
A gas ‘X’ is present with saturated water vapour over water liquid at a total pressure of $1.5{\text{atm}}$. Vapour pressure of ${H_2}O$ at same temperature is $0.5{\text{atm}}$. What is the solubility of gas ‘X’ in terms of moles in $10{\text{ mole }}{H_2}O$.
A.\[1 \times {10^{ - 3}}{\text{mole}}\]
B.$5 \times {10^{ - 2}}{\text{mole}}$
C.$2 \times {10^{ - 3}}{\text{mole}}$
D.$1 \times {10^{ - 2}}{\text{mole}}$

Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint:To solve this question, you must recall Henry’s Law. Henry’s law states that the amount of gas dissolved in a liquid is proportional to its partial pressure above the liquid.
Formula used:
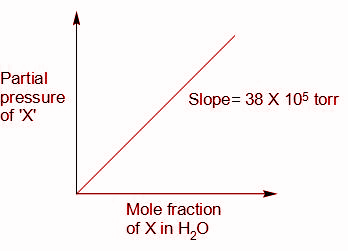
${\text{P }}\alpha {\text{ s}}$
From the graph, we can write,
${\text{P}} = {{\text{K}}_{\text{H}}}{\text{s}}$
Where, ${\text{s}}$is the solubility of gas in moles per litre
${{\text{K}}_{\text{H}}}$ is the Henry’s law constant, and ${K_H} = 38 \times {10^5}{\text{torr}} = \dfrac{{38 \times {{10}^5}}}{{760}}{\text{atm}}$
${\text{P}}$ is the partial pressure of the gas in the mixture in atm
Complete step by step answer:
The total pressure of the system is given to be $1.5{\text{atm}}$
And the vapour pressure of water is $0.5{\text{atm}}$
Thus, the partial pressure of the gas will be $1{\text{atm}}$
Using the formula, ${\text{P}} = {{\text{K}}_{\text{H}}}{\text{s}}$
We can write it as, $P = {K_H}\dfrac{{{n_X}}}{{{n_{{H_2}O}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {n_X} = \dfrac{{P.{n_{{H_2}O}}}}{{{K_H}}}$
Substituting the values:
${n_X} = 1 \times \dfrac{{760}}{{38 \times {{10}^5}}} \times 10$
$\therefore {n_X} = 2 \times {10^{ - 3}}{\text{moles}}$
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note:
Henry’s law has various applications.
It is used in production of carbonated beverages. Under high pressure, solubility of carbon dioxide gas increases. When the bottle is opened and it is exposed to atmospheric pressure, solubility of the gas decreases and the gas bubbles are released from the liquid.
At high altitude, due to low atmospheric pressure concentration of oxygen in the blood and tissues is very low and people feel weak and are unable to think properly.
It also has applications in underwater diving.
Gas can be breathed at ambient pressure which increases with increasing depth due to hydrostatic pressure. Solubility of gases increases at depth as per Henry's law, so the body tissues dissolve more oxygen over time till it is saturated for the depth. When ascending the diver is exposed to lower pressure conditions and the solubility of the oxygen dissolved in the tissues decreases as well. If the supersaturation is too great it can cause blockages in capillaries or distortion in the solid tissues.
Formula used:
${\text{P }}\alpha {\text{ s}}$
From the graph, we can write,
${\text{P}} = {{\text{K}}_{\text{H}}}{\text{s}}$
Where, ${\text{s}}$is the solubility of gas in moles per litre
${{\text{K}}_{\text{H}}}$ is the Henry’s law constant, and ${K_H} = 38 \times {10^5}{\text{torr}} = \dfrac{{38 \times {{10}^5}}}{{760}}{\text{atm}}$
${\text{P}}$ is the partial pressure of the gas in the mixture in atm
Complete step by step answer:
The total pressure of the system is given to be $1.5{\text{atm}}$
And the vapour pressure of water is $0.5{\text{atm}}$
Thus, the partial pressure of the gas will be $1{\text{atm}}$
Using the formula, ${\text{P}} = {{\text{K}}_{\text{H}}}{\text{s}}$
We can write it as, $P = {K_H}\dfrac{{{n_X}}}{{{n_{{H_2}O}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {n_X} = \dfrac{{P.{n_{{H_2}O}}}}{{{K_H}}}$
Substituting the values:
${n_X} = 1 \times \dfrac{{760}}{{38 \times {{10}^5}}} \times 10$
$\therefore {n_X} = 2 \times {10^{ - 3}}{\text{moles}}$
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note:
Henry’s law has various applications.
It is used in production of carbonated beverages. Under high pressure, solubility of carbon dioxide gas increases. When the bottle is opened and it is exposed to atmospheric pressure, solubility of the gas decreases and the gas bubbles are released from the liquid.
At high altitude, due to low atmospheric pressure concentration of oxygen in the blood and tissues is very low and people feel weak and are unable to think properly.
It also has applications in underwater diving.
Gas can be breathed at ambient pressure which increases with increasing depth due to hydrostatic pressure. Solubility of gases increases at depth as per Henry's law, so the body tissues dissolve more oxygen over time till it is saturated for the depth. When ascending the diver is exposed to lower pressure conditions and the solubility of the oxygen dissolved in the tissues decreases as well. If the supersaturation is too great it can cause blockages in capillaries or distortion in the solid tissues.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE

Calculate the equivalent resistance between a and b class 12 physics CBSE

How many states of matter are there in total class 12 chemistry CBSE

Which of the following is the best conductor of electricity class 12 physics CBSE




