
A glass prism of refractive index 1.5 is placed in water of refractive index 1.33. The minimum value of the angle of the prism so that it will not be possible to have any emergent ray is:
A. $150^{\circ}$
B. $125^{\circ}$
C. $165^{\circ}$
D. $180^{\circ}$
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: Condition of grazing emergence should be applied. It is only the geometry of the prism that separates it from regular glass slab. So, angle of incidence, normal and refraction angle geometry (diagram) should be used here.
Formula used:
Angle of prism relation:
$r_1 +r_2 =A$
The angle can be determined using Snell’s law:
$_{w}\mu_{g}=\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}$
Complete step by step solution:
A prism is an elongated triangle-shaped object which separates light in its components (VIBGYOR). This simply happens due to the fact that the speed of light is different for different wavelengths in a medium. A regular glass slab refracts the light in the same way as prism but consider the prism geometry:
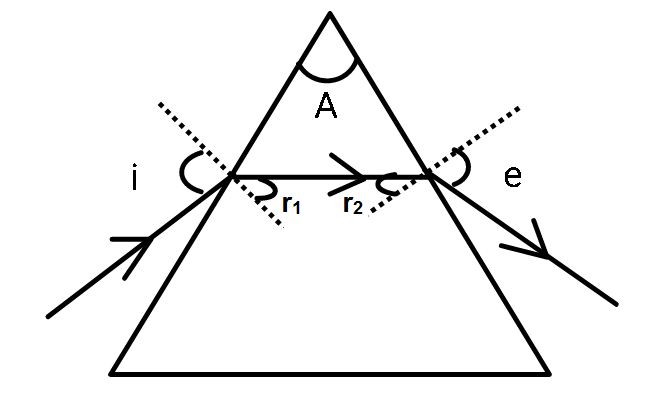
$r_1 +r_2 +some angle =180^{\circ}$ as they form a triangle.
$r_1+r_2$ comes out of it.
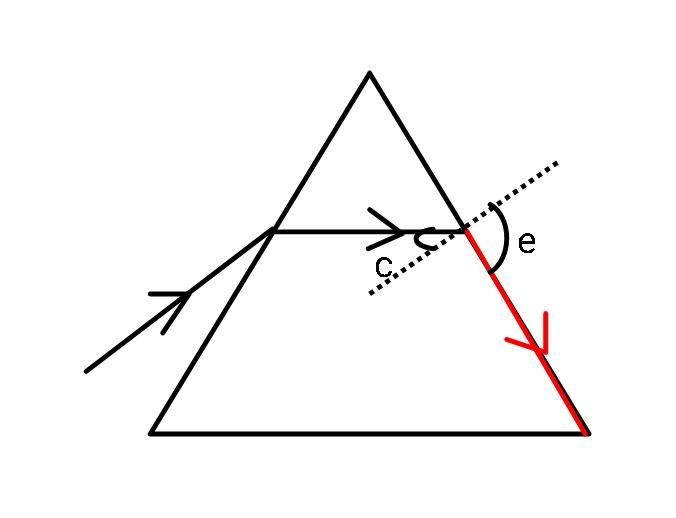
Now, an emergent ray will disappear as it grazes the surface of the prism and makes a right angle with the surface of the prism. Therefore, by using Snell’s law:
$_{w}\mu_{g}=\dfrac{\sin e}{\sin r_2}$
Keeping e=$90^{\circ}$ we get $r_2$ (critical angle c) as:
$r_2=c=\sin^{-1}{\dfrac{1}{_{w}\mu_{g}}}$
For refractive index: as light travels from water to glass:
$_{w}\mu_{g}=\dfrac{\mu_g}{\mu_w}$
We were given a refractive index of glass=1.5 and for water=1.33.
We get, $_{w}\mu_{g}=\dfrac{1.5}{1.33} =1.128$
$r_2=c=\sin^{-1}0.88667 = 62.5^{\circ} $
And for grazing emergence conditions, it is required that A=2c. it is so because, $r_1=r_2=c$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The formula for A has been derived using the properties of the triangle. The 2c condition comes when we apply minimization to both $r_1$ and $r_2$. When A is greater than or equal to 2c, no ray will emerge out of the prism.
Formula used:
Angle of prism relation:
$r_1 +r_2 =A$
The angle can be determined using Snell’s law:
$_{w}\mu_{g}=\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}$
Complete step by step solution:
A prism is an elongated triangle-shaped object which separates light in its components (VIBGYOR). This simply happens due to the fact that the speed of light is different for different wavelengths in a medium. A regular glass slab refracts the light in the same way as prism but consider the prism geometry:


$r_1 +r_2 +some angle =180^{\circ}$ as they form a triangle.
$r_1+r_2$ comes out of it.
Now, an emergent ray will disappear as it grazes the surface of the prism and makes a right angle with the surface of the prism. Therefore, by using Snell’s law:
$_{w}\mu_{g}=\dfrac{\sin e}{\sin r_2}$
Keeping e=$90^{\circ}$ we get $r_2$ (critical angle c) as:
$r_2=c=\sin^{-1}{\dfrac{1}{_{w}\mu_{g}}}$
For refractive index: as light travels from water to glass:
$_{w}\mu_{g}=\dfrac{\mu_g}{\mu_w}$
We were given a refractive index of glass=1.5 and for water=1.33.
We get, $_{w}\mu_{g}=\dfrac{1.5}{1.33} =1.128$
$r_2=c=\sin^{-1}0.88667 = 62.5^{\circ} $
And for grazing emergence conditions, it is required that A=2c. it is so because, $r_1=r_2=c$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The formula for A has been derived using the properties of the triangle. The 2c condition comes when we apply minimization to both $r_1$ and $r_2$. When A is greater than or equal to 2c, no ray will emerge out of the prism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




