
A cube is arranged such that its length, breadth, height are along X, Y and Z directions. One of its corners is situated at the origin. Length of each side of the cube is 25cm. The components of electric field are ${{E}_{x}}=400\sqrt{2}N{{C}^{-1}}$, ${{E}_{y}}=0$ and ${{E}_{z}}=0$ respectively. Then what will be the flux coming out of the cube at one end, whose plane is perpendicular to X axis?
$\text{A}\text{. 25}\sqrt{2}\text{ N}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{C}}^{\text{-1}}}$
$\text{B}\text{. 5}\sqrt{2}\text{ N}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{C}}^{\text{-1}}}$
$\text{C}\text{. 250}\sqrt{2}\text{ N}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{C}}^{\text{-1}}}$
$\text{D}\text{. 25 N}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{C}}^{\text{-1}}}$
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Electric flux is a property of the electric field. Electric flux can be defined as the number of electric field lines passing perpendicular through the surface. In this question, we can calculate electric flux through the required plane by directly using the expression of electric flux.
Formula used: Electric flux ${{\phi }_{E}}=\mathop{{\int\!\!\!\!\!\int}\mkern-21mu \bigcirc}\limits_S
\vec{E}.d\vec{S} $
Complete step by step answer:
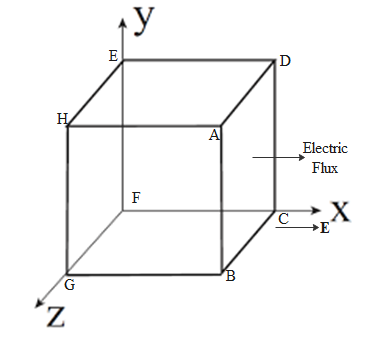
The cube is placed as shown in the diagram below.
“Electric flux is the rate of flow of the electric field through a given area.” Electric flux through a surface $S$ is defined as the surface integral of dot product of electric field and surface area vector.
${{\phi }_{E}}=\mathop{{\int\!\!\!\!\!\int}\mkern-21mu \bigcirc}\limits_S
\vec{E}.d\vec{S} $
Where
$\phi_E=$ Electric flux
$\vec{E}=$ Electric field vector
$d\vec{S}=$ Differential area on the closed surface S with a surface normal in outward direction
Electric Flux has SI unit $N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}}$
According to question,
$\vec{E}=400\sqrt{2}\text{ }\hat{i}$ and $d\vec{S}=A\text{ }\hat{i}$ (where A=surface area of the surface)
Substituting the values in Gauss’ law, we get
${{\phi }_{E}}=\mathop{{\int\!\!\!\!\!\int}\mkern-21mu \bigcirc}\limits_ABCD
(400\sqrt{2}i).({{0.25}^{2}}i) $
${{\phi }_{E}}=25\sqrt{2}\text{ N}{{\text{m}}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information: If we had calculated the electric flux through EFGH surface, we would have gotten the same result but with a negative sign indicating opposite direction.
Note: It can be noted that electric flux through the surface which has its plane parallel to direction of electric field is zero because the surface area vector for the case is perpendicular to the electric field vector.
In this problem, net electric flux through the cube is zero. This is because there is no net charge inside the cube.
Formula used: Electric flux ${{\phi }_{E}}=\mathop{{\int\!\!\!\!\!\int}\mkern-21mu \bigcirc}\limits_S
\vec{E}.d\vec{S} $
Complete step by step answer:
The cube is placed as shown in the diagram below.

“Electric flux is the rate of flow of the electric field through a given area.” Electric flux through a surface $S$ is defined as the surface integral of dot product of electric field and surface area vector.
${{\phi }_{E}}=\mathop{{\int\!\!\!\!\!\int}\mkern-21mu \bigcirc}\limits_S
\vec{E}.d\vec{S} $
Where
$\phi_E=$ Electric flux
$\vec{E}=$ Electric field vector
$d\vec{S}=$ Differential area on the closed surface S with a surface normal in outward direction
Electric Flux has SI unit $N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}}$
According to question,
$\vec{E}=400\sqrt{2}\text{ }\hat{i}$ and $d\vec{S}=A\text{ }\hat{i}$ (where A=surface area of the surface)
Substituting the values in Gauss’ law, we get
${{\phi }_{E}}=\mathop{{\int\!\!\!\!\!\int}\mkern-21mu \bigcirc}\limits_ABCD
(400\sqrt{2}i).({{0.25}^{2}}i) $
${{\phi }_{E}}=25\sqrt{2}\text{ N}{{\text{m}}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information: If we had calculated the electric flux through EFGH surface, we would have gotten the same result but with a negative sign indicating opposite direction.
Note: It can be noted that electric flux through the surface which has its plane parallel to direction of electric field is zero because the surface area vector for the case is perpendicular to the electric field vector.
In this problem, net electric flux through the cube is zero. This is because there is no net charge inside the cube.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




