
A long coaxial cable consists of two thin-walled conducting cylinders with inner radius $2\;cm$ and outer radius $8\;cm$. The inner cylinder carries a steady current 0.1A, while the outer cylinder provides the return path for that current. The current produces a magnetic field between the two cylinders. Find the energy stored in the magnetic field for length $5\;m$ of the cable. Express answer in $nJ$. (Use ln 2 =0.7).
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Recall an expression for the magnetic energy density which is nothing but the energy stored in the magnetic field per unit volume of the cable. Also, since the current flowing through the inner cylinder produces the magnetic field, we assume this to be the only source of magnetic field in our setup. In order to bring about a uniformity to the energy density over a length of the conductor, take an elementary volume and integrate the magnetic energy density over the region between the two cylinders, which will ultimately give you the energy stored in the magnetic field.
Formula Used:
Magnetic field strength $B=\dfrac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi r}$
Magnetic energy density $U = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{B^2}{\mu_0}$
Complete step by step answer:
We have a coaxial cable with an inner radius of $r_1 = 2\;cm = 0.02\;m$ and outer radius $r_2 = 8\;cm = 0.08\;m$
We are given that the inner cylinder carries a current of 0.1A. This current generates a magnetic field in the region between the two cylinders, whose small volume element is given as dV.
The magnetic field thus produced is a consequence of current flowing through the inner cylinder.
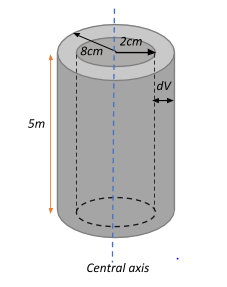
Now, we can define the amount of energy stored in the magnetic field as the magnetic field energy density (distribution) across the volume of the cylinder, which is given as:
$U = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{B^2}{\mu_0}$, where B is the magnetic field strength and $\mu_0$ is the magnetic permeability of free space.
We know that the strength of the magnetic field produced by a current flowing in a conductor is given as:
$B=\dfrac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi r}$, where r is the radius of the conductor and I is the current flowing through the conductor.
Combining the two equations, we get:
$U = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{\left(\dfrac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi r}\right)^2}{\mu_0} = \dfrac{\mu_0 I^2}{8\pi^2 r^2}$
Since U is the energy density, we can obtain just the energy by multiplying it with the volume of the conductor. But since we assume a non-uniform magnetic energy density over the thin walls and the region between them, we assume it to be uniform over a limited region of space dV, which is an elementary volume and integrate it over the concentric region over which our magnetic field acts which gives us the effective magnetic energy over a certain length of the conductor.
$\Rightarrow U = \int dU = \int UdV$
However, $V=A \times l \Rightarrow dV = dA \times l = 2\pi rdr \times l$
$\Rightarrow U = \int U 2\pi l r\;dr$
$\Rightarrow U = \int_{r_1}^{r_{2}} \dfrac{\mu_0 I^2}{8\pi^2 r^2} 2\pi l r\;dr$
$\Rightarrow U = \dfrac{\mu_0 I^2 l}{4\pi}\int_{r_1}^{r_2} \dfrac{1}{r}dr$
$\Rightarrow U = \dfrac{\mu_0 I^2 l}{4\pi} \left[ln\;r\right]_{r_1}^{r_2} = \dfrac{\mu_0 I^2 l}{4\pi} \left[ln\;r_2 – ln\;r_1\right] \Rightarrow U = \dfrac{\mu_0 I^2 l}{4\pi}ln\dfrac{r_2}{r_1}$
Now that we have obtained the expression for the energy stored in the magnetic field over a length of the conductor, we plug in the corresponding values from the question where we get:
$U = \dfrac{(4\pi \times 10^{-7})(0.1)^2 (5)}{4\pi}ln\dfrac{0.08}{0.02} = 5 \times ln(4) = 5 \times ln(2)^2 \times 10^{-9} = 5 \times 2\;ln(2) \times 10^{-9}= 10 \times 0.7 \times 10^{-9}$
$\Rightarrow U = 7 \times 10^{-9} = 7\;nJ$
Therefore, the energy stored in 5m length of the coaxial cable is $7\;nJ$
Note:
Note that we take the differential area to be $dA = 2\pi r dr$ since $\int dA = \int 2\pi r dr \Rightarrow A = \pi r^2$, and therefore $\pi r^2 l$ ultimately gives the total volume of the coaxial cable. This justifies why we took $dA = 2\pi r dr$ in this particular form.
Also, do not forget the distinction between energy density and just energy. The energy density gives the distribution of energy per unit volume of the conductor whereas the energy is just a measure of the field energy over the entire volume of the cylinder. This is also why we used the relation $U = \int dU = \int UdV$, which successfully summarizes our claim.
Formula Used:
Magnetic field strength $B=\dfrac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi r}$
Magnetic energy density $U = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{B^2}{\mu_0}$
Complete step by step answer:
We have a coaxial cable with an inner radius of $r_1 = 2\;cm = 0.02\;m$ and outer radius $r_2 = 8\;cm = 0.08\;m$
We are given that the inner cylinder carries a current of 0.1A. This current generates a magnetic field in the region between the two cylinders, whose small volume element is given as dV.
The magnetic field thus produced is a consequence of current flowing through the inner cylinder.

Now, we can define the amount of energy stored in the magnetic field as the magnetic field energy density (distribution) across the volume of the cylinder, which is given as:
$U = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{B^2}{\mu_0}$, where B is the magnetic field strength and $\mu_0$ is the magnetic permeability of free space.
We know that the strength of the magnetic field produced by a current flowing in a conductor is given as:
$B=\dfrac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi r}$, where r is the radius of the conductor and I is the current flowing through the conductor.
Combining the two equations, we get:
$U = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{\left(\dfrac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi r}\right)^2}{\mu_0} = \dfrac{\mu_0 I^2}{8\pi^2 r^2}$
Since U is the energy density, we can obtain just the energy by multiplying it with the volume of the conductor. But since we assume a non-uniform magnetic energy density over the thin walls and the region between them, we assume it to be uniform over a limited region of space dV, which is an elementary volume and integrate it over the concentric region over which our magnetic field acts which gives us the effective magnetic energy over a certain length of the conductor.
$\Rightarrow U = \int dU = \int UdV$
However, $V=A \times l \Rightarrow dV = dA \times l = 2\pi rdr \times l$
$\Rightarrow U = \int U 2\pi l r\;dr$
$\Rightarrow U = \int_{r_1}^{r_{2}} \dfrac{\mu_0 I^2}{8\pi^2 r^2} 2\pi l r\;dr$
$\Rightarrow U = \dfrac{\mu_0 I^2 l}{4\pi}\int_{r_1}^{r_2} \dfrac{1}{r}dr$
$\Rightarrow U = \dfrac{\mu_0 I^2 l}{4\pi} \left[ln\;r\right]_{r_1}^{r_2} = \dfrac{\mu_0 I^2 l}{4\pi} \left[ln\;r_2 – ln\;r_1\right] \Rightarrow U = \dfrac{\mu_0 I^2 l}{4\pi}ln\dfrac{r_2}{r_1}$
Now that we have obtained the expression for the energy stored in the magnetic field over a length of the conductor, we plug in the corresponding values from the question where we get:
$U = \dfrac{(4\pi \times 10^{-7})(0.1)^2 (5)}{4\pi}ln\dfrac{0.08}{0.02} = 5 \times ln(4) = 5 \times ln(2)^2 \times 10^{-9} = 5 \times 2\;ln(2) \times 10^{-9}= 10 \times 0.7 \times 10^{-9}$
$\Rightarrow U = 7 \times 10^{-9} = 7\;nJ$
Therefore, the energy stored in 5m length of the coaxial cable is $7\;nJ$
Note:
Note that we take the differential area to be $dA = 2\pi r dr$ since $\int dA = \int 2\pi r dr \Rightarrow A = \pi r^2$, and therefore $\pi r^2 l$ ultimately gives the total volume of the coaxial cable. This justifies why we took $dA = 2\pi r dr$ in this particular form.
Also, do not forget the distinction between energy density and just energy. The energy density gives the distribution of energy per unit volume of the conductor whereas the energy is just a measure of the field energy over the entire volume of the cylinder. This is also why we used the relation $U = \int dU = \int UdV$, which successfully summarizes our claim.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




