
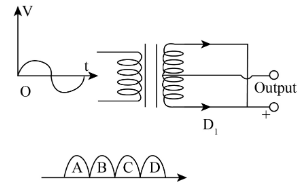
A full-wave rectifier circuit along with the out-put is shown in figure. The contribution from the diode D1 is
(A) A,C
(B) C
(C) B,D
(D) A,B,C,D

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: We can use the given full-wave rectifier circuit to determine the contribution of D1. From the circuit, take the help from the voltage and time graph; analyze one complete cycle of the voltage and effects occur due to variation in voltage on the working of diode D1.
Complete answer:
-A full-wave rectifier is a circuit, which converts an arc voltage into pulsating dc voltage using both half cycles of the applied ac voltage. It uses two diodes of which one conducts during one half while the other conducts during the other half cycle of the applied ac voltage. In a full-wave rectifier, ripple factor is less, and there is no direct current through the transformer windings so that saturation cannot take place. The advantage of the full-wave rectifier is that its efficiency is high, and the transformer utilization factor is better, which makes it durable.
-In the given circuit, initially during the first half cycle, the applied voltage is positive, which means, only diode D1 is in the forward bias and performs work during the first half cycle. So, A gives information about diode D1. In the next half-cycle, the voltage becomes negative, so the diode is in reverse bias. Due to this, the diode D1 is not in an active condition. Another diode is in working condition, so B gives information about another diode. Again when the voltage becomes positive, the diode D1 starts working and C gives information about diode D1. In the last half cycle, the voltage is negative, so the diode D1 will be off.
Therefore, the contribution from the diode D1 is A, C and option (A) is correct.
Note: Remember that whenever the voltage becomes positive or negative, the diode also changes its biasing condition and according to this working of the diode occurs. Some extra information about full-wave rectifiers is that it is the most commonly in dc power supplies. It allows unidirectional current to the load during the entire input cycle differ from the half-wave rectifier that allows current only during one-half of the cycles.
Complete answer:
-A full-wave rectifier is a circuit, which converts an arc voltage into pulsating dc voltage using both half cycles of the applied ac voltage. It uses two diodes of which one conducts during one half while the other conducts during the other half cycle of the applied ac voltage. In a full-wave rectifier, ripple factor is less, and there is no direct current through the transformer windings so that saturation cannot take place. The advantage of the full-wave rectifier is that its efficiency is high, and the transformer utilization factor is better, which makes it durable.
-In the given circuit, initially during the first half cycle, the applied voltage is positive, which means, only diode D1 is in the forward bias and performs work during the first half cycle. So, A gives information about diode D1. In the next half-cycle, the voltage becomes negative, so the diode is in reverse bias. Due to this, the diode D1 is not in an active condition. Another diode is in working condition, so B gives information about another diode. Again when the voltage becomes positive, the diode D1 starts working and C gives information about diode D1. In the last half cycle, the voltage is negative, so the diode D1 will be off.
Therefore, the contribution from the diode D1 is A, C and option (A) is correct.
Note: Remember that whenever the voltage becomes positive or negative, the diode also changes its biasing condition and according to this working of the diode occurs. Some extra information about full-wave rectifiers is that it is the most commonly in dc power supplies. It allows unidirectional current to the load during the entire input cycle differ from the half-wave rectifier that allows current only during one-half of the cycles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




