
A) Differentiate between thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics with an example each.
B) Write the monomer unit of Teflon and write anyone's use of Teflon?
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: For (A): Thermoplastic polymers are weaker and attached by weak van der Waal forces of attraction while thermosetting polymers are stronger and attached by strong H-bonding.
For (B): Teflon is also known as polytetrafluoroethylene and is formed by the polymerisation of a single monomer.
Complete step by step answer:
A) The polymers differ on the basis of their mechanical properties like toughness, elasticity, tensile strength, etc. These mechanical properties depend on their intermolecular forces like hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces of attraction which bind the polymer chains together. Depending on these intermolecular forces polymers are divided into 4 types:
(1) Fibres
(2) Elastomers
(3) Thermoplastic polymers
(4) Thermosetting polymers
-Now let’s differentiate between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.
B) Teflon:
-Teflon is also known as polytetrafluoroethylene and it is a vinyl polymer.
-It is formed by free radical polymerisation of tetrafluoroethylene. Tetrafluoroethylene is heated with a free radical or persulphate catalyst at high pressures to form Teflon.
The net reaction for its formation is written as:
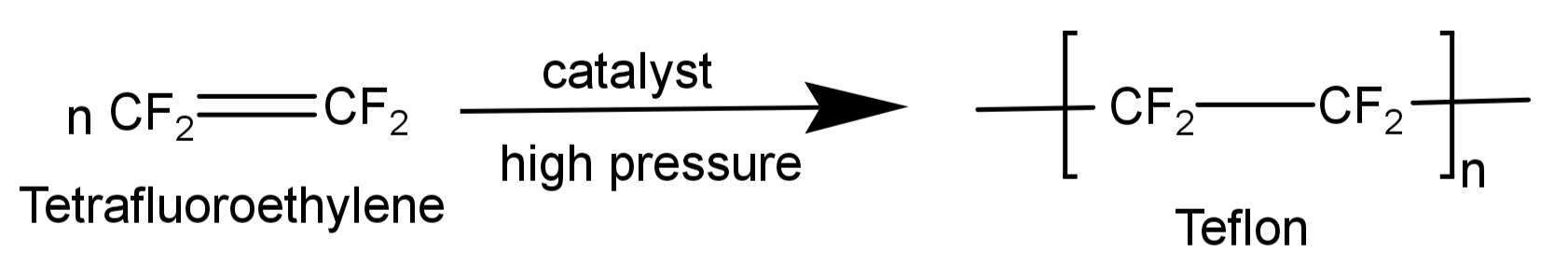
-Hence its monomer is tetrafluoroethylene. Its structure is: $C{F_2} = C{F_2}$
-This polymer is inert chemically and is also resistant to attack by corrosive reagents. It has a melting point of 600 K, high strength, toughness and self lubrication at low temperatures. Teflon has these properties due to the carbon-fluorine (C-F) bonds. It gets depolymerised at temperatures above $650 - {700^ \circ }C$ .
-Uses of Teflon are: in making oil seals, gaskets, non-stick surface coated utensils, production of carbon fibre composites, expansion joints, etc.
Note: For (A): Since the thermosetting polymers are cross linked or 3D structures they are more resistant to any sort of temperature changes, while the thermoplastic polymers are linear in shape and so do not show resistance to temperature variations. For (B): Although Teflon is inert and stable, at temperatures above ${300^ \circ }C$ the Teflon coatings present on the non-stick cookware starts breaking down and toxic chemicals are released which on inhalation may cause polymer fume fever or Teflon fever.
For (B): Teflon is also known as polytetrafluoroethylene and is formed by the polymerisation of a single monomer.
Complete step by step answer:
A) The polymers differ on the basis of their mechanical properties like toughness, elasticity, tensile strength, etc. These mechanical properties depend on their intermolecular forces like hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces of attraction which bind the polymer chains together. Depending on these intermolecular forces polymers are divided into 4 types:
(1) Fibres
(2) Elastomers
(3) Thermoplastic polymers
(4) Thermosetting polymers
-Now let’s differentiate between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.
| Thermoplastic plastics | Thermosetting plastics |
| 1) Such polymers or plastics are usually formed by addition polymerisation. | 1) These plastics are usually formed by condensation polymerisation. |
| 2) They are linear or slightly branched long chain polymers. | 2) They are cross linked or heavily branched. |
| 3) They can be easily soften on heating and hardened on cooling. | 3) It cannot be softened on heating. |
| 4) They are held together by Van der Waal forces of attraction. | 4) They are held together by strong hydrogen bonds. |
| 5) By nature they are soft, weak and less brittle. | 5) They are strong, hard and more brittle in nature. |
| 6) Their molecular weight is low. | 6) Their molecular weight is large. |
| 7) They are quite soluble in organic solvents. | 7) They are insoluble in organic solvents. |
| 8) They can be remoulded into desired shapes. | 8) They cannot be remoulded. |
| 9) Monomers used here do not have more than two reaction sites. | 9) Monomers used here have more than two reaction sites. |
| 10) Examples: polythene, polystyrene, polyvinyls, etc. | 10) Examples: bakelite, urea-formaldehyde resins, etc. |
B) Teflon:
-Teflon is also known as polytetrafluoroethylene and it is a vinyl polymer.
-It is formed by free radical polymerisation of tetrafluoroethylene. Tetrafluoroethylene is heated with a free radical or persulphate catalyst at high pressures to form Teflon.
The net reaction for its formation is written as:

-Hence its monomer is tetrafluoroethylene. Its structure is: $C{F_2} = C{F_2}$
-This polymer is inert chemically and is also resistant to attack by corrosive reagents. It has a melting point of 600 K, high strength, toughness and self lubrication at low temperatures. Teflon has these properties due to the carbon-fluorine (C-F) bonds. It gets depolymerised at temperatures above $650 - {700^ \circ }C$ .
-Uses of Teflon are: in making oil seals, gaskets, non-stick surface coated utensils, production of carbon fibre composites, expansion joints, etc.
Note: For (A): Since the thermosetting polymers are cross linked or 3D structures they are more resistant to any sort of temperature changes, while the thermoplastic polymers are linear in shape and so do not show resistance to temperature variations. For (B): Although Teflon is inert and stable, at temperatures above ${300^ \circ }C$ the Teflon coatings present on the non-stick cookware starts breaking down and toxic chemicals are released which on inhalation may cause polymer fume fever or Teflon fever.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




