
A dihybrid tall plant bearing yellow flowers was crossed with a dwarf plant bearing white flowers. What is the percentage of progeny expected to be homozygous tall bearing yellow flowers?
A. 0%
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:-The genetic condition in which an organism is carrying the same allele that bears the same phenotypic expression is called homozygous. When an individual carries a phenotypically different allele, and possesses dominance, and receives character between them is called heterozygous.
Complete step-by-step solution:-In the given question, a dihybrid tall plant with yellow flowers is crossed with a dwarf plant with white flowers.
Let the genotypic expression of a hybrid tall plant with yellow flowers be TtYy. Here T stands for tall character and the yellow flower is represented by Y.
The genotypic expression of the dwarf plant with white flowers will be ttyy. Here t refers to the dwarf character and y is representing the white flowers.
T is dominant over t and Y is dominant over y. Thus in heterozygous conditions (Tt/ Yy) the dominant character will be expressed phenotypically.
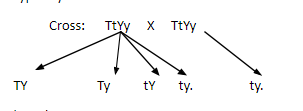
In this cross, 50% heterozygous tall plant with yellow flowers is found.
25% heterozygous tall with white flower is found
a 25% dwarf plant with white flowers is found.
The percentage of having a homozygous tall plant with yellow flowers will be 0.
Note:- To know the actual genotypic expression, always a homozygous recessive is chosen to cross with that individual. This cross is called the test cross. In the dihybrid cross, the phenotypic ratio is always 1:1:1:1. The same ratio is found in the given cross. So it can be concluded that here the test cross is done.
Complete step-by-step solution:-In the given question, a dihybrid tall plant with yellow flowers is crossed with a dwarf plant with white flowers.
Let the genotypic expression of a hybrid tall plant with yellow flowers be TtYy. Here T stands for tall character and the yellow flower is represented by Y.
The genotypic expression of the dwarf plant with white flowers will be ttyy. Here t refers to the dwarf character and y is representing the white flowers.
T is dominant over t and Y is dominant over y. Thus in heterozygous conditions (Tt/ Yy) the dominant character will be expressed phenotypically.

| TY | Ty | tY | ty | |
| ty | TtYyTall yellow | TtyyTall white | TtYyTall yellow | ttyyDwarf white |
| ty | TtYyTall yellow | TtyyTall white | TtYyTall yellow | ttyyDwarf white |
| ty | TtYyTall yellow | TtyyTall white | TtYyTall yellow | ttyyDwarf white |
| ty | TtYyTall yellow | TtyyTall white | TtYyTall yellow | ttyyDwarf white |
In this cross, 50% heterozygous tall plant with yellow flowers is found.
25% heterozygous tall with white flower is found
a 25% dwarf plant with white flowers is found.
The percentage of having a homozygous tall plant with yellow flowers will be 0.
Note:- To know the actual genotypic expression, always a homozygous recessive is chosen to cross with that individual. This cross is called the test cross. In the dihybrid cross, the phenotypic ratio is always 1:1:1:1. The same ratio is found in the given cross. So it can be concluded that here the test cross is done.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




