
A cube of side 15 cm is having an air bubble. The bubble appears at 6 cm from one face and at 4 cm from the opposite face. The refractive index of the cube is:
$\text{A.}\quad \dfrac 52$
$\text{B.}\quad \dfrac 32$
$\text{C.}\quad \dfrac 23$
$\text{D.}\quad \dfrac 25$
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: The speed of light changes if it enters from one medium to another. Refractive index ($\mu$) is a property of medium which is a measure of how slow the speed of light gets on entering a medium. Whenever an object is viewed from a different medium, we observe a shift in its position. The new position is called the apparent position.
Formula used:
$Apparent\ depth = \dfrac{actual\ depth }{\mu}$
Complete step by step answer:
The apparent position of the object lying inside another medium can be determined by extending the rays coming directly into the eyes, in backward direction, as shown in the figure.
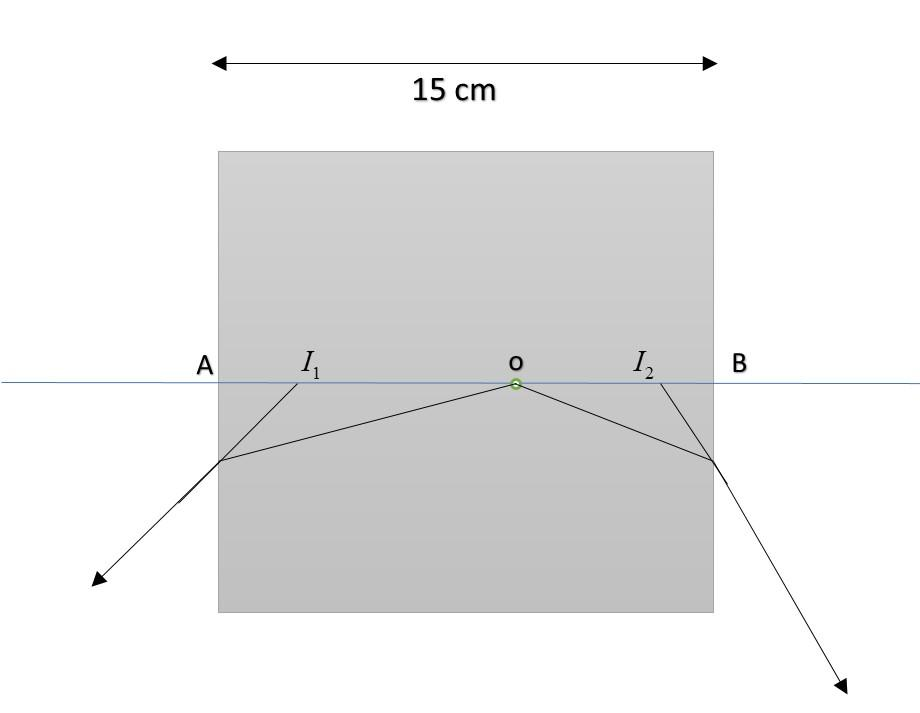
In the figure, we can see that the object (o) is somewhere inside the medium. As the rays move from denser to rarer medium, it changes its path (direction). Hence these rays must be produced backward so that they meet the axis at$I_1\ and\ I_2$. But the actual depth of the object is ‘oB’ and ‘oA’. Whereas apparent depth (which will actually appear to the viewer) is ‘$I_2B \ and\ I_1A$’.
Now using$Apparent\ depth = \dfrac{actual\ depth }{\mu}$, we get;
For $I_1\ :\quad 6 = \dfrac{oA}{\mu}$
Or $oA = 6\mu$ [as object is appearing at 6 cm means apparent depth]
For $I_2:\quad 4 = \dfrac{oB}{\mu}$
Or $oB = 4\mu$
Now, from geometry, we can see that $oA+oB = 15cm$
Thus, putting the values;
$6\mu + 4\mu = 15$
Or $10\mu = 15$
Hence $\mu = \dfrac{15}{10} = \dfrac 32$
Hence option B. is correct.
Note:
Refractive index is a dimensionless quantity which plays an important role in understanding the property of a material. Its definition is the ratio of speed of light in vacuum to that in a medium. Its minimum value is 1 for vacuum. It can’t be lesser than 1 as no medium is rarer than vacuum. Hence we can easily discard option C and D.
Formula used:
$Apparent\ depth = \dfrac{actual\ depth }{\mu}$
Complete step by step answer:
The apparent position of the object lying inside another medium can be determined by extending the rays coming directly into the eyes, in backward direction, as shown in the figure.

In the figure, we can see that the object (o) is somewhere inside the medium. As the rays move from denser to rarer medium, it changes its path (direction). Hence these rays must be produced backward so that they meet the axis at$I_1\ and\ I_2$. But the actual depth of the object is ‘oB’ and ‘oA’. Whereas apparent depth (which will actually appear to the viewer) is ‘$I_2B \ and\ I_1A$’.
Now using$Apparent\ depth = \dfrac{actual\ depth }{\mu}$, we get;
For $I_1\ :\quad 6 = \dfrac{oA}{\mu}$
Or $oA = 6\mu$ [as object is appearing at 6 cm means apparent depth]
For $I_2:\quad 4 = \dfrac{oB}{\mu}$
Or $oB = 4\mu$
Now, from geometry, we can see that $oA+oB = 15cm$
Thus, putting the values;
$6\mu + 4\mu = 15$
Or $10\mu = 15$
Hence $\mu = \dfrac{15}{10} = \dfrac 32$
Hence option B. is correct.
Note:
Refractive index is a dimensionless quantity which plays an important role in understanding the property of a material. Its definition is the ratio of speed of light in vacuum to that in a medium. Its minimum value is 1 for vacuum. It can’t be lesser than 1 as no medium is rarer than vacuum. Hence we can easily discard option C and D.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




