
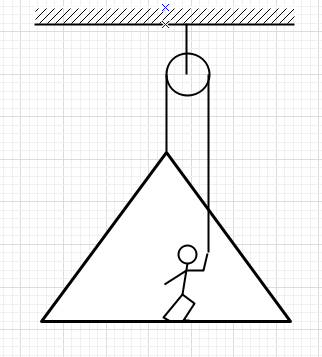
A man of mass 50 kg stands on a frame of mass 30kg. He pulls on a light rope which passes over a pulley. The other end of the rope is attached to the frame. For the system to be in equilibrium what force man must exert on the rope?
$\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{. 40}\times \text{g} \\
& \text{B}\text{. 80}\times \text{g} \\
& \text{C}\text{. 30}\times \text{g} \\
& \text{D}\text{. 50}\times \text{g} \\
\end{align}$

Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: Draw the diagram with the direction of forces for a better understanding. Obtain the total weight on the system and the total tension on the rope. For equilibrium condition, these two forces should be equal. Equate them to find the required solution.
Complete step by step answer:
The mass of the frame is $m=30kg$
The mass of the man is $M=50kg$
The man is standing on the frame. So, the total mass of the system is $M+m=50kg+30kg=80kg$
Now the frame is on a pulley, the other end of the rope is on the hand of the man. The man is pulling the rope to make the system to be in equilibrium.
Let the man is pulling the rope with a force F and the tension on the rope will be T. Again, the frame is also attached to one end of the rope. The weight of the frame is downward. So, we have another tension T on the rope which is also acting upward.
For the system to be in equilibrium, the downward force on the system should be equal to the upward force.
Total downward force m the system will be,
$\begin{align}
& \left( M+m \right)g \\
& 80g \\
\end{align}$
The total upward force will be,
$T+T=2T$
Now, these two forces will be equal.
$\begin{align}
& 2T=80g \\
& T=\dfrac{80g}{2} \\
& T=40g \\
\end{align}$
Since the force with which the man is pulling the rope is equal to the tension on the rope, we can say that the system will be in equilibrium when the man pulls the rope with a force $40\times g$ .
The correct option is (A).
Note:
Pulleys are the simple machines which makes our work easier. Here, we have the rope on both side of the pulley with a downward force on each end. Again, the system is in equilibrium. That’s why we considered the tension on the rope on the both sides of the pulley to be equal.
Complete step by step answer:
The mass of the frame is $m=30kg$
The mass of the man is $M=50kg$
The man is standing on the frame. So, the total mass of the system is $M+m=50kg+30kg=80kg$
Now the frame is on a pulley, the other end of the rope is on the hand of the man. The man is pulling the rope to make the system to be in equilibrium.
Let the man is pulling the rope with a force F and the tension on the rope will be T. Again, the frame is also attached to one end of the rope. The weight of the frame is downward. So, we have another tension T on the rope which is also acting upward.
For the system to be in equilibrium, the downward force on the system should be equal to the upward force.
Total downward force m the system will be,
$\begin{align}
& \left( M+m \right)g \\
& 80g \\
\end{align}$
The total upward force will be,
$T+T=2T$
Now, these two forces will be equal.
$\begin{align}
& 2T=80g \\
& T=\dfrac{80g}{2} \\
& T=40g \\
\end{align}$
Since the force with which the man is pulling the rope is equal to the tension on the rope, we can say that the system will be in equilibrium when the man pulls the rope with a force $40\times g$ .
The correct option is (A).
Note:
Pulleys are the simple machines which makes our work easier. Here, we have the rope on both side of the pulley with a downward force on each end. Again, the system is in equilibrium. That’s why we considered the tension on the rope on the both sides of the pulley to be equal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




