
A hollow cylindrical box of length $1m$ and area of cross-section $25c{m^2}$ is placed in a three dimensional coordinate system as shown in the figure. The electric field in the region is given by $E = 50x\hat i$ , where $E$ is in $N{C^{ - 1}}$ and $x$ is in meters.
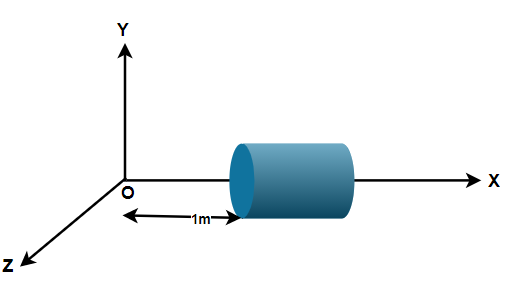
Find
$\left( i \right)$ Net flux through the cylinder
$\left( {ii} \right)$ Charge enclosed by the cylinder

Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint: So in this question, we have to find the electric flux and for this, we have the formula for flux given by $\vec E \cdot \vartriangle \vec S$ . By using this formula we will find the electric flux. For finding the enclosed charge we will use the gauss formula, which is given by $\oint {\vec E \cdot d\vec S} = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _ \circ }}}$ . So by using this we will get the enclosed charge.
Formula used:
Gauss’s law,
${\phi _E} = \oint {\vec E \cdot d\vec S} = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _ \circ }}}$
Here, ${\phi _E}$ will be the electric flux through a closed surface and enclosing volume.
$q$ , will be the total charge.
${\varepsilon _ \circ }$ , is the electric constant.
Complete step by step answer: So we have the area of cross-section given as
$\vartriangle S = 25c{m^2} = 25 \times {10^{ - 4}}{m^2}$
$\left( i \right)$ Since, from the question it is clear that the electric field is only along the x-axis, therefore the flux will pass through the cross-section of the cylinder.
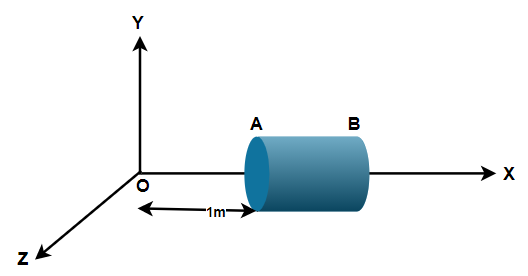
Hence, the magnitude of electric field at cross-section $A$,
$ \Rightarrow {E_A} = 50 \times 1 = 50N/C$
Similarly, the magnitude of electric field at cross-section $B$,
$ \Rightarrow {E_B} = 50 \times 2 = 100N/C$
Therefore, the electric flux will become
$ \Rightarrow \oint {{\phi _A} = \vec E \cdot \vartriangle \vec S} $
And on substituting the values, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \oint {{\phi _A} = 50 \times 25 \times {{10}^{ - 4}} \times \cos {{180}^ \circ }} \]
And on solving it, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \oint {{\phi _A} = - 0.125N{m^2}/{C^2}} \]
Similarly for $B$ also, it will be
$ \Rightarrow \oint {{\phi _B} = \vec E \cdot \vartriangle \vec S} $
And on substituting the values, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \oint {{\phi _B} = 100 \times 25 \times {{10}^{ - 4}} \times \cos {0^ \circ }} \]
And on solving it, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \oint {{\phi _B} = 0.25N{m^2}/{C^2}} \]
Therefore, the net flux through the cylinder will be equals to
\[ \Rightarrow \oint {\phi = } \,\,\oint {{\phi _A}} + \oint {{\phi _B}} \]
And on substituting the values, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \oint {\phi = } \,\,0.125 + 0.25\]
And on solving it, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \oint {\phi = } \,\,0.375N{m^2}/{C^2}\]
Therefore, the net flux through the cylinder is equal to \[0.375N{m^2}/{C^2}\] .
$\left( {ii} \right)$ Now by using the Gauss’s law, we have
$\phi = \oint {\vec E \cdot d\vec S} = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _ \circ }}}$
Now on substituting the values, we get
$ \Rightarrow 0.375 = \dfrac{q}{{8.85 \times {{10}^{ - 12}}}}$
And on solving it, we get
$ \Rightarrow q = 8.85 \times {10^{ - 12}} \times 0.375$
And on solving,
$ \Rightarrow q = 3.3 \times {10^{ - 12}}C$
Therefore, the charge enclosed by the cylinder equals $3.3 \times {10^{ - 12}}C$ .
Note: The final goal of Gauss’s law in electrostatics is to calculate the electric field for a given charge distribution, surrounded by a closed surface. The purpose of the electric field becomes much modest if the body due to a closed surface shows some symmetry in relation to the given charge distribution.
Formula used:
Gauss’s law,
${\phi _E} = \oint {\vec E \cdot d\vec S} = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _ \circ }}}$
Here, ${\phi _E}$ will be the electric flux through a closed surface and enclosing volume.
$q$ , will be the total charge.
${\varepsilon _ \circ }$ , is the electric constant.
Complete step by step answer: So we have the area of cross-section given as
$\vartriangle S = 25c{m^2} = 25 \times {10^{ - 4}}{m^2}$
$\left( i \right)$ Since, from the question it is clear that the electric field is only along the x-axis, therefore the flux will pass through the cross-section of the cylinder.

Hence, the magnitude of electric field at cross-section $A$,
$ \Rightarrow {E_A} = 50 \times 1 = 50N/C$
Similarly, the magnitude of electric field at cross-section $B$,
$ \Rightarrow {E_B} = 50 \times 2 = 100N/C$
Therefore, the electric flux will become
$ \Rightarrow \oint {{\phi _A} = \vec E \cdot \vartriangle \vec S} $
And on substituting the values, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \oint {{\phi _A} = 50 \times 25 \times {{10}^{ - 4}} \times \cos {{180}^ \circ }} \]
And on solving it, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \oint {{\phi _A} = - 0.125N{m^2}/{C^2}} \]
Similarly for $B$ also, it will be
$ \Rightarrow \oint {{\phi _B} = \vec E \cdot \vartriangle \vec S} $
And on substituting the values, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \oint {{\phi _B} = 100 \times 25 \times {{10}^{ - 4}} \times \cos {0^ \circ }} \]
And on solving it, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \oint {{\phi _B} = 0.25N{m^2}/{C^2}} \]
Therefore, the net flux through the cylinder will be equals to
\[ \Rightarrow \oint {\phi = } \,\,\oint {{\phi _A}} + \oint {{\phi _B}} \]
And on substituting the values, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \oint {\phi = } \,\,0.125 + 0.25\]
And on solving it, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \oint {\phi = } \,\,0.375N{m^2}/{C^2}\]
Therefore, the net flux through the cylinder is equal to \[0.375N{m^2}/{C^2}\] .
$\left( {ii} \right)$ Now by using the Gauss’s law, we have
$\phi = \oint {\vec E \cdot d\vec S} = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _ \circ }}}$
Now on substituting the values, we get
$ \Rightarrow 0.375 = \dfrac{q}{{8.85 \times {{10}^{ - 12}}}}$
And on solving it, we get
$ \Rightarrow q = 8.85 \times {10^{ - 12}} \times 0.375$
And on solving,
$ \Rightarrow q = 3.3 \times {10^{ - 12}}C$
Therefore, the charge enclosed by the cylinder equals $3.3 \times {10^{ - 12}}C$ .
Note: The final goal of Gauss’s law in electrostatics is to calculate the electric field for a given charge distribution, surrounded by a closed surface. The purpose of the electric field becomes much modest if the body due to a closed surface shows some symmetry in relation to the given charge distribution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




