
(a) Define crystal lattice.
(b) What is the relation between the angles $\alpha $, $\beta $ and $\gamma $ in a simple hexagonal crystal?
Answer
513k+ views
Hint: A solid can exist in two forms i.e., as a crystalline solid and as an amorphous solid. In crystalline solids, the components have regular ordered arrays and are held together by uniform intermolecular forces whereas the atoms in amorphous solids are not arranged in a regular array. The atoms in a crystalline solid are arranged in a regular repeating three-dimensional array known as crystal lattice.
Complete answer: Crystal lattice: It is defined as the geometrical and symmetrical three-dimensional arrangement of atoms, ions or components inside a crystalline solid as points.
Characteristics of a crystal lattice:
1.The crystal is made up of many atoms which are represented as points in a lattice and hence known as lattice points in a crystal lattice.
2.On combining the lattice points, the shape of a crystal can be determined.
3.There exists a total fourteen Bravais lattices and all have unique shapes and properties.
A crystal lattice is further divided into seven systems which are as follows:
In a simple hexagonal system, the structure consists of four axes in which three axes are of the same length and are present on the same plane. The fourth axis intersects the other three axes at the right angle. The structure of hexagonal crystal system is represented as follows:
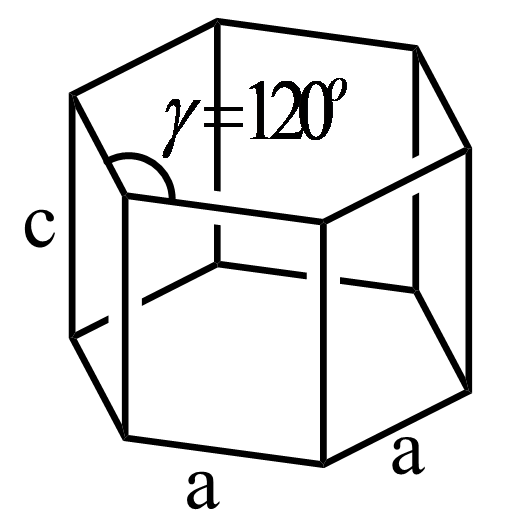
Hence, the relation between the angles $\alpha $, $\beta $ and $\gamma $ in simple hexagonal crystal is as follows:
\[\alpha = \beta = {90^o}\,\,\,\gamma = {120^o}\]
Note:
A crystal system can be described in fourteen different three-dimensional configurations known as Bravais lattice. It is an array of distinct points with an orientation and arrangement which look similar from any distinct point. In the hexagonal crystal system, only one type of Bravais lattice is possible i.e., simple hexagonal cell.
Complete answer: Crystal lattice: It is defined as the geometrical and symmetrical three-dimensional arrangement of atoms, ions or components inside a crystalline solid as points.
Characteristics of a crystal lattice:
1.The crystal is made up of many atoms which are represented as points in a lattice and hence known as lattice points in a crystal lattice.
2.On combining the lattice points, the shape of a crystal can be determined.
3.There exists a total fourteen Bravais lattices and all have unique shapes and properties.
A crystal lattice is further divided into seven systems which are as follows:
| Crystal system | Edge length | Angles |
| Cubic | $a = b = c$ | $\alpha = \beta = \gamma = {90^o}$ |
| Tetragonal | $a = b \ne c$ | $\alpha = \beta = \gamma = {90^o}$ |
| Orthorhombic | $a \ne b \ne c$ | $\alpha = \beta = \gamma = {90^o}$ |
| Monoclinic | $a \ne b \ne c$ | $\alpha = \beta = {90^o}$$\gamma \ne {90^o}$ |
| Hexagonal | $a = b \ne c$ | $\alpha = \beta = {90^o}$$\gamma = {120^o}$ |
| Rhombohedral | $a = b = c$ | $\alpha \ne \beta \ne \gamma \ne {90^o}$ |
| Triclinic | $a \ne b \ne c$ | $\alpha \ne \beta \ne \gamma \ne {90^o}$ |
In a simple hexagonal system, the structure consists of four axes in which three axes are of the same length and are present on the same plane. The fourth axis intersects the other three axes at the right angle. The structure of hexagonal crystal system is represented as follows:

Hence, the relation between the angles $\alpha $, $\beta $ and $\gamma $ in simple hexagonal crystal is as follows:
\[\alpha = \beta = {90^o}\,\,\,\gamma = {120^o}\]
Note:
A crystal system can be described in fourteen different three-dimensional configurations known as Bravais lattice. It is an array of distinct points with an orientation and arrangement which look similar from any distinct point. In the hexagonal crystal system, only one type of Bravais lattice is possible i.e., simple hexagonal cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




