
A girl riding a bicycle with a speed of 5 m/s towards north direction, observes rain falling vertically down. If she increases her speed to 10 m/s, rain appears to meet her at 45° to the vertical. What is the speed of the rain? In what direction does rain fall as observed by a ground based observer?
Answer
540.6k+ views
Hint :Assume north to be $ i $ direction and vertically downwards to $ - j $ . Let the rain velocity $ {v_r} $ be $ ai + bj $ . The velocity of the rain observed by the girl is always $ {v_r} - {v_g} $ . Draw vector diagrams for the information given and find $ a $ and $ b $ . We may draw all vectors in the reference frame of the ground-based observer.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
We will separately calculate for both the given cases.
Case-1:
It is given that the velocity of the girl $ {v_g} = 5m/s $ .
We can calculate the velocity of the rain with respect to the girl $ {v_{rg}} $ by using the formula.
$ {v_{rg}} = {v_r} - {v_g} $
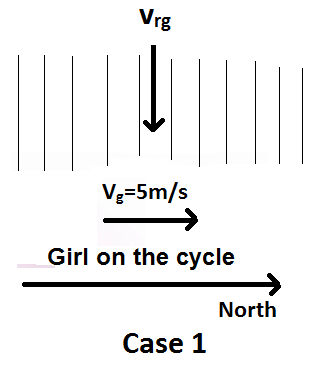
Let the rain velocity $ {v_r} $ be $ ai + bj $ .
$ \Rightarrow {v_{rg}} = ai + bj - 5i = \left( {a - 5} \right)i + bj $
But, it is given that rain is falling vertically down and therefore, its horizontal component will be zero.
$
\Rightarrow a - 5 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow a = 5 \\
$
Case-2:
Now, the girl increases her speed to 10 m/s and the rain appears to meet her at 45° to the vertical as shown in the diagram.
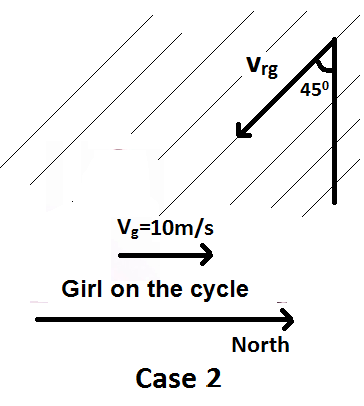
In this case, the velocity of rain with respect to girl is given by:
$ {v_{rg}} = {v_r} - {v_g} = ai + bj - 10i = \left( {a - 10} \right)i + bj $
As the rain appears to meet the girl at 45° to the vertical as shown in the diagram, we can say that
$ \tan {45^ \circ } = \dfrac{b}{{a - 10}} $
We know that $ \tan {45^ \circ } = 1 $ and $ a = 5 $ as determined in the first case.
$
\dfrac{b}{{5 - 10}} = 1 \\
\Rightarrow b = - 5 \\
$
Now we have both the values of $ a $ and $ b $ .
Therefore the velocity of rain $ ai + bj $ is:
$ {v_r} = 5i - 5j $
And the speed of rain will be:
$ \left| {{v_r}} \right| = \sqrt {{{\left( 5 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 5} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {50} = 5\sqrt 2 m/s $
Note :
In this question, we have used the concept of relative velocity. Let us consider two objects M and N moving with velocities $ {v_M} $ and $ {v_N} $ respectively with respect to a common stationary frame of reference.
Then, the relative velocity of object M with respect to object N is given as $ {v_{MN}} = {v_M} - {v_N} $ .
Complete Step By Step Answer:
We will separately calculate for both the given cases.
Case-1:
It is given that the velocity of the girl $ {v_g} = 5m/s $ .
We can calculate the velocity of the rain with respect to the girl $ {v_{rg}} $ by using the formula.
$ {v_{rg}} = {v_r} - {v_g} $

Let the rain velocity $ {v_r} $ be $ ai + bj $ .
$ \Rightarrow {v_{rg}} = ai + bj - 5i = \left( {a - 5} \right)i + bj $
But, it is given that rain is falling vertically down and therefore, its horizontal component will be zero.
$
\Rightarrow a - 5 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow a = 5 \\
$
Case-2:
Now, the girl increases her speed to 10 m/s and the rain appears to meet her at 45° to the vertical as shown in the diagram.

In this case, the velocity of rain with respect to girl is given by:
$ {v_{rg}} = {v_r} - {v_g} = ai + bj - 10i = \left( {a - 10} \right)i + bj $
As the rain appears to meet the girl at 45° to the vertical as shown in the diagram, we can say that
$ \tan {45^ \circ } = \dfrac{b}{{a - 10}} $
We know that $ \tan {45^ \circ } = 1 $ and $ a = 5 $ as determined in the first case.
$
\dfrac{b}{{5 - 10}} = 1 \\
\Rightarrow b = - 5 \\
$
Now we have both the values of $ a $ and $ b $ .
Therefore the velocity of rain $ ai + bj $ is:
$ {v_r} = 5i - 5j $
And the speed of rain will be:
$ \left| {{v_r}} \right| = \sqrt {{{\left( 5 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 5} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {50} = 5\sqrt 2 m/s $
Note :
In this question, we have used the concept of relative velocity. Let us consider two objects M and N moving with velocities $ {v_M} $ and $ {v_N} $ respectively with respect to a common stationary frame of reference.
Then, the relative velocity of object M with respect to object N is given as $ {v_{MN}} = {v_M} - {v_N} $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




