
A line drawn through the point P (4, 7) cuts the circle \[{x^2} + {y^2} = 9\]at the point A and B. Then PA.PB equal to
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: When a line is drawn from a point outside of a circle and meets at only one point on the circle then the line is known as a tangent. The tangent is always perpendicular to the line drawn from the radius of the circle to the point of contact of the tangent. When the line is drawn from outside of the circle and it touches two points on the circle then the line is secant.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the question, the length of the tangent can be determined using the tangent theorem and Pythagoras theorem along with some properties of the circle.
Given the point outside the circle P(4, 7)
The equation of the circle is \[{x^2} + {y^2} = 9\]
The standard equation of a circle is given as\[{x^2} + {y^2} = {r^2}\] , by comparing this equation with the equation of the circle OC we get the radius of the circle, \[r = 3\].
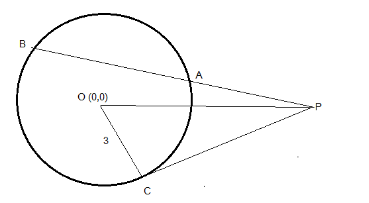
Now find the length OP by determining the distance between two points i.e. OP by
\[
OP = \sqrt {{{\left( {{P_x} - {O_x}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{P_y} - {O_y}} \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {7 - 0} \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {16 + 49} \\
= \sqrt {65} \\
\]
In \[\vartriangle OPC\], \[\angle C = {90^ \circ }\]so \[\vartriangle OPC\]is right angle triangle hence we can apply Pythagoras theorem which states as:
\[
{\left( {OP} \right)^2} = {\left( {PC} \right)^2} + {\left( {OC} \right)^2} \\
PC = \sqrt {{{\left( {\sqrt {65} } \right)}^2} + {3^2}} \\
= \sqrt {65 + 9} \\
= \sqrt {74} \\
\]
Now use the Tangent secant theorem as:
\[
PA.AB = {\left( {PC} \right)^2} \\
= {\left( {\sqrt {74} } \right)^2} \\
= 74 \\
\]
Hence we can say PA.AB is equal to 74.
Note: Whenever a line is drawn which is tangent to the circle it will always be perpendicular to the radius of the circle. The tangent secant theorem states that the product of the length of the secant outside the circle with secant inside the circle is equal to the square of the length of the tangent from the point outside the circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the question, the length of the tangent can be determined using the tangent theorem and Pythagoras theorem along with some properties of the circle.
Given the point outside the circle P(4, 7)
The equation of the circle is \[{x^2} + {y^2} = 9\]
The standard equation of a circle is given as\[{x^2} + {y^2} = {r^2}\] , by comparing this equation with the equation of the circle OC we get the radius of the circle, \[r = 3\].

Now find the length OP by determining the distance between two points i.e. OP by
\[
OP = \sqrt {{{\left( {{P_x} - {O_x}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{P_y} - {O_y}} \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {7 - 0} \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {16 + 49} \\
= \sqrt {65} \\
\]
In \[\vartriangle OPC\], \[\angle C = {90^ \circ }\]so \[\vartriangle OPC\]is right angle triangle hence we can apply Pythagoras theorem which states as:
\[
{\left( {OP} \right)^2} = {\left( {PC} \right)^2} + {\left( {OC} \right)^2} \\
PC = \sqrt {{{\left( {\sqrt {65} } \right)}^2} + {3^2}} \\
= \sqrt {65 + 9} \\
= \sqrt {74} \\
\]
Now use the Tangent secant theorem as:
\[
PA.AB = {\left( {PC} \right)^2} \\
= {\left( {\sqrt {74} } \right)^2} \\
= 74 \\
\]
Hence we can say PA.AB is equal to 74.
Note: Whenever a line is drawn which is tangent to the circle it will always be perpendicular to the radius of the circle. The tangent secant theorem states that the product of the length of the secant outside the circle with secant inside the circle is equal to the square of the length of the tangent from the point outside the circle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is the Full Form of ISI and RAW

How do you find the valency of chlorine sulphur and class 9 chemistry CBSE

What are the major achievements of the UNO class 9 social science CBSE

Explain the importance of pH in everyday life class 9 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma class 9 biology CBSE




