
A luminous object is placed at a distance 0f 30cm from the convex lens of focal length 20cm. On the other side of the lens, at what distance from the lens a convex mirror of radius of curvature 10cm be placed in order to have an upright image of the object coincident with it.
A. 30cm
B. 60cm
C. 50cm
D. 12cm
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: As a first step, you could make a neat ray diagram of the given situation recalling where the image of the lens to be formed such that the final image coincides with the object. Then, you could recall the lens formula and thus find the image distance. After that you could accordingly find the distance of the mirror from the lens.
Formula used:
Lens formula,
$\dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}+\dfrac{1}{u}$
Complete Step by step solution:
In the question, we are given a luminous object that is placed at 30cm from a convex lens which has a focal length of 20cm. We are asked to find the distance at which a convex mirror should be kept on the other side of the lens so as to form the upright image of the object coincident with it. We are also given the radius of curvature of the mirror as 10cm.
As a first step, let us represent the given situation in a neat ray diagram.
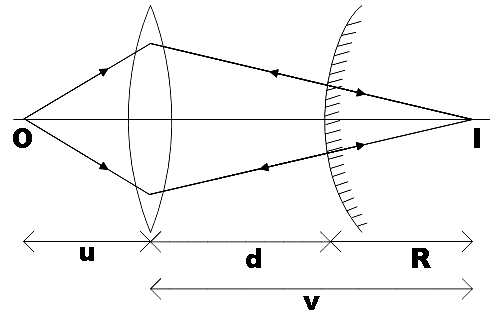
The main concept you have to recall here is that, for the final image formed by the mirror to coincide with the object, the image formed by the convex lens should be at the mirror’s centre of curvature. This is because, only then will the rays retrace its path.
Now let us find the image distance of the lens using the lens formula.
$\dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}+\dfrac{1}{u}$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{uf}{u+f}$
We have,
$u=-30cm$
$f=20cm$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{-30\times 20}{-30+20}$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{-600}{-10}$
$\therefore v=60cm$
The distance between the lens and mirror is marked in the figure as d and is given by,
$d=v-R$
$\Rightarrow d=60-10$
$\therefore d=50cm$
Therefore, we found the distance between the mirror and lens to be 50cm so as to satisfy the given condition.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note:
While dealing with numerical problems related to optics we should always take care of the signs of the quantities. We always measure these quantities from the optical centre of the lens. The measurements taken to the left of this point are considered negative and right to be positive. Hence, signs assigned to the quantities in the solution.
Formula used:
Lens formula,
$\dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}+\dfrac{1}{u}$
Complete Step by step solution:
In the question, we are given a luminous object that is placed at 30cm from a convex lens which has a focal length of 20cm. We are asked to find the distance at which a convex mirror should be kept on the other side of the lens so as to form the upright image of the object coincident with it. We are also given the radius of curvature of the mirror as 10cm.
As a first step, let us represent the given situation in a neat ray diagram.

The main concept you have to recall here is that, for the final image formed by the mirror to coincide with the object, the image formed by the convex lens should be at the mirror’s centre of curvature. This is because, only then will the rays retrace its path.
Now let us find the image distance of the lens using the lens formula.
$\dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}+\dfrac{1}{u}$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{uf}{u+f}$
We have,
$u=-30cm$
$f=20cm$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{-30\times 20}{-30+20}$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{-600}{-10}$
$\therefore v=60cm$
The distance between the lens and mirror is marked in the figure as d and is given by,
$d=v-R$
$\Rightarrow d=60-10$
$\therefore d=50cm$
Therefore, we found the distance between the mirror and lens to be 50cm so as to satisfy the given condition.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note:
While dealing with numerical problems related to optics we should always take care of the signs of the quantities. We always measure these quantities from the optical centre of the lens. The measurements taken to the left of this point are considered negative and right to be positive. Hence, signs assigned to the quantities in the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




