
A glass tube of uniform internal radius (r) has a valve separating the two identical ends. initially, the valve is in a tightly closed position. End 1 has a hemispherical soap bubble of radius r. End 2 has a sub-hemispherical soap bubble as shown in the figure. Just after opening the valve.
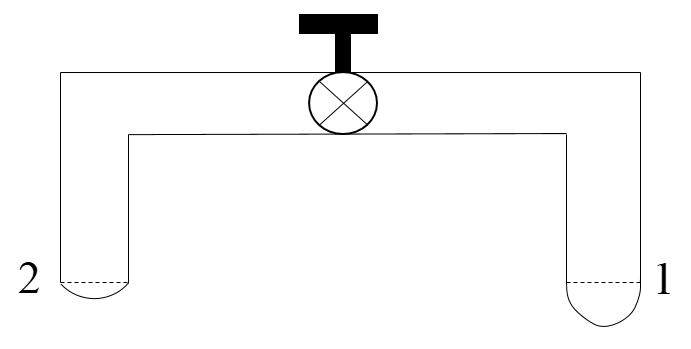
A. Air from end 1 flows towards end 2. No change in the volume of the soap bubbles.
B. Air from end 1 flows towards end 2. Volume of the soap bubble at end 1 decreases.
C. No change occurs.
D. Air from end 2 flows towards end 1. Volume of the soap bubble at end 1 increases.

Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: The question clearly mentions the radius. Also, the options mention about the movement of air. This implies there is air pressure which is talked about. Hence, we are going to find the amount of excess pressure present on both sides and then comment upon the answer.
Formula used:
$\Delta P \propto \dfrac{1}{r}$
Complete answer:
Here, it is asked to comment about the movement of air within the pipe. Along with that, it is also asked about to comment upon the size of the bubbles, if they will increase or decrease.
Here, we are going to comment upon the movement of air within the pipe by finding out and comparing the excess pressure on both sides.
We know that the excess pressure expression of the soap bubble represents an inverse relation between the excess pressure present within the soap bubble and the radius of the bubble. This can be mathematically represented as:
$\Delta P \propto \dfrac{1}{r}$ ----(i)
Where, $\Delta P$ is the excess pressure within the bubble and $r$ is the radius of the bubble.
We know that the radius of a hemispherical bubble present at the end 1 will be less than the radius of a semi-hemispherical bubble present at the end 2. This implies that the excess pressure present at the bubble 1 will be more than the excess pressure associated with the bubble present at the end 2, i.e.,
$\Delta {{P}_{1}}>\Delta {{P}_{2}}$ -----(ii)
Hence, due to more excess pressure present at the end 1, air from end 1 will move towards the end 2. In this process, the size of the bubble present at end 1 will decrease and that at the end 2 will increase.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
We need to look for excess pressure and not absolute pressure. The excess pressure ($\Delta P$) is inversely proportional to the radius of the bubble and not directly proportional to the radius. More excess pressure will push the air from point with more pressure to less pressure.
Formula used:
$\Delta P \propto \dfrac{1}{r}$
Complete answer:
Here, it is asked to comment about the movement of air within the pipe. Along with that, it is also asked about to comment upon the size of the bubbles, if they will increase or decrease.
Here, we are going to comment upon the movement of air within the pipe by finding out and comparing the excess pressure on both sides.
We know that the excess pressure expression of the soap bubble represents an inverse relation between the excess pressure present within the soap bubble and the radius of the bubble. This can be mathematically represented as:
$\Delta P \propto \dfrac{1}{r}$ ----(i)
Where, $\Delta P$ is the excess pressure within the bubble and $r$ is the radius of the bubble.
We know that the radius of a hemispherical bubble present at the end 1 will be less than the radius of a semi-hemispherical bubble present at the end 2. This implies that the excess pressure present at the bubble 1 will be more than the excess pressure associated with the bubble present at the end 2, i.e.,
$\Delta {{P}_{1}}>\Delta {{P}_{2}}$ -----(ii)
Hence, due to more excess pressure present at the end 1, air from end 1 will move towards the end 2. In this process, the size of the bubble present at end 1 will decrease and that at the end 2 will increase.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
We need to look for excess pressure and not absolute pressure. The excess pressure ($\Delta P$) is inversely proportional to the radius of the bubble and not directly proportional to the radius. More excess pressure will push the air from point with more pressure to less pressure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




