
(a) In Young’s double slit experiment, derive the condition for
(i) constructive interference and
(ii) destructive interference at a point on the screen.
(b) A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths, 800 nm and 600 nm is used to obtain the interference fringes in a Young’s double slit experiment on a screen placed 1.4 m away. If the two slits are separated by 0.28 mm, calculate the least distance from the central bright maximum where the bright fringes of the two wavelengths coincide.
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: We can find the conditions for constructive and destructive interference by considering two coherent sources of light passing through the two slits and forming fringes on a screen placed at some distance from the slits. We will find the path difference of the two wavelengths of lights and will then find that at what intervals from the central maxima, the constructive or destructive interference will occur.
Later in the second part of the problem, we can use the condition obtained for constructive interference to find the location where the bright fringes of given two wavelengths of light coincides.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(a) let us consider ${S}_{1}$ and ${S}_{2}$ be two narrow slits placed perpendicular to the plane of a paper and a screen is placed on the perpendicular bisector of ${S}_{1}{S}_{2}$, which is illuminated by monochromatic light.
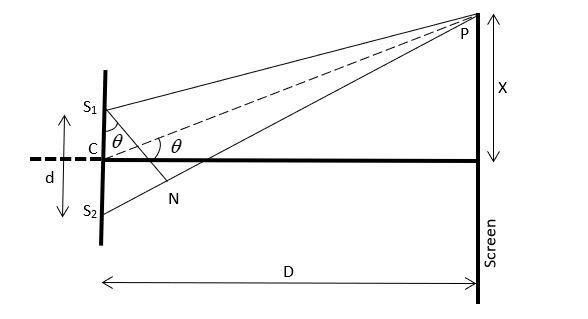
The slits have been placed $d$ distance apart and a screen at a distance D from the slits.
Now, we have a point P on the screen at $x$ distance away from point O on the screen.
Now, the path difference at P between the waves reaching from ${S}_{1}$ and ${S}_{2}$ is $\delta x={S}_{2}P-{S}_{1}P$.
Now, we will draw a perpendicular ${S}_{1}N$ on ${S}_{2}P$
Therefore, $\delta x={S}_{2}P-{S}_{1}P={S}_{2}P-NP={S}_{2}N$
Now, from the triangle ${S}_{1}{S}_{2}N$, we can write that $sin\theta=\dfrac{{S}_{2}N}{{S}_{2}{S}_{1}}$
Therefore, $\delta x={S}_{2}N={S}_{2}{S}_{1}sin\theta =dsin\theta$
Since, here$\theta$ is so small, we can write $sin\theta \simeq \theta =tan\theta =\dfrac{x}{D}$
Thus, path difference $\delta x=\dfrac{xd}{D}$
(i) Now, we can find the condition for constructive interference as
$\dfrac{xd}{D}=n\lambda ;n=0,1,2.....$
Thus, the position of $n{th}$ bright fringe, ${X}_{n}=\dfrac{nD\lambda}{d}$, where n=0 and ${X}_{n}=0$, central bright fringe will be formed at O.
(ii) The condition for destructive interference can be given by
$\dfrac{xd}{D}=(2n-1)\dfrac{\lambda}{2}$, for n = 1, 2…..
(b) We have been given two wavelengths of light ${\lambda}_{1}$ and ${\lambda}_{2}$ with values 800 nm and 600 nm respectively. The distance between slits and the screen, D = 1.4 m and distance between slits, d = 0.28 mm.
We need to find out the least distance of the point on the screen where the bright fringes of two wavelengths of light coincide with each other.
So, let us consider the ${n}_{1}^{th}$ fringe of wavelength ${\lambda}_{1}$ coincides with the ${n}_{2}^{th}$ fringe of wavelength ${\lambda}_{2}$.
So, we can write that $\dfrac{{n}_{1}{\lambda}_{1}D}{d}=\dfrac{{n}_{2}{\lambda}_{2}D}{d}$
$\implies {n}_{1}{\lambda}_{1}={n}_{2}{\lambda}_{2}\implies \dfrac{{n}_{1}}{{n}_{2}}=\dfrac{{\lambda}_{2}}{{\lambda}_{1}}=\dfrac{600}{800}=\dfrac{3}{4}$
Thus, third bright fringe of light of wavelength ${n}_{1}$ will coincide with the fourth bright fringe of light of wavelength ${n}_{2}$
So, now least distance of the bright fringe from central bright maxima $=\dfrac{3\times {\lambda}_{1}D}{d}=\dfrac{3\times 800\times 10^{-9}\times 1.4}{0.28\times 10^{-3}}=12 mm$
Hence the least distance from the central bright maxima, where the two light wavelengths bright fringe will coincide is 12mm.
Note: One more method, we can use to derive the conditions for constructive and destructive interferences by using the wave equations for the two light sources and finding the phase difference or the path difference.
In the second part of the question we can use both the wavelengths to find the distance required but the condition is to find the distance of that bright fringe only respective to that wavelength as which number bright fringe will coincide in case of both wavelengths will be different.
Later in the second part of the problem, we can use the condition obtained for constructive interference to find the location where the bright fringes of given two wavelengths of light coincides.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(a) let us consider ${S}_{1}$ and ${S}_{2}$ be two narrow slits placed perpendicular to the plane of a paper and a screen is placed on the perpendicular bisector of ${S}_{1}{S}_{2}$, which is illuminated by monochromatic light.

The slits have been placed $d$ distance apart and a screen at a distance D from the slits.
Now, we have a point P on the screen at $x$ distance away from point O on the screen.
Now, the path difference at P between the waves reaching from ${S}_{1}$ and ${S}_{2}$ is $\delta x={S}_{2}P-{S}_{1}P$.
Now, we will draw a perpendicular ${S}_{1}N$ on ${S}_{2}P$
Therefore, $\delta x={S}_{2}P-{S}_{1}P={S}_{2}P-NP={S}_{2}N$
Now, from the triangle ${S}_{1}{S}_{2}N$, we can write that $sin\theta=\dfrac{{S}_{2}N}{{S}_{2}{S}_{1}}$
Therefore, $\delta x={S}_{2}N={S}_{2}{S}_{1}sin\theta =dsin\theta$
Since, here$\theta$ is so small, we can write $sin\theta \simeq \theta =tan\theta =\dfrac{x}{D}$
Thus, path difference $\delta x=\dfrac{xd}{D}$
(i) Now, we can find the condition for constructive interference as
$\dfrac{xd}{D}=n\lambda ;n=0,1,2.....$
Thus, the position of $n{th}$ bright fringe, ${X}_{n}=\dfrac{nD\lambda}{d}$, where n=0 and ${X}_{n}=0$, central bright fringe will be formed at O.
(ii) The condition for destructive interference can be given by
$\dfrac{xd}{D}=(2n-1)\dfrac{\lambda}{2}$, for n = 1, 2…..
(b) We have been given two wavelengths of light ${\lambda}_{1}$ and ${\lambda}_{2}$ with values 800 nm and 600 nm respectively. The distance between slits and the screen, D = 1.4 m and distance between slits, d = 0.28 mm.
We need to find out the least distance of the point on the screen where the bright fringes of two wavelengths of light coincide with each other.
So, let us consider the ${n}_{1}^{th}$ fringe of wavelength ${\lambda}_{1}$ coincides with the ${n}_{2}^{th}$ fringe of wavelength ${\lambda}_{2}$.
So, we can write that $\dfrac{{n}_{1}{\lambda}_{1}D}{d}=\dfrac{{n}_{2}{\lambda}_{2}D}{d}$
$\implies {n}_{1}{\lambda}_{1}={n}_{2}{\lambda}_{2}\implies \dfrac{{n}_{1}}{{n}_{2}}=\dfrac{{\lambda}_{2}}{{\lambda}_{1}}=\dfrac{600}{800}=\dfrac{3}{4}$
Thus, third bright fringe of light of wavelength ${n}_{1}$ will coincide with the fourth bright fringe of light of wavelength ${n}_{2}$
So, now least distance of the bright fringe from central bright maxima $=\dfrac{3\times {\lambda}_{1}D}{d}=\dfrac{3\times 800\times 10^{-9}\times 1.4}{0.28\times 10^{-3}}=12 mm$
Hence the least distance from the central bright maxima, where the two light wavelengths bright fringe will coincide is 12mm.
Note: One more method, we can use to derive the conditions for constructive and destructive interferences by using the wave equations for the two light sources and finding the phase difference or the path difference.
In the second part of the question we can use both the wavelengths to find the distance required but the condition is to find the distance of that bright fringe only respective to that wavelength as which number bright fringe will coincide in case of both wavelengths will be different.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




