
A golf ball has a diameter equal to 4.2 cm. Its surface has 200 dimples each of a radius of 2 mm. Calculate the total surface area which is exposed to the surroundings assuming that the dimples are hemispherical.
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: We start solving the problem by drawing the figure representing the given information. We then find the surface area of the golf ball by using the fact that the surface area of a sphere with diameter ‘d’ is \[\pi {{d}^{2}}\]. We then find the surface and base area of each dimple by using facts that the curved surface area and the base area of the hemisphere with radius ‘r’ is \[2\pi {{r}^{2}}\] and \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\]. We then filled them with 200 in order to include all the 200 dimples. We then add the curved surface area and subtract the base area of dimples from the surface area of the golf ball to find the total exposed surface area.
Complete step-by-step solution:
According to the problem, we are given that a golf ball has a diameter equal to 4.2 cm and its surface has 200 dimples each of radius 2 mm. We need to find the total surface area which is exposed to the surroundings assuming that the dimples are hemispherical.
Let us draw the figure to represent the given information.
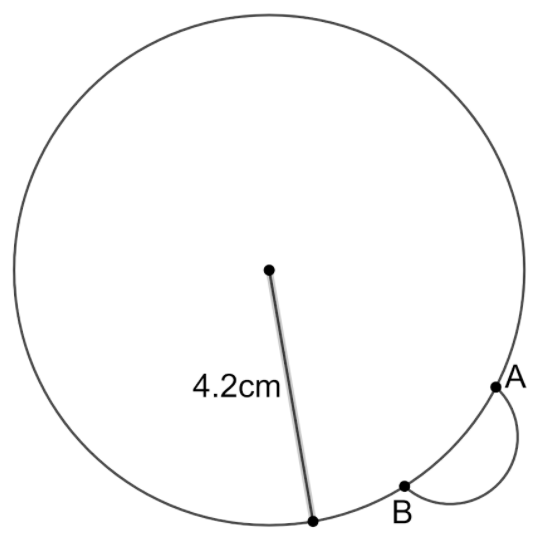
This figure cross-section of the golf ball and curve AB represents one of the dimples on the golf ball.
Let us first find the surface area of a spherical golf ball.
We know that the surface area of a sphere with diameter ‘d’ is defined as \[\pi {{d}^{2}}\].
So, the surface area of the golf ball is $\pi {{\left( 4.2 \right)}^{2}}=17.64\pi c{{m}^{2}}$.
From the figure, we can see that the dimple’s curved surface area is exposed to the surrounding but the base area is covering the exposed surface area of the golf ball.
We know that the curved surface area and base area of the hemisphere with radius ‘r’ is \[2\pi {{r}^{2}}\] and \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\].
We know that $1mm=\dfrac{1}{10}cm$.
So, the curved surface area of each dimple is \[2\pi {{\left( \dfrac{2}{10} \right)}^{2}}=2\pi {{\left( 0.2 \right)}^{2}}=0.08\pi c{{m}^{2}}\].
And the base area of each dimple is \[\pi {{\left( \dfrac{2}{10} \right)}^{2}}=\pi {{\left( 0.2 \right)}^{2}}=0.04\pi c{{m}^{2}}\].
According to the problem, we are given that there are 200 dimples.
So, the curved surface area of 200 dimples is $200\times 0.08\pi =16\pi c{{m}^{2}}$ and the base area of 200 dimples is $200\times 0.04\pi =8\pi c{{m}^{2}}$.
We need to find the total exposed area on the golf ball. We can see that the base area of the dimple is covering the surface area of the golf ball and the curved surface of the dimple is exposed to the surroundings. So, we need to add the curved surface area and subtract the base area of the dimple from the surface area of the golf ball to find the total exposed surface area.
So, the total exposed surface area of the golf ball = $17.64\pi +16\pi -8\pi =25.64\pi c{{m}^{2}}$.
We have found the total exposed surface area on the golf ball as $25.64\pi c{{m}^{2}}$.
Note: We should draw the figure perfectly while solving this problem as we can see that the figure itself gives us half of the answer. We should not confuse with the formulas of the surface area of the sphere and hemisphere while solving this problem. We should know that the base of the hemisphere is a circle with a radius the same as the radius of the hemisphere. Similarly, we can expect problems to find the percentage of curved surface area in the total exposed surface area.
Complete step-by-step solution:
According to the problem, we are given that a golf ball has a diameter equal to 4.2 cm and its surface has 200 dimples each of radius 2 mm. We need to find the total surface area which is exposed to the surroundings assuming that the dimples are hemispherical.
Let us draw the figure to represent the given information.

This figure cross-section of the golf ball and curve AB represents one of the dimples on the golf ball.
Let us first find the surface area of a spherical golf ball.
We know that the surface area of a sphere with diameter ‘d’ is defined as \[\pi {{d}^{2}}\].
So, the surface area of the golf ball is $\pi {{\left( 4.2 \right)}^{2}}=17.64\pi c{{m}^{2}}$.
From the figure, we can see that the dimple’s curved surface area is exposed to the surrounding but the base area is covering the exposed surface area of the golf ball.
We know that the curved surface area and base area of the hemisphere with radius ‘r’ is \[2\pi {{r}^{2}}\] and \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\].
We know that $1mm=\dfrac{1}{10}cm$.
So, the curved surface area of each dimple is \[2\pi {{\left( \dfrac{2}{10} \right)}^{2}}=2\pi {{\left( 0.2 \right)}^{2}}=0.08\pi c{{m}^{2}}\].
And the base area of each dimple is \[\pi {{\left( \dfrac{2}{10} \right)}^{2}}=\pi {{\left( 0.2 \right)}^{2}}=0.04\pi c{{m}^{2}}\].
According to the problem, we are given that there are 200 dimples.
So, the curved surface area of 200 dimples is $200\times 0.08\pi =16\pi c{{m}^{2}}$ and the base area of 200 dimples is $200\times 0.04\pi =8\pi c{{m}^{2}}$.
We need to find the total exposed area on the golf ball. We can see that the base area of the dimple is covering the surface area of the golf ball and the curved surface of the dimple is exposed to the surroundings. So, we need to add the curved surface area and subtract the base area of the dimple from the surface area of the golf ball to find the total exposed surface area.
So, the total exposed surface area of the golf ball = $17.64\pi +16\pi -8\pi =25.64\pi c{{m}^{2}}$.
We have found the total exposed surface area on the golf ball as $25.64\pi c{{m}^{2}}$.
Note: We should draw the figure perfectly while solving this problem as we can see that the figure itself gives us half of the answer. We should not confuse with the formulas of the surface area of the sphere and hemisphere while solving this problem. We should know that the base of the hemisphere is a circle with a radius the same as the radius of the hemisphere. Similarly, we can expect problems to find the percentage of curved surface area in the total exposed surface area.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

What is the color of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this color change after heating? Name the products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this type of change.

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Explain the importance of pH in everyday life class 9 chemistry CBSE




