
A ladder is placed along a wall of a house such that its upper end is touching the top of the wall. The foot of the ladder is 2 meter away from the wall and the ladder is making an angle of ${{60}^{\circ }}$ with the level of the ground. Determine the height of the wall.
Answer
609.6k+ views
Hint:Considering the foot of the ladder i.e 2 meter away from wall as Base and $\theta$ be the angle made by ladder with ground.We will apply the formula of trigonometric ratios of tangent. And this formula is given by $\tan \left( \theta \right)=\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$.The length of the perpendicular from formula gives required answer i.e the height of the wall.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The diagram for the question is shown below.
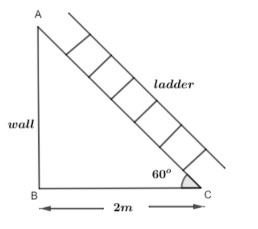
In the diagram we can clearly see that AC represents the ladder. The distance between the bottom of the ladder to the wall is given as 2 meters. And AB is the wall here. The angle of $\angle ACB$ is equal to ${{60}^{\circ }}$. We are asked to find the value of AB which is the height of the wall.
Now, we will apply the formula of trigonometric ratios for tangent. And this formula is given by $\tan \left( \theta \right)=\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$. So, we will first substitute the value of $\theta ={{60}^{\circ }}$ and perpendicular is AB which is the height of the wall also we will put base as BC = 2 meters. Therefore, we have
$\begin{align}
& \tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{AB}{BC} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{AB}{2} \\
\end{align}$
As we know that the value of $\tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\sqrt{3}$ therefore we get
$\begin{align}
& \tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{AB}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}=\dfrac{AB}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{3}\times 2 \\
& \Rightarrow AB=2\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}$
Now, at this step we will substitute the value of $\sqrt{3}=1.73$ in $AB=2\sqrt{3}$. Therefore we get
$\begin{align}
& AB=2\sqrt{3} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=2\times 1.73 \\
& \Rightarrow AB=3.46 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the height of the wall is 3.46 meters.
Note: We can solve it by using other trigonometric ratios like $\sin \left( \theta \right)=\dfrac{\text{perpendicular}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$ or $\cos \left( \theta \right)=\dfrac{\text{Base}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$. But we need to do the substitutions. One of the alternate method is been done below.
Consider the formula $\sin \left( \theta \right)=\dfrac{\text{perpendicular}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$. Here we will do the substitution as $\theta ={{60}^{\circ }}$ and perpendicular as AB and hypotenuse as AC. Thus we get $\sin \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{AB}{AC}$. Since, the value of $\sin \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ therefore, we have $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{AB}{AC}$ or $AC=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\times AB...(i)$.
And we will now consider the formula $\cos \left( \theta \right)=\dfrac{\text{Base}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$. Here we will do the substitution as $\theta ={{60}^{\circ }}$ and base as BC and hypotenuse as AC. Thus we get $\cos \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{BC}{AC}$. Since, the value of $\cos \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}$ therefore, we have $\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{BC}{AC}$ or $AC=2\times BC...(ii)$.
Now, we will equate equations (i) and (ii) and we get $\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\times AB=2\times BC$. Since, the value of BC = 2 meters thus we have
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\times AB=2\times 2 \\
& \Rightarrow AB=2\times 2\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=2\times \sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}$
Now, at this step we will substitute the value of $\sqrt{3}=1.73$ in $AB=2\times \sqrt{3}$. Therefore, we get
$\begin{align}
& AB=2\sqrt{3} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=2\times 1.73 \\
& \Rightarrow AB=3.46 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the height of the wall is 3.46 meters.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The diagram for the question is shown below.

In the diagram we can clearly see that AC represents the ladder. The distance between the bottom of the ladder to the wall is given as 2 meters. And AB is the wall here. The angle of $\angle ACB$ is equal to ${{60}^{\circ }}$. We are asked to find the value of AB which is the height of the wall.
Now, we will apply the formula of trigonometric ratios for tangent. And this formula is given by $\tan \left( \theta \right)=\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$. So, we will first substitute the value of $\theta ={{60}^{\circ }}$ and perpendicular is AB which is the height of the wall also we will put base as BC = 2 meters. Therefore, we have
$\begin{align}
& \tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{AB}{BC} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{AB}{2} \\
\end{align}$
As we know that the value of $\tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\sqrt{3}$ therefore we get
$\begin{align}
& \tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{AB}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}=\dfrac{AB}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{3}\times 2 \\
& \Rightarrow AB=2\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}$
Now, at this step we will substitute the value of $\sqrt{3}=1.73$ in $AB=2\sqrt{3}$. Therefore we get
$\begin{align}
& AB=2\sqrt{3} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=2\times 1.73 \\
& \Rightarrow AB=3.46 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the height of the wall is 3.46 meters.
Note: We can solve it by using other trigonometric ratios like $\sin \left( \theta \right)=\dfrac{\text{perpendicular}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$ or $\cos \left( \theta \right)=\dfrac{\text{Base}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$. But we need to do the substitutions. One of the alternate method is been done below.
Consider the formula $\sin \left( \theta \right)=\dfrac{\text{perpendicular}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$. Here we will do the substitution as $\theta ={{60}^{\circ }}$ and perpendicular as AB and hypotenuse as AC. Thus we get $\sin \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{AB}{AC}$. Since, the value of $\sin \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ therefore, we have $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{AB}{AC}$ or $AC=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\times AB...(i)$.
And we will now consider the formula $\cos \left( \theta \right)=\dfrac{\text{Base}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$. Here we will do the substitution as $\theta ={{60}^{\circ }}$ and base as BC and hypotenuse as AC. Thus we get $\cos \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{BC}{AC}$. Since, the value of $\cos \left( {{60}^{\circ }} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}$ therefore, we have $\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{BC}{AC}$ or $AC=2\times BC...(ii)$.
Now, we will equate equations (i) and (ii) and we get $\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\times AB=2\times BC$. Since, the value of BC = 2 meters thus we have
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\times AB=2\times 2 \\
& \Rightarrow AB=2\times 2\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=2\times \sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}$
Now, at this step we will substitute the value of $\sqrt{3}=1.73$ in $AB=2\times \sqrt{3}$. Therefore, we get
$\begin{align}
& AB=2\sqrt{3} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=2\times 1.73 \\
& \Rightarrow AB=3.46 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the height of the wall is 3.46 meters.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




