
A domestic refrigerator working between melting point of ice and room temperature $27{}^\circ C$ is found to freeze 2kg of water at $0{}^\circ C$ in 1 hour. Calculate the power consumed under ideal conditions given latent heat of fusion of ice $335\times {{10}^{3}}J$
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: As a first step, you could recall the expression for coefficient of performance and then rearrange the same to get the energy supplied or the work done on the refrigerator. Substitute the expression for heat supplied in terms of latent heat of fusion of ice. This work done per unit time will give us the required power consumed.
Formula used:
Coefficient of performance of refrigerator,
$COP=\dfrac{{{Q}_{2}}}{W}=\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}}}$
Heat supplied,
$Q=m{{L}_{f}}$
Complete answer:
In the question, we are given a domestic refrigerator that works between the melting point of ice and room temperature. It is also found that this refrigerator freezes 2kg of water at $0{}^\circ C$ in a duration of 1 hour. We are asked to find the power consumed under ideal conditions. We are also given the value of latent heat of fusion of ice as,
${{L}_{f}}=335\times {{10}^{3}}J$ ………………………………………….. (1)
We are given the room temperature as,
${{T}_{1}}=27{}^\circ C=\left( 27+273 \right)K=300K$
We know that the melting point of ice is$0{}^\circ C$, therefore,
${{T}_{2}}=0{}^\circ C=\left( 0+273 \right)K=273K$
We know that the coefficient of performance (COP) of a refrigerator is given by,
$COP=\dfrac{{{Q}_{2}}}{W}=\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}}}$
Where, ${{Q}_{2}}$ is the heat supplied and W is the input work on the refrigerator.
Therefore, we see that the amount of energy supplied to the refrigerator is given by,
$W=\dfrac{{{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{2}}}\times {{Q}_{2}}$ …………………………………… (2)
But we know that heat supplied for freezing $mkg$ of a substance is given by,
$Q=m{{L}_{f}}$
Where, ${{L}_{f}}$ is the latent heat of fusion.
Here, the heat supplied would be,
${{Q}_{2}}=2\times 335\times {{10}^{3}}J=670\times {{10}^{3}}J$ …………………………………………… (3)
Substituting (3) in (2) we get,
$W=\dfrac{300-273}{273}\times 670\times {{10}^{3}}$
$\therefore W=66.26\times {{10}^{3}}J$
Therefore we found that in one hour the refrigerator is supplied with $66.26KJ$ energy to freeze 2kg of water. You may recall that power is the work done per unit time. So,
$P=\dfrac{W}{t}$
Substituting the values,
$P=\dfrac{66.26\times {{10}^{3}}J}{1hr}$
$\Rightarrow P=66.26KJh{{r}^{-1}}$
But we know that,
$1J/hr=2.78\times {{10}^{-7}}kW$
$\Rightarrow P=66.26\times {{10}^{3}}\times 2.78\times {{10}^{-7}}kW$
$\therefore P=184.20\times {{10}^{-4}}kW=18.42W$
Therefore, we found that the power consumed by the refrigerator under ideal conditions is 18.42W.
Note:
The refrigeration cycle would look something like this,
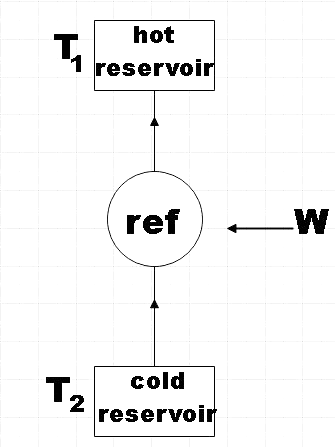
From the figure you will get a clear idea as to how a refrigerator works. The refrigerant which is one among the basic components is found to absorb the heat inside the fridge and thereby cooling down the air.
Formula used:
Coefficient of performance of refrigerator,
$COP=\dfrac{{{Q}_{2}}}{W}=\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}}}$
Heat supplied,
$Q=m{{L}_{f}}$
Complete answer:
In the question, we are given a domestic refrigerator that works between the melting point of ice and room temperature. It is also found that this refrigerator freezes 2kg of water at $0{}^\circ C$ in a duration of 1 hour. We are asked to find the power consumed under ideal conditions. We are also given the value of latent heat of fusion of ice as,
${{L}_{f}}=335\times {{10}^{3}}J$ ………………………………………….. (1)
We are given the room temperature as,
${{T}_{1}}=27{}^\circ C=\left( 27+273 \right)K=300K$
We know that the melting point of ice is$0{}^\circ C$, therefore,
${{T}_{2}}=0{}^\circ C=\left( 0+273 \right)K=273K$
We know that the coefficient of performance (COP) of a refrigerator is given by,
$COP=\dfrac{{{Q}_{2}}}{W}=\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}}}$
Where, ${{Q}_{2}}$ is the heat supplied and W is the input work on the refrigerator.
Therefore, we see that the amount of energy supplied to the refrigerator is given by,
$W=\dfrac{{{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{2}}}\times {{Q}_{2}}$ …………………………………… (2)
But we know that heat supplied for freezing $mkg$ of a substance is given by,
$Q=m{{L}_{f}}$
Where, ${{L}_{f}}$ is the latent heat of fusion.
Here, the heat supplied would be,
${{Q}_{2}}=2\times 335\times {{10}^{3}}J=670\times {{10}^{3}}J$ …………………………………………… (3)
Substituting (3) in (2) we get,
$W=\dfrac{300-273}{273}\times 670\times {{10}^{3}}$
$\therefore W=66.26\times {{10}^{3}}J$
Therefore we found that in one hour the refrigerator is supplied with $66.26KJ$ energy to freeze 2kg of water. You may recall that power is the work done per unit time. So,
$P=\dfrac{W}{t}$
Substituting the values,
$P=\dfrac{66.26\times {{10}^{3}}J}{1hr}$
$\Rightarrow P=66.26KJh{{r}^{-1}}$
But we know that,
$1J/hr=2.78\times {{10}^{-7}}kW$
$\Rightarrow P=66.26\times {{10}^{3}}\times 2.78\times {{10}^{-7}}kW$
$\therefore P=184.20\times {{10}^{-4}}kW=18.42W$
Therefore, we found that the power consumed by the refrigerator under ideal conditions is 18.42W.
Note:
The refrigeration cycle would look something like this,

From the figure you will get a clear idea as to how a refrigerator works. The refrigerant which is one among the basic components is found to absorb the heat inside the fridge and thereby cooling down the air.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




