
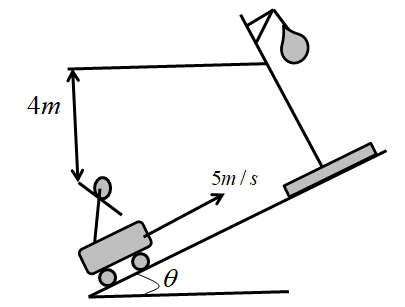
A man is traveling on a flat car which is moving up a plane inclined at $\cos \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}$ to the horizontal with a speed $5{\text{ m/s}}$. He throws a ball towards a stationary hoop located perpendicular to the incline in such a way that the ball moves parallel to the slope of the incline while going through the center of the hoop. The center of the hoop is $4m$ high from the man’s hand. Calculate the time taken by the ball to reach the hoop.


Answer
506.4k+ views
Hint: First, the formula of maximum height that the ball reaches due to throwing towards the stationary hoop is to be used to find the initial velocity. Next, by putting the value of the sine component of initial velocity from the above relation in the formula of time taken by the ball to reach the hoop. Note that, all the formulas or equations of motion are used here regarding projectile motion.
Formula used:
The maximum height that the ball reaches due to throwing towards the stationary hoop, ${H_{\max }} = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\alpha }}{{2g\cos \theta }}$
$\theta $ is the angle of inclination
$u\sin \alpha $ is the sine component of the initial velocity of the ball.
The time is taken by the ball to reach the hoop, $T = \dfrac{{2u\sin \alpha }}{{2g\cos \theta }}$
Complete step by step answer:
Given that, A man is traveling in a flat car which is moving up an inclined plane with a speed $5{\text{ m/s}}$.
$\theta $ is the angle of inclination to the horizontal.
Given, $\cos \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}$
The ball is thrown towards a stationary hoop located perpendicular to the incline.
The maximum height that the ball reaches due to throwing towards the stationary hoop, ${H_{\max }} = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\alpha }}{{2g\cos \theta }}$
Where, ${H_{\max }} = 4$
$ \Rightarrow 4 = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\alpha }}{{2 \times 10 \times \dfrac{4}{5}}}$ [ the acceleration due to gravity is taken here, $g = 10m/{s^2}$ ]
On simplification,
\[ \Rightarrow {u^2}{\sin ^2}\alpha = 2 \times 10 \times \dfrac{4}{5} \times 4\]
On further simplification, we get
\[ \Rightarrow u\sin \alpha = \sqrt {64} \]
\[ \Rightarrow u\sin \alpha = 8\] We will use this value to find $T$ value.
Thereafter, the ball moves parallel to the slope of the incline that goes through the center of the hoop.
The time is taken by the ball to reach the hoop, $T = \dfrac{{2u\sin \alpha }}{{2g\cos \theta }}$
$ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{2 \times 8}}{{2 \times 10 \times \dfrac{4}{5}}}$
On simplification,
$ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{2 \times 8}}{{2 \times 2 \times 4}}$
$ \Rightarrow T = 1$
Therefore, the required time is $1\sec $.
Note:
Projectile motion is the motion of a body that is thrown or projected into the air and accelerates due to gravity. The body is called a projectile, and its path is known as trajectory. The motion of falling objects, as covered in Problem-Solving Basics for 1D Kinematics, is a general one-dimensional type of projectile motion in which there is a lack of horizontal motion. In this topic, we consider two-dimensional projectile motion, the air resistance is negligible.
Formula used:
The maximum height that the ball reaches due to throwing towards the stationary hoop, ${H_{\max }} = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\alpha }}{{2g\cos \theta }}$
$\theta $ is the angle of inclination
$u\sin \alpha $ is the sine component of the initial velocity of the ball.
The time is taken by the ball to reach the hoop, $T = \dfrac{{2u\sin \alpha }}{{2g\cos \theta }}$
Complete step by step answer:
Given that, A man is traveling in a flat car which is moving up an inclined plane with a speed $5{\text{ m/s}}$.
$\theta $ is the angle of inclination to the horizontal.
Given, $\cos \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}$
The ball is thrown towards a stationary hoop located perpendicular to the incline.

The maximum height that the ball reaches due to throwing towards the stationary hoop, ${H_{\max }} = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\alpha }}{{2g\cos \theta }}$
Where, ${H_{\max }} = 4$
$ \Rightarrow 4 = \dfrac{{{u^2}{{\sin }^2}\alpha }}{{2 \times 10 \times \dfrac{4}{5}}}$ [ the acceleration due to gravity is taken here, $g = 10m/{s^2}$ ]
On simplification,
\[ \Rightarrow {u^2}{\sin ^2}\alpha = 2 \times 10 \times \dfrac{4}{5} \times 4\]
On further simplification, we get
\[ \Rightarrow u\sin \alpha = \sqrt {64} \]
\[ \Rightarrow u\sin \alpha = 8\] We will use this value to find $T$ value.
Thereafter, the ball moves parallel to the slope of the incline that goes through the center of the hoop.
The time is taken by the ball to reach the hoop, $T = \dfrac{{2u\sin \alpha }}{{2g\cos \theta }}$
$ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{2 \times 8}}{{2 \times 10 \times \dfrac{4}{5}}}$
On simplification,
$ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{2 \times 8}}{{2 \times 2 \times 4}}$
$ \Rightarrow T = 1$
Therefore, the required time is $1\sec $.
Note:
Projectile motion is the motion of a body that is thrown or projected into the air and accelerates due to gravity. The body is called a projectile, and its path is known as trajectory. The motion of falling objects, as covered in Problem-Solving Basics for 1D Kinematics, is a general one-dimensional type of projectile motion in which there is a lack of horizontal motion. In this topic, we consider two-dimensional projectile motion, the air resistance is negligible.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




