
A hydrocarbon $A$ with molecular formula ${C_9}{H_{10}}$ adds $B{r_2}$ to give $B$ ${C_9}{H_{10}}B{r_2}$ .On hydrolysis give $C$ , which on oxidation gives benzoic acid and acetic acid. $B$ in this sequence will be:
a)
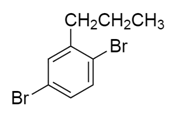
b)
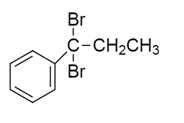
c)
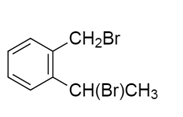
d)
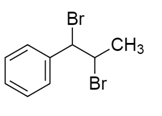




Answer
567k+ views
Hint: We can determine the type of hydrocarbon with the help of general formula of alkane, alkenes or alkynes. Also we can determine the type of hydrocarbon with the help of HUckel’s rule.The reaction proceeds through hydrolysis and later on oxidation takes place to give product as benzoic acid and acetic acid.
Complete step by step answer:
Given data:
Molecular formula of hydrocarbon $A$ is ${C_9}{H_{10}}$ .
Now we will see which type of hydrocarbon it is. Whether it is an alkane, alkene or alkyne or an aromatic compound.
The molecular formula of Alkane: ${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}$
The molecular formula of Alkene: ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$
The molecular formula of Alkyne: ${C_n}{H_{2n - 2}}$
The molecular formula of aromatic compound: ${C_n}{H_n}$
Even after all this we cannot predict the structure, so we will check the structure of hydrocarbon with the help of huckel rule.
Huckel’s rule:$4n + 2\pi $
Using the Huckel’s rule we will get to know which type of compound it is:
$4n + 2\pi $
$ = \left( {4 \times 9} \right) + 2$
$ = 38$
The number of pi electrons present in the hydrocarbon is even.
Since, it is an even integer, the given hydrocarbon may be aromatic which means it consists of one benzene ring.
Now using this the above data we will see the structure of the hydrocarbon $A$ .
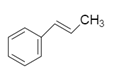
To this we will add bromine because the reaction is addition reaction of bromine:
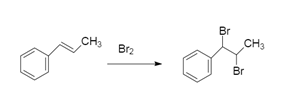
So, the correct answer will be option D.
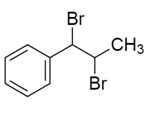
Note:
In the addition of bromine, the bromination takes place at the opposite faces of the double bond. So this type of addition is known as anti addition as the product we get are the vicinal dibromides.
Complete step by step answer:
Given data:
Molecular formula of hydrocarbon $A$ is ${C_9}{H_{10}}$ .
Now we will see which type of hydrocarbon it is. Whether it is an alkane, alkene or alkyne or an aromatic compound.
The molecular formula of Alkane: ${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}$
The molecular formula of Alkene: ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$
The molecular formula of Alkyne: ${C_n}{H_{2n - 2}}$
The molecular formula of aromatic compound: ${C_n}{H_n}$
Even after all this we cannot predict the structure, so we will check the structure of hydrocarbon with the help of huckel rule.
Huckel’s rule:$4n + 2\pi $
Using the Huckel’s rule we will get to know which type of compound it is:
$4n + 2\pi $
$ = \left( {4 \times 9} \right) + 2$
$ = 38$
The number of pi electrons present in the hydrocarbon is even.
Since, it is an even integer, the given hydrocarbon may be aromatic which means it consists of one benzene ring.
Now using this the above data we will see the structure of the hydrocarbon $A$ .

To this we will add bromine because the reaction is addition reaction of bromine:

So, the correct answer will be option D.

Note:
In the addition of bromine, the bromination takes place at the opposite faces of the double bond. So this type of addition is known as anti addition as the product we get are the vicinal dibromides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




