
A hemisphere is uniformly charged positively. The electric field at a point on a diameter away from the centre is directed:
A. perpendicular to the diameter
B. parallel to the diameter
C. at an angle tilted towards the diameter
D. at angle tilted away from the diameter
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: We can approach this problem with the help of basic concepts of electrostatics. When the charge $q$ is given to a hemisphere shell then it is automatically distributed on its whole surface.The electric field $E$ by hemisphere shell is away from the shell by positive charge but for negative charge towards the shell.
Complete step by step answer:
Hence we can solve this problem with the help of Gauss Law. According to this law the net flux through a closed surface is directly proportional to the net charge enclosed by the whole surface.
If we put two symmetrical hemisphere by coinciding their plane surface so then we can consider it a closed shell hence the net electric flux through this is given by the equation, $\Phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$ where $\Phi $ represents electric flux and ${\varepsilon _0}$ represents permittivity constant. As we know that this is the flux when two identical hemispheres are joined together by their plane surface so the electric flux by a hemisphere shell is half of the whole shell . We know that magnitude of electric flux is given by the product of intensity electric field and magnitude of area vector perpendicular to it. Thus $ \Rightarrow \Phi = \oint {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dA} } $ . The following figure shows the direction of electric field at a point on a diameter away from the centre is directed perpendicular to the diameter.
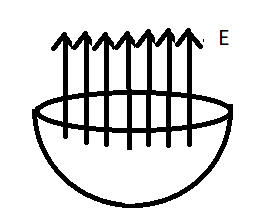
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Hence we have solved this problem by making a complete sphere as we have joined two hemispheres in order to make a complete sphere. When the electric field is perpendicular to the diameter then this orientation of the electric field will give a vector sum equal to zero.
Complete step by step answer:
Hence we can solve this problem with the help of Gauss Law. According to this law the net flux through a closed surface is directly proportional to the net charge enclosed by the whole surface.
If we put two symmetrical hemisphere by coinciding their plane surface so then we can consider it a closed shell hence the net electric flux through this is given by the equation, $\Phi = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$ where $\Phi $ represents electric flux and ${\varepsilon _0}$ represents permittivity constant. As we know that this is the flux when two identical hemispheres are joined together by their plane surface so the electric flux by a hemisphere shell is half of the whole shell . We know that magnitude of electric flux is given by the product of intensity electric field and magnitude of area vector perpendicular to it. Thus $ \Rightarrow \Phi = \oint {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dA} } $ . The following figure shows the direction of electric field at a point on a diameter away from the centre is directed perpendicular to the diameter.

So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Hence we have solved this problem by making a complete sphere as we have joined two hemispheres in order to make a complete sphere. When the electric field is perpendicular to the diameter then this orientation of the electric field will give a vector sum equal to zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




