
A double star system consists of two stars A and B which have time periods ${T_A}$ and ${T_B}$. Radius $R_A$ and $R_B$ and mass $M_A$ and $M_B$. Choose the correct option.
(A) ${\left( {\dfrac{{{T_A}}}{{{T_B}}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{R_A}}}{{{R_B}}}} \right)^2}$
(B) if ${T_A}\,\rangle \,{T_B}$ then ${R_A}\,\rangle \,{R_B}$
(C) ${T_A} = {T_B}$
(D) if ${T_A}\,\rangle \,{T_B}$ then ${M_A}\,\rangle \,{M_B}$
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint:The above problem can be solved using the formula of angular moment of the double star or a binary star system along with the binary star or the double star system theory. A star system is a small number of stars that orbit each other that are bound together by gravitational attraction between them.
Formulae Used:
Angular momentum of a double star system or binary star system is given by;
$\omega = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{T}$
Where, $\omega $ denotes the angular momentum of the double star system, $T$ is the time periods of the stars
Complete step-by-step solution:
The data given by the problem are:
Time period of star $A$ is, ${T_A}$.
Time period of star $B$ is, ${T_B}$.
Radius of star $A$ is, ${R_A}$.
Radius of star $B$ is, ${R_B}$
Mass of star $A$ is, ${M_A}$.
Mass of star $B$ is, ${M_B}$.
The formula for double star system is ${M_A}{R_A} = {M_B}{R_B}$
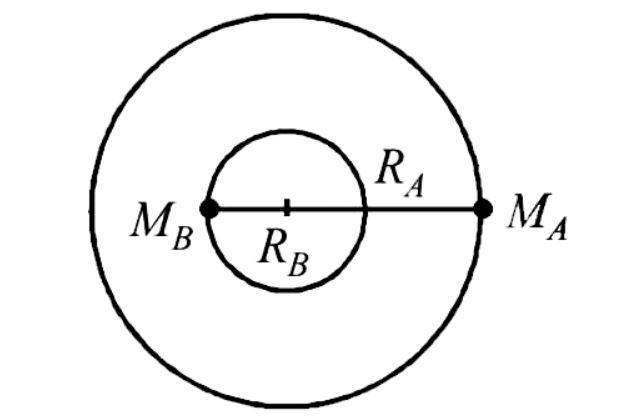
But the Angular momentum of a double star system or binary star system is given by;
${\omega _A} = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{{T_A}}}$
${\omega _B} = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{{T_B}}}$
since the gravitational force of attraction between the two stars provides the required centripetal forces, that is in this case the angular velocity or momentum of both stars is the same. Therefore, the time period of the stars remains the same.
Therefore, ${\omega _A} = {\omega _B}$; twin
$
\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{{T_A}}} = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{{T_B}}} \\
{T_A} = {T_B} \\
$
Therefore, the time period of the stars remains the same, that is ${T_A} = {T_B}$.
Hence, the option (C) ${T_A} = {T_B}$ is the correct answer.
Note:- In inspectional astronomy, a double star or visual double is a pair of stars that appear to be close to each other as they are viewed from Earth, especially with the help of an optical telescope. Optical doubles are unattached stars that seem to be close together through chance orientation with Earth.
Formulae Used:
Angular momentum of a double star system or binary star system is given by;
$\omega = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{T}$
Where, $\omega $ denotes the angular momentum of the double star system, $T$ is the time periods of the stars
Complete step-by-step solution:
The data given by the problem are:
Time period of star $A$ is, ${T_A}$.
Time period of star $B$ is, ${T_B}$.
Radius of star $A$ is, ${R_A}$.
Radius of star $B$ is, ${R_B}$
Mass of star $A$ is, ${M_A}$.
Mass of star $B$ is, ${M_B}$.
The formula for double star system is ${M_A}{R_A} = {M_B}{R_B}$

But the Angular momentum of a double star system or binary star system is given by;
${\omega _A} = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{{T_A}}}$
${\omega _B} = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{{T_B}}}$
since the gravitational force of attraction between the two stars provides the required centripetal forces, that is in this case the angular velocity or momentum of both stars is the same. Therefore, the time period of the stars remains the same.
Therefore, ${\omega _A} = {\omega _B}$; twin
$
\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{{T_A}}} = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{{T_B}}} \\
{T_A} = {T_B} \\
$
Therefore, the time period of the stars remains the same, that is ${T_A} = {T_B}$.
Hence, the option (C) ${T_A} = {T_B}$ is the correct answer.
Note:- In inspectional astronomy, a double star or visual double is a pair of stars that appear to be close to each other as they are viewed from Earth, especially with the help of an optical telescope. Optical doubles are unattached stars that seem to be close together through chance orientation with Earth.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




