
A driver looking up through the water sees the outside world contained in a circular horizon. The refractive index of water is $ \dfrac{4}{3} $, and the diver’s eyes are $ 15cm $ below the surface of water. Then the radius of the circle is
(A) $ 15 \times 3 \times \sqrt 5 cm $
(B) $ 15 \times 3\sqrt 7 cm $
(C) $ \dfrac{{15 \times \sqrt 7 }}{3}cm $
(D) $ \dfrac{{15 \times 3}}{{\sqrt 7 }}cm $
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint
To solve this question, we need to use the concept of total internal reflection. We have to use the geometry of the physical situation given, and then by applying trigonometry to that we can get the final answer.
Formula Used: The formula used to solve this question is given by
$\Rightarrow \sin {\theta _c} = \dfrac{1}{\mu } $
Here $ {\theta _c} $ is the critical angle of incidence, and $ \mu $ is the refractive index of the medium.
Complete step by step answer
The situation is shown in the figure below.
Let the eyes of the diver be fixed at point A.
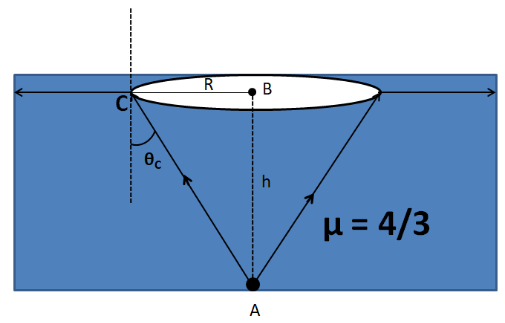
For the outside world to be contained in the circular horizon shown in the figure, the rays of light originating from A should suffer total internal reflection at the whole perimeter of the circle. So these rays must be incident at the critical angle of incidence with the normal. Consider the triangle ABC as shown in the figure.
We have $ \angle BAC = {\theta _C} $ (Alternate Interior Angles)
Taking tan both the sides, we get
$\Rightarrow \tan \left( {\angle BAC} \right) = \tan {\theta _C} $
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{BC}}{{AB}} = \tan {\theta _C} $
From the figure
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{R}{h} = \tan {\theta _C} $
$\Rightarrow R = h\tan {\theta _C} $ (1)
We know that
$\Rightarrow \sin {\theta _C} = \dfrac{1}{\mu } $
This implies
$\Rightarrow \tan {\theta _C} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{\mu ^2} - 1} }} $
Substituting in (1), we get
$\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{h}{{\sqrt {{\mu ^2} - 1} }} $
According to the question, we have $ h = 15cm $, and $ \mu = \dfrac{4}{3} $. Putting these values we get
$\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{15}}{{\sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)}^2} - 1} }} $
$\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{15 \times 3}}{{\sqrt {16 - 9} }} $
Finally we get
$\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{15 \times 3}}{{\sqrt 7 }}cm $
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note
Before using the effect of total internal reflection, always check its condition. The condition for total internal reflection to take place is that the light ray should be travelling from an optically denser medium to an optically rarer medium. In this question, the light rays from the diver’s eyes were travelling from water, an optically denser medium to air, an optically rarer medium. So we could use this phenomenon.
To solve this question, we need to use the concept of total internal reflection. We have to use the geometry of the physical situation given, and then by applying trigonometry to that we can get the final answer.
Formula Used: The formula used to solve this question is given by
$\Rightarrow \sin {\theta _c} = \dfrac{1}{\mu } $
Here $ {\theta _c} $ is the critical angle of incidence, and $ \mu $ is the refractive index of the medium.
Complete step by step answer
The situation is shown in the figure below.
Let the eyes of the diver be fixed at point A.

For the outside world to be contained in the circular horizon shown in the figure, the rays of light originating from A should suffer total internal reflection at the whole perimeter of the circle. So these rays must be incident at the critical angle of incidence with the normal. Consider the triangle ABC as shown in the figure.
We have $ \angle BAC = {\theta _C} $ (Alternate Interior Angles)
Taking tan both the sides, we get
$\Rightarrow \tan \left( {\angle BAC} \right) = \tan {\theta _C} $
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{BC}}{{AB}} = \tan {\theta _C} $
From the figure
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{R}{h} = \tan {\theta _C} $
$\Rightarrow R = h\tan {\theta _C} $ (1)
We know that
$\Rightarrow \sin {\theta _C} = \dfrac{1}{\mu } $
This implies
$\Rightarrow \tan {\theta _C} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{\mu ^2} - 1} }} $
Substituting in (1), we get
$\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{h}{{\sqrt {{\mu ^2} - 1} }} $
According to the question, we have $ h = 15cm $, and $ \mu = \dfrac{4}{3} $. Putting these values we get
$\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{15}}{{\sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)}^2} - 1} }} $
$\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{15 \times 3}}{{\sqrt {16 - 9} }} $
Finally we get
$\Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{15 \times 3}}{{\sqrt 7 }}cm $
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note
Before using the effect of total internal reflection, always check its condition. The condition for total internal reflection to take place is that the light ray should be travelling from an optically denser medium to an optically rarer medium. In this question, the light rays from the diver’s eyes were travelling from water, an optically denser medium to air, an optically rarer medium. So we could use this phenomenon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




