
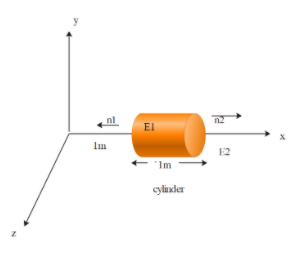
A hollow cylindrical box of length 1m and area of cross section $25c{{m}^{2}}$ is placed in a three dimensional coordinate system as shown in fig, the electric field in the
region is given by $E=50x\hat{i}$, where e is in $N{{C}^{-1}}$ and x is in meter. Find
(i) net flux through the cylinder
(ii) charge enclosed by the cylinder.
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint:The net flux flowing through the cylinder will be equal to the sum of flux flowing through the left-hand side and the flux flowing through the right-hand side of the cylinder. Assume the cylinder is placed at unit distance from the coordinate axis. We can easily find it out.
Formulas used:
$\phi =Eds\cos \theta $
Complete answer:
Let us write done the given parameters,
$\begin{align}
& ds=25c{{m}^{2}} \\
& ds=25\times {{10}^{-4}}{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Also, the electric field is changing with the distance x. If we assume the cylinder is placed at unit distance from axis,
We get the flux through the left side of the cylinder as ,.
$\begin{align}
& {{\phi }_{1}}={{E}_{1}}ds\cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow {{\phi }_{1}}=50\times 25\times {{10}^{-4}}(-1) \\
& \Rightarrow {{\phi }_{1}}=-0.125N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Similarly, for the right-hand side of the cylinder, the electric field changes and the flux will be,
$\begin{align}
& {{\phi }_{2}}={{E}_{2}}ds\cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow {{\phi }_{2}}=100\times 25\times {{10}^{-4}}(1) \\
& \Rightarrow {{\phi }_{2}}=0.250N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the net flux will be,
$\begin{align}
& \phi ={{\phi }_{1}}+{{\phi }_{2}} \\
& \phi =-0.125+0.250 \\
& \phi =0.125N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
also, the charge can be found by,
$\begin{align}
& q={{\varepsilon }_{0}}\phi \\
& \Rightarrow q=8.85\times {{10}^{-12}}\times 0.125 \\
& \Rightarrow q=1.106\times {{10}^{-12}}C \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the charge and the electric flux is calculated as above.
Additional information:
Electric flux is the rate of flow of the electric field through a given area. Take flax is proportional to the number of electric field lines going through a virtual surface. For a non-uniform electric field, directrix flux through a small surface area is calculated, integration is applied for finding the electric flux for the whole surface area. Gauss law describes the electric flux over a surface as the surface integral. The angle between electric field lines and a normal to s is taken in the flux formula.
The electric flux is not affected by charges that are not within the close to the surface. The Dunnett electric field can be affected by charges that like outside the closed surface. But the electric flux will not be changed.
Note:
The electric flux is affected only by the amount of charges present inside the surface taken or the closed surface. The charge outside the flux doesn’t affect the flux. Electric fields will get affected by the charges present inside and outside the closed surface.
Formulas used:
$\phi =Eds\cos \theta $
Complete answer:
Let us write done the given parameters,
$\begin{align}
& ds=25c{{m}^{2}} \\
& ds=25\times {{10}^{-4}}{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Also, the electric field is changing with the distance x. If we assume the cylinder is placed at unit distance from axis,
We get the flux through the left side of the cylinder as ,.
$\begin{align}
& {{\phi }_{1}}={{E}_{1}}ds\cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow {{\phi }_{1}}=50\times 25\times {{10}^{-4}}(-1) \\
& \Rightarrow {{\phi }_{1}}=-0.125N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Similarly, for the right-hand side of the cylinder, the electric field changes and the flux will be,
$\begin{align}
& {{\phi }_{2}}={{E}_{2}}ds\cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow {{\phi }_{2}}=100\times 25\times {{10}^{-4}}(1) \\
& \Rightarrow {{\phi }_{2}}=0.250N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the net flux will be,
$\begin{align}
& \phi ={{\phi }_{1}}+{{\phi }_{2}} \\
& \phi =-0.125+0.250 \\
& \phi =0.125N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
also, the charge can be found by,
$\begin{align}
& q={{\varepsilon }_{0}}\phi \\
& \Rightarrow q=8.85\times {{10}^{-12}}\times 0.125 \\
& \Rightarrow q=1.106\times {{10}^{-12}}C \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the charge and the electric flux is calculated as above.

Additional information:
Electric flux is the rate of flow of the electric field through a given area. Take flax is proportional to the number of electric field lines going through a virtual surface. For a non-uniform electric field, directrix flux through a small surface area is calculated, integration is applied for finding the electric flux for the whole surface area. Gauss law describes the electric flux over a surface as the surface integral. The angle between electric field lines and a normal to s is taken in the flux formula.
The electric flux is not affected by charges that are not within the close to the surface. The Dunnett electric field can be affected by charges that like outside the closed surface. But the electric flux will not be changed.
Note:
The electric flux is affected only by the amount of charges present inside the surface taken or the closed surface. The charge outside the flux doesn’t affect the flux. Electric fields will get affected by the charges present inside and outside the closed surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




