
(a) Define the optical centre of a spherical lens.
(b) A diverging lens has a focal length of $20 \mathrm{~cm}$. At what distance should an object of height $4 \mathrm{~cm}$ from the optical centre of the lens be placed so that its image is formed $10 \mathrm{~cm}$ away from the lens. Find the size of the image also.
Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint: A diverging lens is a concave lens. The refraction of light rays as they pass through the lens determines how well the lens works. When light rays enter a concave lens, they diverge, causing the lens to behave like a diverging lens. By the help of the Mirror Formula calculate the object distance after calculating Object distance Take out the magnification of the object.
Formula used:
By lens Formula -
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}$
Size of the image - $h_{i}=\dfrac{v}{u} h_{0}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
a) Optical centre is the point lying on the principal axis of a lens through which light passes through without undergoing any deviation.
b) Given
Focal length, $\mathrm{f}=-20 \mathrm{~cm}$
Height of the object, $\mathrm{h}_{1}=4 \mathrm{~cm}$
Image distance, $v=-10 \mathrm{~cm}$
To find: Object distance $=?$ Size of the image, $\mathrm{h}_{2}=$ ?
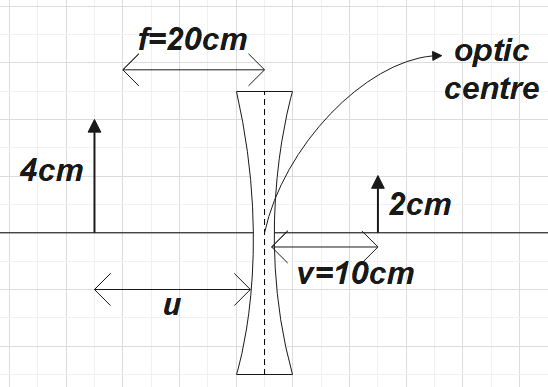
Now, using the lens formula,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}$
$=\dfrac{-1}{-10}-\dfrac{1}{-20}$
$=\dfrac{-1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{20}$
$=\dfrac{-2+1}{20}$
$u=-20 \mathrm{~cm}$
Therefore, the object is at a distance of $20 \mathrm{~cm}$ on the left side of the lens.
Size of the image is given by,
$h_{i}=\dfrac{v}{u} h_{0}$
$=\dfrac{-10}{-20} \times 4$
$=2 \mathrm{~cm}$
Size of the object is $=2 \mathrm{~cm}$
Note: A converging lens is usually followed by a diverging lens, which is then followed by another converging lens. By moving toward or away from the object, the first lens adjusts the magnification level of the image. The inverted image is flipped by passing light through the first lens and the diverging lens. After refraction through the concave lens, a ray of light that is parallel to the principal axis diverges, and when we produce these rays backward, they appear to meet at a point called focus. Because the lens diverges the ray of light, it is called a diverging lens.
Formula used:
By lens Formula -
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}$
Size of the image - $h_{i}=\dfrac{v}{u} h_{0}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
a) Optical centre is the point lying on the principal axis of a lens through which light passes through without undergoing any deviation.
b) Given
Focal length, $\mathrm{f}=-20 \mathrm{~cm}$
Height of the object, $\mathrm{h}_{1}=4 \mathrm{~cm}$
Image distance, $v=-10 \mathrm{~cm}$
To find: Object distance $=?$ Size of the image, $\mathrm{h}_{2}=$ ?

Now, using the lens formula,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}$
$=\dfrac{-1}{-10}-\dfrac{1}{-20}$
$=\dfrac{-1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{20}$
$=\dfrac{-2+1}{20}$
$u=-20 \mathrm{~cm}$
Therefore, the object is at a distance of $20 \mathrm{~cm}$ on the left side of the lens.
Size of the image is given by,
$h_{i}=\dfrac{v}{u} h_{0}$
$=\dfrac{-10}{-20} \times 4$
$=2 \mathrm{~cm}$
Size of the object is $=2 \mathrm{~cm}$
Note: A converging lens is usually followed by a diverging lens, which is then followed by another converging lens. By moving toward or away from the object, the first lens adjusts the magnification level of the image. The inverted image is flipped by passing light through the first lens and the diverging lens. After refraction through the concave lens, a ray of light that is parallel to the principal axis diverges, and when we produce these rays backward, they appear to meet at a point called focus. Because the lens diverges the ray of light, it is called a diverging lens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




