
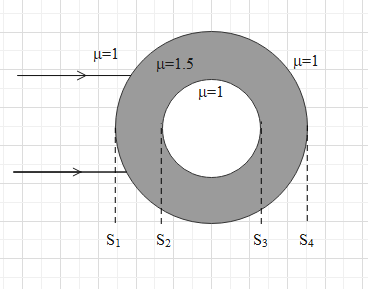
A glass sphere, refractive index 1.5 and radius 10cm, has a spherical cavity of radius 5cm concentric with it. A narrow beam of light is directed into the sphere. Find the final image and its nature.
$\text{A}\text{. 25cm left of }{{\text{S}}_{\text{4}}}\text{, virtual}$
$\text{B}\text{. 25cm right of }{{\text{S}}_{\text{4}}}\text{, virtual}$
$\text{C}\text{. 15cm left of }{{\text{S}}_{\text{4}}}\text{, virtual}$
$\text{D}\text{. 20cm right of }{{\text{S}}_{\text{4}}}\text{, virtual}$

Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: The will be four images formed due the refraction of the light rays at the four surfaces. The first three are intermediate and the last one is the final image. The image found due to one surface will act as an object for the surface. Use the formula $\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{v}-\dfrac{{{\mu }_{1}}}{u}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}-{{\mu }_{1}}}{R}$ to locate the positions of the images.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{v}-\dfrac{{{\mu }_{1}}}{u}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}-{{\mu }_{1}}}{R}$
Complete step by step answer:
When rays of light from an object pass into a different medium, the rays refract and an image of the object is created. If the refracted rays of light intersect at a point, then the image is called a real image. If the rays of light appear to be emerging from a point, then the image is called a virtual image.
If the rays light pass through a spherical surface, the relation between the positions of the object and its image is given as $\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{v}-\dfrac{{{\mu }_{1}}}{u}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}-{{\mu }_{1}}}{R}$.
Here, ${{\mu }_{1}}$ and ${{\mu }_{2}}$ are the refractive indices of the incident medium and refracted medium respectively. v and u are the positions of the object and image respectively, according to the sign convection. R is the radius of the spherical surface.
Here, the rays of light will refract at all the four surfaces. Therefore, there will be four images formed. The final image of the object will form when the light is refracted at surface ${{S}_{1}}$.
First, it will refract at surface ${{S}_{1}}$.
Here, ${{\mu }_{1}}=1$, ${{\mu }_{2}}=1.5$, $u=-\infty $ and R=10cm. Let $v={{v}_{1}}$
Hence, we get
$\dfrac{1.5}{{{v}_{1}}}-\dfrac{1}{-\infty }=\dfrac{1.5-1}{10}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1.5}{{{v}_{1}}}-0=\dfrac{0.5}{10}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v}_{1}}}=\dfrac{0.5}{15}=\dfrac{1}{30}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{1}}=30cm$
Therefore, the first image is formed at a distance of 30cm from surface ${{S}_{1}}$, towards right.
Now, this image will act as an object from surface ${{S}_{2}}$ as the light will again refract at surface ${{S}_{2}}$.
The first image are formed at a position +30cm from ${{S}_{1}}$ and the distance between ${{S}_{1}}$ and ${{S}_{2}}$ is 5cm. Therefore, the position of the first image from ${{S}_{2}}$ is +25cm.
Hence, this case, $u=25cm$, ${{\mu }_{1}}=1.5$, ${{\mu }_{2}}=1$and R=5cm. Let $v={{v}_{2}}$
This implies that
$\dfrac{1}{{{v}_{2}}}-\dfrac{1.5}{25}=\dfrac{1-1.5}{5}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v}_{2}}}-\dfrac{0.3}{5}=\dfrac{-0.5}{5}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v}_{2}}}=\dfrac{0.3}{5}-\dfrac{0.5}{5}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v}_{2}}}=-\dfrac{0.2}{5}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{2}}=-\dfrac{5}{0.2}=-25cm$
This means the second image is formed towards the left of ${{S}_{2}}$ at a distance of 25cm.
Now, this image will act as an object for surface ${{S}_{3}}$.
The second image is formed at a distance of 25cm towards left of ${{S}_{2}}$ and the distance between ${{S}_{2}}$ and ${{S}_{3}}$ is 10cm. Therefore, the position of the second image from ${{S}_{3}}$ is -35cm.
Hence, now $u=-35cm$, ${{\mu }_{1}}=1$, ${{\mu }_{2}}=1.5$and R= -5cm. Let $v={{v}_{3}}$
This implies that
$\dfrac{1.5}{{{v}_{3}}}-\dfrac{1}{-35}=\dfrac{1.5-1}{-5}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1.5}{{{v}_{3}}}+\dfrac{1}{35}=-\dfrac{0.5}{5}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1.5}{{{v}_{3}}}=-\dfrac{0.5}{5}-\dfrac{1}{35}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1.5}{{{v}_{3}}}=\dfrac{-3.5-1}{35}=\dfrac{-4.5}{35}=\dfrac{-0.9}{7}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{3}}=-\dfrac{1.5\times 7}{0.9}=-\dfrac{35}{3}cm$
This means the third image is formed towards the left of ${{S}_{3}}$ at a distance of $-\dfrac{35}{3}$cm.
Now, this image will act as an object for surface ${{S}_{4}}$.
The third image is formed at a distance of $-\dfrac{35}{3}$cm towards left of ${{S}_{3}}$ and the distance between ${{S}_{3}}$ and ${{S}_{4}}$ is 5cm. Therefore, the position of the second image from ${{S}_{3}}$ is $-\left( \dfrac{35}{3}+5 \right)=-\dfrac{50}{3}cm$.
Hence, now $u=-\dfrac{50}{3}cm$, ${{\mu }_{1}}=1.5$, ${{\mu }_{2}}=1$ and R= -10cm. Let $v={{v}_{4}}$
This implies that
$\dfrac{1}{{{v}_{4}}}-\dfrac{1.5}{\dfrac{-50}{3}}=\dfrac{1-1.5}{-10}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v}_{4}}}+\dfrac{4.5}{50}=\dfrac{-0.5}{-10}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v}_{4}}}=\dfrac{0.5}{10}-\dfrac{4.5}{50}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v}_{4}}}=\dfrac{2.5-4.5}{50}=\dfrac{-2.5}{50}=\dfrac{-1}{25}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{4}}=-25cm$
This means that the fourth and the final image is towards the left of ${{S}_{4}}$ at the distance of 25 cm. Since, the image is towards the left, the light will diverge at the surface and will appear to emerge from a point. Hence, the image is a virtual image.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: Students can make mistakes while writing the values of u, v and R. These values can be positive as well as negative, according to the sign convection.
The positions from the refracting surface that are directed along the direction of the incident rays, are positive. If the direction of the positions are towards the opposite direction of incident rays, then the positions are considered to be negative.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{v}-\dfrac{{{\mu }_{1}}}{u}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}-{{\mu }_{1}}}{R}$
Complete step by step answer:
When rays of light from an object pass into a different medium, the rays refract and an image of the object is created. If the refracted rays of light intersect at a point, then the image is called a real image. If the rays of light appear to be emerging from a point, then the image is called a virtual image.
If the rays light pass through a spherical surface, the relation between the positions of the object and its image is given as $\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{v}-\dfrac{{{\mu }_{1}}}{u}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}-{{\mu }_{1}}}{R}$.
Here, ${{\mu }_{1}}$ and ${{\mu }_{2}}$ are the refractive indices of the incident medium and refracted medium respectively. v and u are the positions of the object and image respectively, according to the sign convection. R is the radius of the spherical surface.
Here, the rays of light will refract at all the four surfaces. Therefore, there will be four images formed. The final image of the object will form when the light is refracted at surface ${{S}_{1}}$.
First, it will refract at surface ${{S}_{1}}$.
Here, ${{\mu }_{1}}=1$, ${{\mu }_{2}}=1.5$, $u=-\infty $ and R=10cm. Let $v={{v}_{1}}$
Hence, we get
$\dfrac{1.5}{{{v}_{1}}}-\dfrac{1}{-\infty }=\dfrac{1.5-1}{10}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1.5}{{{v}_{1}}}-0=\dfrac{0.5}{10}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v}_{1}}}=\dfrac{0.5}{15}=\dfrac{1}{30}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{1}}=30cm$
Therefore, the first image is formed at a distance of 30cm from surface ${{S}_{1}}$, towards right.
Now, this image will act as an object from surface ${{S}_{2}}$ as the light will again refract at surface ${{S}_{2}}$.
The first image are formed at a position +30cm from ${{S}_{1}}$ and the distance between ${{S}_{1}}$ and ${{S}_{2}}$ is 5cm. Therefore, the position of the first image from ${{S}_{2}}$ is +25cm.
Hence, this case, $u=25cm$, ${{\mu }_{1}}=1.5$, ${{\mu }_{2}}=1$and R=5cm. Let $v={{v}_{2}}$
This implies that
$\dfrac{1}{{{v}_{2}}}-\dfrac{1.5}{25}=\dfrac{1-1.5}{5}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v}_{2}}}-\dfrac{0.3}{5}=\dfrac{-0.5}{5}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v}_{2}}}=\dfrac{0.3}{5}-\dfrac{0.5}{5}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v}_{2}}}=-\dfrac{0.2}{5}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{2}}=-\dfrac{5}{0.2}=-25cm$
This means the second image is formed towards the left of ${{S}_{2}}$ at a distance of 25cm.
Now, this image will act as an object for surface ${{S}_{3}}$.
The second image is formed at a distance of 25cm towards left of ${{S}_{2}}$ and the distance between ${{S}_{2}}$ and ${{S}_{3}}$ is 10cm. Therefore, the position of the second image from ${{S}_{3}}$ is -35cm.
Hence, now $u=-35cm$, ${{\mu }_{1}}=1$, ${{\mu }_{2}}=1.5$and R= -5cm. Let $v={{v}_{3}}$
This implies that
$\dfrac{1.5}{{{v}_{3}}}-\dfrac{1}{-35}=\dfrac{1.5-1}{-5}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1.5}{{{v}_{3}}}+\dfrac{1}{35}=-\dfrac{0.5}{5}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1.5}{{{v}_{3}}}=-\dfrac{0.5}{5}-\dfrac{1}{35}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1.5}{{{v}_{3}}}=\dfrac{-3.5-1}{35}=\dfrac{-4.5}{35}=\dfrac{-0.9}{7}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{3}}=-\dfrac{1.5\times 7}{0.9}=-\dfrac{35}{3}cm$
This means the third image is formed towards the left of ${{S}_{3}}$ at a distance of $-\dfrac{35}{3}$cm.
Now, this image will act as an object for surface ${{S}_{4}}$.
The third image is formed at a distance of $-\dfrac{35}{3}$cm towards left of ${{S}_{3}}$ and the distance between ${{S}_{3}}$ and ${{S}_{4}}$ is 5cm. Therefore, the position of the second image from ${{S}_{3}}$ is $-\left( \dfrac{35}{3}+5 \right)=-\dfrac{50}{3}cm$.
Hence, now $u=-\dfrac{50}{3}cm$, ${{\mu }_{1}}=1.5$, ${{\mu }_{2}}=1$ and R= -10cm. Let $v={{v}_{4}}$
This implies that
$\dfrac{1}{{{v}_{4}}}-\dfrac{1.5}{\dfrac{-50}{3}}=\dfrac{1-1.5}{-10}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v}_{4}}}+\dfrac{4.5}{50}=\dfrac{-0.5}{-10}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v}_{4}}}=\dfrac{0.5}{10}-\dfrac{4.5}{50}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{v}_{4}}}=\dfrac{2.5-4.5}{50}=\dfrac{-2.5}{50}=\dfrac{-1}{25}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{4}}=-25cm$
This means that the fourth and the final image is towards the left of ${{S}_{4}}$ at the distance of 25 cm. Since, the image is towards the left, the light will diverge at the surface and will appear to emerge from a point. Hence, the image is a virtual image.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: Students can make mistakes while writing the values of u, v and R. These values can be positive as well as negative, according to the sign convection.
The positions from the refracting surface that are directed along the direction of the incident rays, are positive. If the direction of the positions are towards the opposite direction of incident rays, then the positions are considered to be negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




