest, it is mathematically expressed as
$P=\dfrac{1}{f}$ where, $f$ is the focal length of the lens.
For a convex or converging lens, the power is positive and for a concave or diverging lens, the power is negative.
Here, given that power of lens is $+2D$, which means that the given lens is a concave lens with focal length $f$ given as
$f=\dfrac{1}{P}=\dfrac{100}{2}= 0.5 m$
Converting the focal length into cm, we have from the image
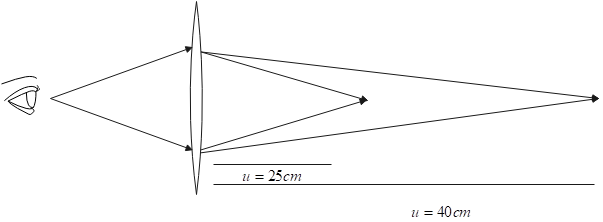
$f=0.5\times 100=50 cm$
Since the book is at $u=40cm$. Then from lens law, we have
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
$\implies \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{50}-\dfrac{1}{40}$
$\implies \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{4-5}{200}$
$\implies \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{-1}{200}$
$\implies v=-200 cm$
Now to read the same book from $u=25cm$, the power of the lens required is due to the focal length $f\prime$. Then using the lens law again we have
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f\prime}$
$\implies \dfrac{1}{-200}+\dfrac{1}{25}=\dfrac{1}{f\prime}$
$\implies \dfrac{-1+8}{200}=\dfrac{1}{f\prime}$
$\implies \dfrac{1}{f\prime}=\dfrac{7}{200}$
Here the focal length is in terms of cm, and hence converting it into meter, we get power in terms of dioptre as
$\therefore P=\dfrac{1}{f\prime}=\dfrac{7}{200}\times 100=3.5D$
Thus, the correct answer is C. $+3.5D$
Note: More the power of the lens, more is the refracting ability of it to bend the light, and similarly, less the power of the lens, less is its refracting ability. For convex lens, it is the ability to converge and for concave lens, it is the ability to diverge the incident ray.
Formula used:
$P=\dfrac{1}{f}$ and $\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Since power is the ability to bend or focus the incident light to a given point of interest, it is mathematically expressed as
$P=\dfrac{1}{f}$ where, $f$ is the focal length of the lens.
For a convex or converging lens, the power is positive and for a concave or diverging lens, the power is negative.
Here, given that power of lens is $+2D$, which means that the given lens is a concave lens with focal length $f$ given as
$f=\dfrac{1}{P}=\dfrac{100}{2}= 0.5 m$
Converting the focal length into cm, we have from the image

$f=0.5\times 100=50 cm$
Since the book is at $u=40cm$. Then from lens law, we have
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
$\implies \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{50}-\dfrac{1}{40}$
$\implies \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{4-5}{200}$
$\implies \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{-1}{200}$
$\implies v=-200 cm$
Now to read the same book from $u=25cm$, the power of the lens required is due to the focal length $f\prime$. Then using the lens law again we have
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f\prime}$
$\implies \dfrac{1}{-200}+\dfrac{1}{25}=\dfrac{1}{f\prime}$
$\implies \dfrac{-1+8}{200}=\dfrac{1}{f\prime}$
$\implies \dfrac{1}{f\prime}=\dfrac{7}{200}$
Here the focal length is in terms of cm, and hence converting it into meter, we get power in terms of dioptre as
$\therefore P=\dfrac{1}{f\prime}=\dfrac{7}{200}\times 100=3.5D$
Thus, the correct answer is C. $+3.5D$
Note: More the power of the lens, more is the refracting ability of it to bend the light, and similarly, less the power of the lens, less is its refracting ability. For convex lens, it is the ability to converge and for concave lens, it is the ability to diverge the incident ray.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




