
A galvanometer having a resistance of $ 50\Omega $ gives a full scale deflection for a current of $ 0.05A $ . The length in meter of resistance wire of area of cross section $ 2.97 \times {10^{ - 3}}c{m^2} $ that can be used to convert the galvanometer in to an ammeter which can read a maximum of $ 5A $ current is:
[Specific resistance of the wire, $ \rho = 5 \times {10^{ - 7}}\Omega m $ ]
(A) $ 9m $
(B) $ 6m $
(C) $ 3m $
(D) $ 1.5m $
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint :We must know the concept that the galvanometer acts like an ammeter only when we apply shunt in parallel to the galvanometer. For this we have to connect a resistor in parallel to the galvanometer and that resistor works like a shunt in the circuit. Use a formula for calculating shunt as the resistance of the galvanometer is already given.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us first draw a suitable diagram according to the given conditions.
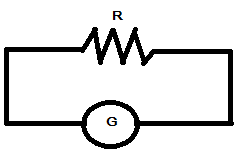
In the above diagram $ R $ is referred as the shunt in the circuit $ G $ is galvanometer resistance in galvanometer is $ G = 50\Omega $ , let $ {i_g} $ be the current in galvanometer which shows full scale deflection i.e. $ {i_g} = 0.05A $ , current in the wire is $ i = 5A $ and specific resistance of the wire, $ \rho = 5 \times {10^{ - 7}}\Omega m $ .
Now let us put all these values in the formula as given below
$ \dfrac{i}{{{i_g}}} = 1 + \dfrac{G}{R} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{5}{{0.05}} = 1 + \dfrac{{50}}{R} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{50}}{R} = \dfrac{{500}}{5} - 1 = \dfrac{{495}}{5} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{50}}{R} = \dfrac{{495}}{5} $
$ \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{50}}{{99}}\Omega $
But we are instructed to find out the length of the wire of resistance $ R $
Therefore, $ R = \rho \dfrac{l}{A} $
In the above formula for resistance , we have value of $ R $ , $ \rho $ and $ A $
Therefore,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{50}}{{99}} = 5 \times {10^{ - 7}} \times \dfrac{l}{{2.97 \times {{10}^{ - 3}} \times {{10}^{ - 4}}}} $ …(area is given in centimeters thus we have to convert it to meters.)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{50}}{{99}} = 5 \times \dfrac{l}{{2.97}} $
$ \Rightarrow l = \dfrac{{2.97 \times 10}}{{99}} = 0.3 \times 10 = 3 $
$ \therefore l = 3m $
Thus, we have calculated the length of wire as $ 3m $ .
The correct option is C.
Note :
We have to make the use of the shunting concept to make the galvanometer work like an ammeter. So, we have been able to calculate the length of the wire whose resistance was unknown, we calculated unknown resistance with the help of galvanic resistance and shunt applied to it. Here we converted the area given in centimeters to meters for our convenience. We can do so as per the requirement and according to the options.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us first draw a suitable diagram according to the given conditions.

In the above diagram $ R $ is referred as the shunt in the circuit $ G $ is galvanometer resistance in galvanometer is $ G = 50\Omega $ , let $ {i_g} $ be the current in galvanometer which shows full scale deflection i.e. $ {i_g} = 0.05A $ , current in the wire is $ i = 5A $ and specific resistance of the wire, $ \rho = 5 \times {10^{ - 7}}\Omega m $ .
Now let us put all these values in the formula as given below
$ \dfrac{i}{{{i_g}}} = 1 + \dfrac{G}{R} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{5}{{0.05}} = 1 + \dfrac{{50}}{R} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{50}}{R} = \dfrac{{500}}{5} - 1 = \dfrac{{495}}{5} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{50}}{R} = \dfrac{{495}}{5} $
$ \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{50}}{{99}}\Omega $
But we are instructed to find out the length of the wire of resistance $ R $
Therefore, $ R = \rho \dfrac{l}{A} $
In the above formula for resistance , we have value of $ R $ , $ \rho $ and $ A $
Therefore,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{50}}{{99}} = 5 \times {10^{ - 7}} \times \dfrac{l}{{2.97 \times {{10}^{ - 3}} \times {{10}^{ - 4}}}} $ …(area is given in centimeters thus we have to convert it to meters.)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{50}}{{99}} = 5 \times \dfrac{l}{{2.97}} $
$ \Rightarrow l = \dfrac{{2.97 \times 10}}{{99}} = 0.3 \times 10 = 3 $
$ \therefore l = 3m $
Thus, we have calculated the length of wire as $ 3m $ .
The correct option is C.
Note :
We have to make the use of the shunting concept to make the galvanometer work like an ammeter. So, we have been able to calculate the length of the wire whose resistance was unknown, we calculated unknown resistance with the help of galvanic resistance and shunt applied to it. Here we converted the area given in centimeters to meters for our convenience. We can do so as per the requirement and according to the options.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




