
A galvanometer has a coil of resistance 100 ohm and gives a full scale deflection for 30 mA current. If it is to work as a voltmeter of 30 volt range, the resistance required to be added will be
\[
A.{\text{ }}1000\Omega \\
B.{\text{ }}900\Omega \\
C.{\text{ }}1800\Omega \\
D.{\text{ }}500\Omega \\
\]
Answer
609k+ views
- Hint: In order to deal with this question we will use the concept to convert the galvanometer into a voltmeter of a given range by connecting a resistance R in series of appropriate resistance according to the problem. Further we will use the formula to find the value of R which is mentioned in solution to get the required answer.
Formula used- $V = {I_g}\left( {G + R} \right)$
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given that
Resistance of galvanometer, $G = 100Q$
Current for full scale deflection:
${I_g} = 30mA = 30 \times {10^{ - 3}}A$
Range of voltmeter, $V = 30V$
To convert the galvanometer into a voltmeter of a given range, a resistance R is connected in series with it as shown in the figure.
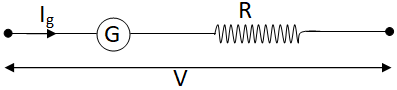
From the above figure the voltage V across the points is:
$V = {I_g}\left( {G + R} \right)$
The above equation can be written as:
\[
\because V = {I_g}\left( {G + R} \right) \\
\Rightarrow G + R = \dfrac{V}{{{I_g}}} \\
\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{V}{{{I_g}}} - G \\
\]
Substitute the given values in above formula we have
\[
\because R = \dfrac{V}{{{I_g}}} - G \\
\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{30}}{{30 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}} - 100\Omega \\
\Rightarrow R = 1000\Omega - 100\Omega \\
\Rightarrow R = 900\Omega \\
\]
Hence, the resistance required to be added will be \[900\Omega \]
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note- A galvanometer is an electromechanical device which is used to measure and signify electrical current. A galvanometer acts as an actuator in response to electrical current flowing through a coil in a continuous magnetic field, by generating a rotary deflection (of a "pointer"). Galvanometer is an instrument which is used by deflection of a moving coil to measure a specific electrical current or a current operation. The deflection is a mechanical rotation which is derived from the current forces.
Formula used- $V = {I_g}\left( {G + R} \right)$
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given that
Resistance of galvanometer, $G = 100Q$
Current for full scale deflection:
${I_g} = 30mA = 30 \times {10^{ - 3}}A$
Range of voltmeter, $V = 30V$
To convert the galvanometer into a voltmeter of a given range, a resistance R is connected in series with it as shown in the figure.

From the above figure the voltage V across the points is:
$V = {I_g}\left( {G + R} \right)$
The above equation can be written as:
\[
\because V = {I_g}\left( {G + R} \right) \\
\Rightarrow G + R = \dfrac{V}{{{I_g}}} \\
\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{V}{{{I_g}}} - G \\
\]
Substitute the given values in above formula we have
\[
\because R = \dfrac{V}{{{I_g}}} - G \\
\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{30}}{{30 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}} - 100\Omega \\
\Rightarrow R = 1000\Omega - 100\Omega \\
\Rightarrow R = 900\Omega \\
\]
Hence, the resistance required to be added will be \[900\Omega \]
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note- A galvanometer is an electromechanical device which is used to measure and signify electrical current. A galvanometer acts as an actuator in response to electrical current flowing through a coil in a continuous magnetic field, by generating a rotary deflection (of a "pointer"). Galvanometer is an instrument which is used by deflection of a moving coil to measure a specific electrical current or a current operation. The deflection is a mechanical rotation which is derived from the current forces.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




