
A man of height $ 2meters $ walks at a uniform speed of $ 6\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $ away from a lamp post which is $ 6meters $ high. Find the rate at which the length of his shadow increases. Also find the rate at which the tip of the shadow is moving away from the lamp post.
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: In this question, we will construct a figure using the given and consider $ x $ and $ y $ as the distance between the lamp post and the man and the man and the tip of the shadow respectively. Also, we will use the similar triangle theorem and equate $ x $ and $ y $ . Then, differentiate with respect to time and determine the rate at which the length of his shadow increases and also the rate at which the tip of the shadow is moving away from the lamp post respectively.
Complete step-by-step answer:
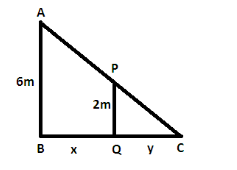
Let us consider $ AB $ as the height of the lamp post.
i.e., $ AB = 6\,m $
Then, let $ PQ $ be the height of the man.
i.e., $ PQ = 2\,m $
Now, consider the distance between the man and the lamp post is $ BQ = x $ .
Here, $ QC $ is the shadow of the man.
Let the length of shadow $ QC = y $ .
Therefore, $ BC = x + y $
It is given that the man walks at speed $ 6\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}} = 6\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $
Hence, by similar triangle theorem,
$
\dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{{PQ}}{{QC}}
\dfrac{6}{{x + y}} = \dfrac{2}{y}
6y = 2x + 2y
2x = 6y - 2y
2x = 4y
x = 2y
$
Consider $ x = 2y $ as equation 1.
Now, differentiating the equation 1 with respect to time, $ t $ , we have,
$ \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = 2\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} $
$ \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = 6\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $
$ 2\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = 6 $
$ \dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = 3\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $
Hence, the rate at which the length of his shadow increases is $ 3\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $ .
So, the correct answer is “ $ 3\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $ ”.
Also, we need to find the rate at which the tip of the shadow is moving away from the lamp post.
Here, we know that $ BC = x + y $ .
Now, differentiating the equation $ BC = x + y $ with respect to time, $ t $ , we have,
$ \dfrac{{d(BC)}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} + \dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} $
Thus, substituting the values of $ \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = 6\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $ and $ \dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = 3\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $ in the equation,
Therefore, $ \dfrac{{d\left( {BC} \right)}}{{dt}} = 6\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} + 3\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $
Hence, $ \dfrac{{d\left( {BC} \right)}}{{dt}} = 9\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $
Hence, the rate at which the tip of the shadow is moving away from the lamp post is $ 9\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $ .
So, the correct answer is “ $ 9\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $ ”.
Note: In this question, it is worthy to note here that to determine the rate of change we will always differentiate it with respect to time in such types of questions. The similar triangle theorem states that if two triangles are similar, then the ratio of the area of both triangles is proportional to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us consider $ AB $ as the height of the lamp post.
i.e., $ AB = 6\,m $
Then, let $ PQ $ be the height of the man.
i.e., $ PQ = 2\,m $
Now, consider the distance between the man and the lamp post is $ BQ = x $ .
Here, $ QC $ is the shadow of the man.
Let the length of shadow $ QC = y $ .
Therefore, $ BC = x + y $

It is given that the man walks at speed $ 6\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}} = 6\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $
Hence, by similar triangle theorem,
$
\dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{{PQ}}{{QC}}
\dfrac{6}{{x + y}} = \dfrac{2}{y}
6y = 2x + 2y
2x = 6y - 2y
2x = 4y
x = 2y
$
Consider $ x = 2y $ as equation 1.
Now, differentiating the equation 1 with respect to time, $ t $ , we have,
$ \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = 2\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} $
$ \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = 6\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $
$ 2\dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = 6 $
$ \dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = 3\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $
Hence, the rate at which the length of his shadow increases is $ 3\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $ .
So, the correct answer is “ $ 3\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $ ”.
Also, we need to find the rate at which the tip of the shadow is moving away from the lamp post.
Here, we know that $ BC = x + y $ .
Now, differentiating the equation $ BC = x + y $ with respect to time, $ t $ , we have,
$ \dfrac{{d(BC)}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} + \dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} $
Thus, substituting the values of $ \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = 6\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $ and $ \dfrac{{dy}}{{dt}} = 3\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $ in the equation,
Therefore, $ \dfrac{{d\left( {BC} \right)}}{{dt}} = 6\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} + 3\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $
Hence, $ \dfrac{{d\left( {BC} \right)}}{{dt}} = 9\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $
Hence, the rate at which the tip of the shadow is moving away from the lamp post is $ 9\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $ .
So, the correct answer is “ $ 9\,kmh{r^{ - 1}} $ ”.
Note: In this question, it is worthy to note here that to determine the rate of change we will always differentiate it with respect to time in such types of questions. The similar triangle theorem states that if two triangles are similar, then the ratio of the area of both triangles is proportional to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




