
A crossed lens is used to minimize spherical aberration. The ratio of the radii of curvatures is ($\mu =1.5$)
a) 1/6
b) -1/6
c) 6
d)-6
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: A crossed lens is basically a lens of the same material but the radius of curvatures for both the lenses are different. This is basically done to reduce spherical aberration. Let us say a lens consists of two different radius of curvatures i.e. ${{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ and }{{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}$. The relation between These two radius of curvatures such that they reduce spherical aberration is given by $\dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{2{{\mu }^{2}}-\mu -4}{\mu (1+2\mu )}...(1)$. Hence from this expression we can obtain the required ratio.
Complete step by step answer:
To begin with let us first understand what does spherical aberration mean from the below diagram.
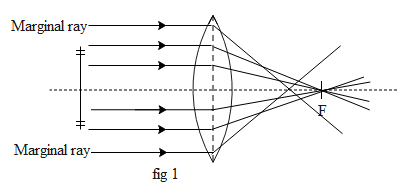
In the above diagram fig 1we can see that the marginal rays and the paraxial rays meet the optical axis at two different points. This phenomenon is defined as the spherical aberration. This aberration cab be reduced by increasing the thickness of the lens at the periphery of the lens. Hence lenses with two different radius of curvatures are made such that the marginal rays suffer less deviation. Figure below fig 2 shows an example of crossed lens to reduce aberration.
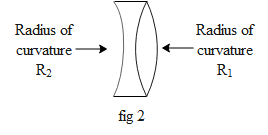
In the above diagram let us say the lens of two different radius of curvatures are made of the same material. Hence from equation 1 the ratio of their radius of curvature is given by,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{2{{\mu }^{2}}-\mu -4}{\mu (1+2\mu )} \\
& \dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{2{{\left( 1.5 \right)}^{2}}-1.5-4}{1.5(1+2\left( 1.5 \right))} \\
& \dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{4.5-1.5-4}{1.5\left( 4 \right)}=\dfrac{-1}{6} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the correct answer to the above question is option b.
Note:
The basic cause of aberration in the lens is the aperture of the lens and it’s thickness. There are many other ways as well wherein spherical aberration can be reduced. One of the ways is stopping the marginal rays from entering the lens. It is to be noted that till now there are no strategies generated such that the aberration is reduced to zero.
Complete step by step answer:
To begin with let us first understand what does spherical aberration mean from the below diagram.

In the above diagram fig 1we can see that the marginal rays and the paraxial rays meet the optical axis at two different points. This phenomenon is defined as the spherical aberration. This aberration cab be reduced by increasing the thickness of the lens at the periphery of the lens. Hence lenses with two different radius of curvatures are made such that the marginal rays suffer less deviation. Figure below fig 2 shows an example of crossed lens to reduce aberration.

In the above diagram let us say the lens of two different radius of curvatures are made of the same material. Hence from equation 1 the ratio of their radius of curvature is given by,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{2{{\mu }^{2}}-\mu -4}{\mu (1+2\mu )} \\
& \dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{2{{\left( 1.5 \right)}^{2}}-1.5-4}{1.5(1+2\left( 1.5 \right))} \\
& \dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{4.5-1.5-4}{1.5\left( 4 \right)}=\dfrac{-1}{6} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the correct answer to the above question is option b.
Note:
The basic cause of aberration in the lens is the aperture of the lens and it’s thickness. There are many other ways as well wherein spherical aberration can be reduced. One of the ways is stopping the marginal rays from entering the lens. It is to be noted that till now there are no strategies generated such that the aberration is reduced to zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




