
A foreign DNA and plasmid cut by the same restriction endonuclease can be joined to form a recombinant plasmid using
(a) Polymerase III
(b) Ligase
(c) Eco R1
(d) Taq polymerase
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: This catalyses the formation of phosphodiester bonds between the 5’- phosphate of one strand of DNA or RNA and the 3’- hydroxyl of another. This enzyme is used in covalently linking or ligate fragments of DNA together.
Complete step by step answer:
Ligase from the Latin verb ligase — "to bind" or "to glue together" is an enzyme that can catalyze the joining of two large molecules by forming a new chemical bond, usually with association of hydrolysis of a small chemical group dependent to one of the larger molecules or the enzyme catalyzing the linking together of two compounds, e.g., enzymes that catalyze joining of C- O, C- S, C- N, etc. The DNA ligases used in molecular cloning differ in their abilities to ligate noncanonical substrates, such as blunt ended duplex DNA: RNA hybrid or ssDNAs.
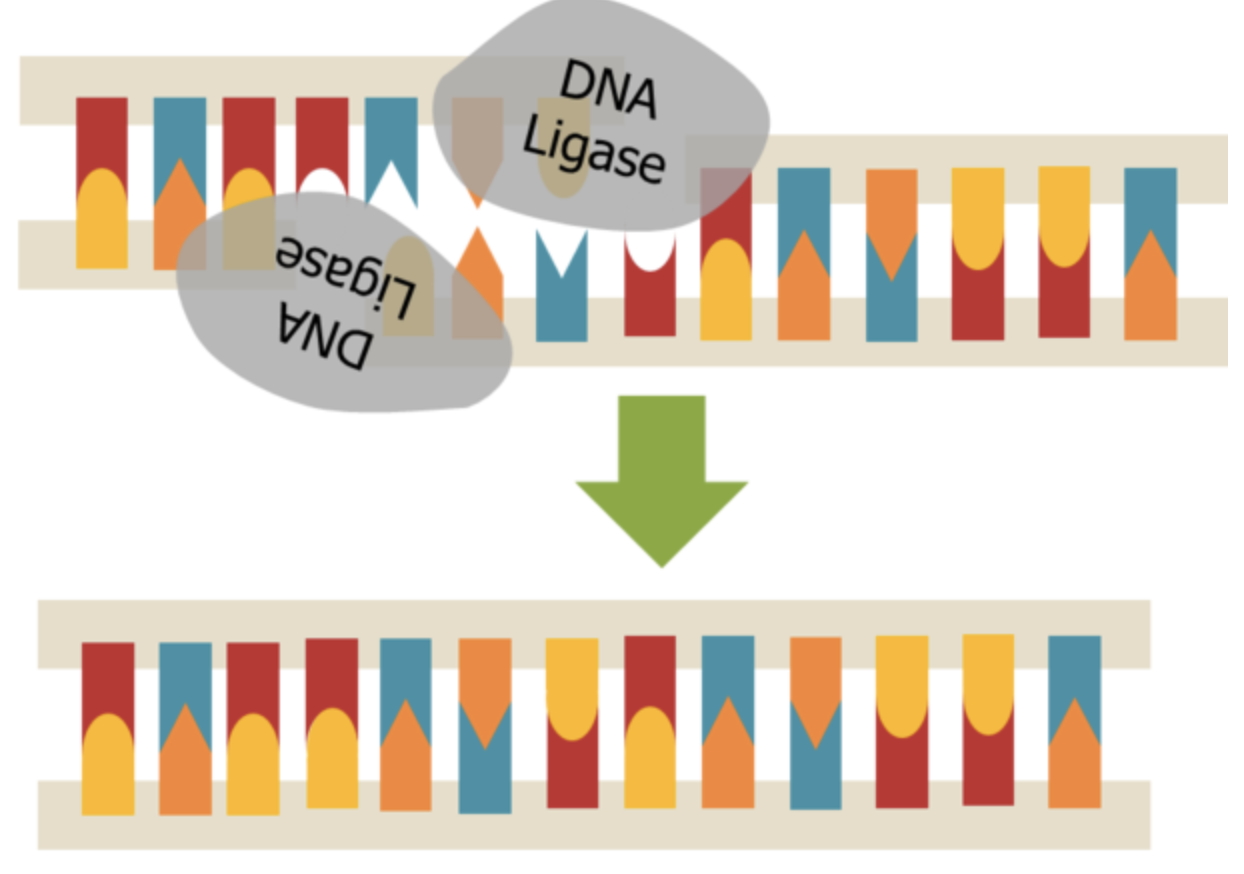
So, the correct answer is ‘Ligase.’
Additional Information:
Mechanism of DNA Ligase:
- The mechanism of DNA ligase is the formation of two covalent phosphodiester bonds between acceptor and donor or between 3' hydroxyl ends of single nucleotide, with the 5' phosphate end of another respectively.
- ATP is required for the ligase reaction, which completes in three steps:
- Adenylation (addition of AMP) of a residue within the active center of the enzyme, pyrophosphate is released.
- Transfer of the AMP to the 5' phosphate so- called donor, formation of a pyrophosphate bond.
- Formation of a phosphodiester bond between the 5' phosphate of the donor and therefore the 3' hydroxyl of the acceptor.
Application:
- Ligation of cohesive ends.
- Ligation of blunt ended termini: This reaction is far slower than ligation of sticky ends and therefore the ligation is improved by addition of monovalent cation and low concentration of PEG .
- Ligation of synthetic linkers or adapters.
Note:
- For all ligases, one Weiss unit is that amount of Enzyme required in conversion of 1 n mol of radiolabeled phosphate from pyrophosphate into absorbable material within 20 min at 370 c under standard assay condition. One Weiss unit equals about 67 cohesive end ligation units.
- Bacteriophage T4 DNA Ligase (ATP) the foremost widely used DNA ligase is from the T4 bacteriophage. It’s a monomeric polypeptide. It’s broader specificity and repairs single stranded nicks in duplex DNA, RNA or DNA: RNA hybrids.
Complete step by step answer:
Ligase from the Latin verb ligase — "to bind" or "to glue together" is an enzyme that can catalyze the joining of two large molecules by forming a new chemical bond, usually with association of hydrolysis of a small chemical group dependent to one of the larger molecules or the enzyme catalyzing the linking together of two compounds, e.g., enzymes that catalyze joining of C- O, C- S, C- N, etc. The DNA ligases used in molecular cloning differ in their abilities to ligate noncanonical substrates, such as blunt ended duplex DNA: RNA hybrid or ssDNAs.

So, the correct answer is ‘Ligase.’
Additional Information:
Mechanism of DNA Ligase:
- The mechanism of DNA ligase is the formation of two covalent phosphodiester bonds between acceptor and donor or between 3' hydroxyl ends of single nucleotide, with the 5' phosphate end of another respectively.
- ATP is required for the ligase reaction, which completes in three steps:
- Adenylation (addition of AMP) of a residue within the active center of the enzyme, pyrophosphate is released.
- Transfer of the AMP to the 5' phosphate so- called donor, formation of a pyrophosphate bond.
- Formation of a phosphodiester bond between the 5' phosphate of the donor and therefore the 3' hydroxyl of the acceptor.
Application:
- Ligation of cohesive ends.
- Ligation of blunt ended termini: This reaction is far slower than ligation of sticky ends and therefore the ligation is improved by addition of monovalent cation and low concentration of PEG .
- Ligation of synthetic linkers or adapters.
Note:
- For all ligases, one Weiss unit is that amount of Enzyme required in conversion of 1 n mol of radiolabeled phosphate from pyrophosphate into absorbable material within 20 min at 370 c under standard assay condition. One Weiss unit equals about 67 cohesive end ligation units.
- Bacteriophage T4 DNA Ligase (ATP) the foremost widely used DNA ligase is from the T4 bacteriophage. It’s a monomeric polypeptide. It’s broader specificity and repairs single stranded nicks in duplex DNA, RNA or DNA: RNA hybrids.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




