
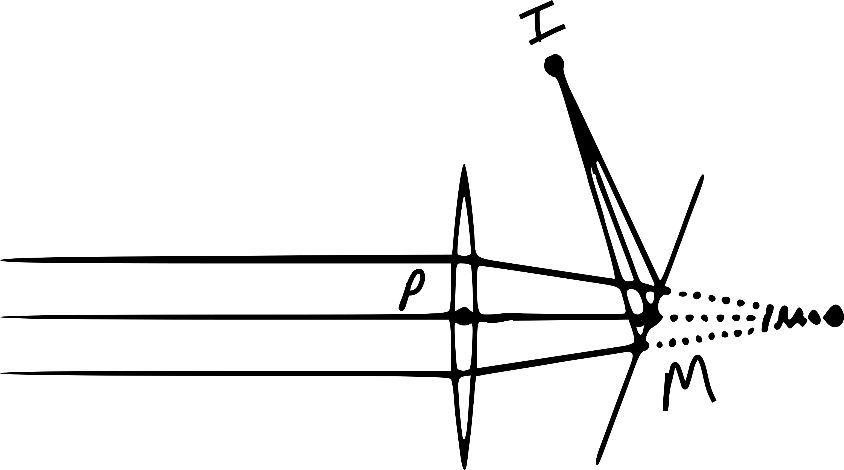
A horizontal parallel beam of light passes through a vertical convex lens of focal
length $20 \mathrm{cm}$ and is then reflected by a tilted plane mirror so that it coverages to a point I. The distance PI is $10 \mathrm{cm}$. $\mathrm{M}$ is a point at which the axis of the lens intersects the mirror. The distance $\mathrm{PM}$ is 10 $\mathrm{cm}$. The angle which the mirror makes with the horizontal is
A. ${{15}^{o}}$
B. ${{30}^{o}}$
C. ${{45}^{o}}$
D. ${{60}^{o}}$

Answer
534k+ views
Hint: We know that the Snell's law, in optics, a relationship between the path taken by a ray of light in crossing the boundary or surface of separation between two contacting substances and the refractive index of each. This law was discovered in 1621 by the Dutch astronomer and mathematician Willebrand Snell (also called Snellius). The point on the surface where the incident ray strikes the surface is called the point of incidence. The ray of light that bounces back from the surface of an object is called a reflected ray of light. When a line is drawn perpendicular to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence, this line is known as normal. The normal ray is incident at 90 degrees to the reflecting surface.
Complete answer:
We know that an incident ray is a ray of light that strikes a surface. The angle between this ray and the perpendicular or normal to the surface is the angle of incidence. The reflected ray corresponding to a given incident ray, is the ray that represents the light reflected by the surface.
We can say that refraction is an effect that occurs when a light wave, incident at an angle away from the normal, passes a boundary from one medium into another in which there is a change in velocity of the light. The wavelength decreases as the light enters the medium and the light wave changes direction.
Observing the figure, $\angle \mathrm{PMI}=60^{\circ}$ as $\triangle \mathrm{PMI}$ is equilateral.
Thus, the normal to the mirror surface at M makes an angle of $30^{\circ}$
with $\mathrm{P} \mathrm{M}$the is Normal to the mirror makes an angle of $30^{\circ}$ with the Horizontal
Thus, the mirror makes $60^{\circ}$ with the horizontal.
So, the correct answer is option D.
Note:
We can conclude that the two laws followed by a beam of light traversing through two media are:
The incident ray refracted ray, and the normal to the interface of two media at the point of incidence all lie on the same plane.
The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant.
The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the reflection surface at the point of the incidence lie in the same plane. The angle which the incident ray makes with the normal is equal to the angle which the reflected ray makes to the same normal.
Complete answer:
We know that an incident ray is a ray of light that strikes a surface. The angle between this ray and the perpendicular or normal to the surface is the angle of incidence. The reflected ray corresponding to a given incident ray, is the ray that represents the light reflected by the surface.
We can say that refraction is an effect that occurs when a light wave, incident at an angle away from the normal, passes a boundary from one medium into another in which there is a change in velocity of the light. The wavelength decreases as the light enters the medium and the light wave changes direction.
Observing the figure, $\angle \mathrm{PMI}=60^{\circ}$ as $\triangle \mathrm{PMI}$ is equilateral.
Thus, the normal to the mirror surface at M makes an angle of $30^{\circ}$
with $\mathrm{P} \mathrm{M}$the is Normal to the mirror makes an angle of $30^{\circ}$ with the Horizontal
Thus, the mirror makes $60^{\circ}$ with the horizontal.
So, the correct answer is option D.
Note:
We can conclude that the two laws followed by a beam of light traversing through two media are:
The incident ray refracted ray, and the normal to the interface of two media at the point of incidence all lie on the same plane.
The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant.
The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the reflection surface at the point of the incidence lie in the same plane. The angle which the incident ray makes with the normal is equal to the angle which the reflected ray makes to the same normal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




