
A double convex lens has focal length 25 cm. The radius of curvature of one of the surfaces is double of the other. Find the radii, if the refractive index of the material of the lens is 1.5.
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint :A double convex lens is a converging lens which is thicker at the middle and thinner on the sides. Unlike mirrors, the light in the lens can pass through both sides of the lens. Hence, it has two focal lengths. In the following question we use lens maker’s formula to calculate the focal length. And after substituting the values we get the value of radii.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The figure of a double convex lens is as follows:
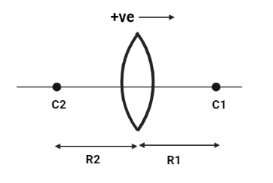
It’s given in the question that:
$f = 25cm$
$\mu = 1.5$
Let us consider ${R_1} = R$
Then,${R_2} = - 2R$
Since, ${R_2}$is on the negative side. Hence according to sign convention we will add a minus sign to the ${R_2}$
The formula to calculate the focal length of a double convex lens is:
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{R1}} - \dfrac{1}{{R2}}} \right)$
Substituting the values we get,
$ \dfrac{1}{{25}} = \left( {1.5 - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{{ - 2R}}} \right) \\
\dfrac{1}{{25}} = 0.5\left( {\dfrac{{2 + 1}}{{2R}}} \right) \\
\dfrac{1}{{25}} = 0.5\left( {\dfrac{3}{{2R}}} \right) \\
R = \dfrac{5}{{10}} \times \dfrac{{25}}{2} \times 3 \\
R = \dfrac{{25}}{4} \times 3 \\
R = 18.75cm \\ $
Hence,
${R_1} = 18.75$
${R_2} = 37.5$
Note :
The lens creates a real , inverted and enlarged image beyond 2F if the object is between 2F and F. It creates an imaginary, inverted and enlarged image on the same side as that of the object when the object is placed inside F. It also creates an inverted, diminished and real image between F and 2F on the opposite side of the object when the object is placed outside 2F.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The figure of a double convex lens is as follows:

It’s given in the question that:
$f = 25cm$
$\mu = 1.5$
Let us consider ${R_1} = R$
Then,${R_2} = - 2R$
Since, ${R_2}$is on the negative side. Hence according to sign convention we will add a minus sign to the ${R_2}$
The formula to calculate the focal length of a double convex lens is:
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{R1}} - \dfrac{1}{{R2}}} \right)$
Substituting the values we get,
$ \dfrac{1}{{25}} = \left( {1.5 - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{{ - 2R}}} \right) \\
\dfrac{1}{{25}} = 0.5\left( {\dfrac{{2 + 1}}{{2R}}} \right) \\
\dfrac{1}{{25}} = 0.5\left( {\dfrac{3}{{2R}}} \right) \\
R = \dfrac{5}{{10}} \times \dfrac{{25}}{2} \times 3 \\
R = \dfrac{{25}}{4} \times 3 \\
R = 18.75cm \\ $
Hence,
${R_1} = 18.75$
${R_2} = 37.5$
Note :
The lens creates a real , inverted and enlarged image beyond 2F if the object is between 2F and F. It creates an imaginary, inverted and enlarged image on the same side as that of the object when the object is placed inside F. It also creates an inverted, diminished and real image between F and 2F on the opposite side of the object when the object is placed outside 2F.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




