
A cube of edge 'a' has its parallel to the x, y, z-axis of a rectangular coordinate system. A uniform electric field E parallel to the y-axis and a uniform magnetic field is parallel to the x-axis. The rate at which energy flow through each face of the cube is:
A. zero in all faces
B. $\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}EB}{2{{\mu }_{\circ }}}$ parallel to xy plane face and zero in others
C. $\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}EB}{{{\mu }_{\circ }}}$ parallel to xy plane face and zero on others
D. $\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}EB}{2{{\mu }_{\circ }}}$ all faces

Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: The Poynting vector is a vector that represents the direction of energy flux. Energy transfer per unit area per unit time of the Electromagnetic wave. The SI unit is given by watt per meter square.
Complete step by step answer:
Poynting vector is denoted by N or S. When we consider two fields (electric and magnetic field) the direction of this vector is perpendicular to both the electric field and the magnetic field. The vector is represented as the cross product of the electric field and the magnetizing force in that region.
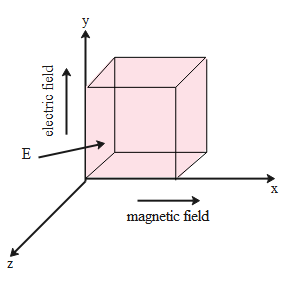
Mathematically:
$\begin{align}
& S=E\times H \\
& S=EH\sin \theta \\
\end{align}$
Where, $S$ is the Poynting vector
$E$ is electric field
$H$ is the magnetizing force
As both the magnetic and electric fields are perpendicular to each other. The value of $\sin \theta $ will be one.
Therefore, the above equation can be written as,
$S=E(H)$
As we know the magnetic field is${{\mu }_{\circ }}$ times the value of magnetic force.
Mathematically,
$\begin{align}
& B={{\mu }_{\circ }}H \\
& H=\dfrac{B}{{{\mu }_{\circ }}} \\
\end{align}$
So, by putting the value of $H$ in equation of $S$:
$S=\dfrac{EB}{{{\mu }_{\circ }}}$
The energy through the faces which are parallel to the x-y plane is given by the product of the value of the poynting vector and the area of the surface. Mathematically;
$P=(A)(S)$
By putting the values of $A$ and $S$in the above equation:
$\begin{align}
& P={{a}^{2}}\times \dfrac{EB}{{{\mu }_{\circ }}} \\
& P=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}EB}{{{\mu }_{\circ }}} \\
\end{align}$
Energy flow from the other axis which is not parallel to the x-y plane will be zero.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The Poynting vector was introduced by John Henry Poynting in the year 1884. At the microscopic level, it becomes important to state the Poynting vector in the teams of electric field (E) and magnetic field (B). The surface of the cube which is perpendicular to the Poynting vector will have an energy flow, other surfaces will experience zero energy transfer.
Complete step by step answer:
Poynting vector is denoted by N or S. When we consider two fields (electric and magnetic field) the direction of this vector is perpendicular to both the electric field and the magnetic field. The vector is represented as the cross product of the electric field and the magnetizing force in that region.

Mathematically:
$\begin{align}
& S=E\times H \\
& S=EH\sin \theta \\
\end{align}$
Where, $S$ is the Poynting vector
$E$ is electric field
$H$ is the magnetizing force
As both the magnetic and electric fields are perpendicular to each other. The value of $\sin \theta $ will be one.
Therefore, the above equation can be written as,
$S=E(H)$
As we know the magnetic field is${{\mu }_{\circ }}$ times the value of magnetic force.
Mathematically,
$\begin{align}
& B={{\mu }_{\circ }}H \\
& H=\dfrac{B}{{{\mu }_{\circ }}} \\
\end{align}$
So, by putting the value of $H$ in equation of $S$:
$S=\dfrac{EB}{{{\mu }_{\circ }}}$
The energy through the faces which are parallel to the x-y plane is given by the product of the value of the poynting vector and the area of the surface. Mathematically;
$P=(A)(S)$
By putting the values of $A$ and $S$in the above equation:
$\begin{align}
& P={{a}^{2}}\times \dfrac{EB}{{{\mu }_{\circ }}} \\
& P=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}EB}{{{\mu }_{\circ }}} \\
\end{align}$
Energy flow from the other axis which is not parallel to the x-y plane will be zero.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The Poynting vector was introduced by John Henry Poynting in the year 1884. At the microscopic level, it becomes important to state the Poynting vector in the teams of electric field (E) and magnetic field (B). The surface of the cube which is perpendicular to the Poynting vector will have an energy flow, other surfaces will experience zero energy transfer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




