
A fish is looking at a 1.0 m high plant at the edge of a pond. Will the planet appear to the fish short?
Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint:When the light ray passes through a rare medium to a denser medium, the path of the light bends towards the normal. Draw the ray diagram of the image formation from the fish’s perspective. Extend the refracted ray backwards to find out the size of the planet.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that when the light ray passes through a rare medium to a denser medium, the path of the light bends towards the normal. In this case, the light rays reflected from the top of the plant undergo refraction at the boundary between air and water. Since the water is the denser medium compared to the air medium, the path of the incident ray bends towards the normal and meets at the eye of the fish as shown in the figure below. Let’s extend the ray EM backwards where it meets at point P. The light ray will appear to be reflected from the point P from the fish’s perspective. Therefore, the image of the plant will be PB instead of AB and thus the planet will appear taller.
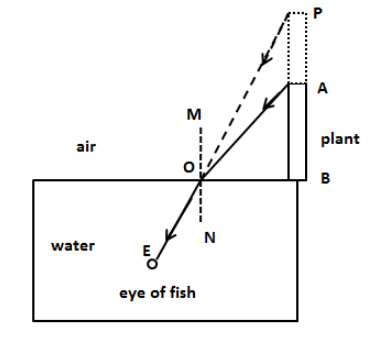
Let the height of the plant is AB which is 1 m. The relation between refractive index, apparent height and real height of the object is,
\[{\mu _w} = \dfrac{{{h_{app}}}}{{{h_{real}}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {h_{app}} = {\mu _w}{h_{real}}\]
Substituting 1.3 for \[{\mu _w}\] and 1 m for \[{h_{real}}\] in the above equation, we get,
\[{h_{app}} = \left( {1.3} \right)\left( 1 \right)\]
\[ \therefore {h_{app}} = 1.3\,{\text{m}}\]
Thus, the plant will appear 1.3 m for the fish.
Note:While drawing the ray diagrams, always check the direction of the incident ray and refracted ray. The incident ray is always reflected from the object towards our eye and not from our eye to the object. While answering these questions, the essential step is to remember the refractive index of the commonly given mediums such as air, liquid or vacuum.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that when the light ray passes through a rare medium to a denser medium, the path of the light bends towards the normal. In this case, the light rays reflected from the top of the plant undergo refraction at the boundary between air and water. Since the water is the denser medium compared to the air medium, the path of the incident ray bends towards the normal and meets at the eye of the fish as shown in the figure below. Let’s extend the ray EM backwards where it meets at point P. The light ray will appear to be reflected from the point P from the fish’s perspective. Therefore, the image of the plant will be PB instead of AB and thus the planet will appear taller.

Let the height of the plant is AB which is 1 m. The relation between refractive index, apparent height and real height of the object is,
\[{\mu _w} = \dfrac{{{h_{app}}}}{{{h_{real}}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {h_{app}} = {\mu _w}{h_{real}}\]
Substituting 1.3 for \[{\mu _w}\] and 1 m for \[{h_{real}}\] in the above equation, we get,
\[{h_{app}} = \left( {1.3} \right)\left( 1 \right)\]
\[ \therefore {h_{app}} = 1.3\,{\text{m}}\]
Thus, the plant will appear 1.3 m for the fish.
Note:While drawing the ray diagrams, always check the direction of the incident ray and refracted ray. The incident ray is always reflected from the object towards our eye and not from our eye to the object. While answering these questions, the essential step is to remember the refractive index of the commonly given mediums such as air, liquid or vacuum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




