
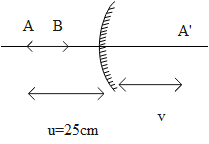
A convex mirror of focal length 10cm is shown in the figure. A linear object AB=5cm is placed along the optical axis. Point B is at a distance 20cm from the pole of the mirror. Then size of image of AB will be:-
$\begin{align}
& (1)\dfrac{5}{14}cm \\
& (2)\dfrac{10}{21}cm \\
& (3)\dfrac{10}{14}cm \\
& (4)2.5cm \\
\end{align}$

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: By using the mirror equation we will find the dimensions of image AB. By knowing the worth of focal distance and object distance using mirror equations we will find the dimensions of the image. Also use sign convention while considering the thing distance , focal distance and image size.
Formula used: Mirror equation,
$\dfrac{1}{u}+\dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete step by step answer:
For point A,
f= 10cm
Object distance AB = 5cm
u = -25cm
Now using mirror equation and substituting the value of f & u we get v,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}-\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{10}-\dfrac{1}{-25} \\
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{35}{250}=\dfrac{7}{50} \\
& v=\dfrac{50}{7}cm=7.14cm \\
& \\
\end{align}$
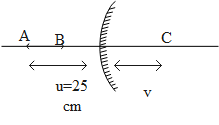
For point B,
Again applying mirror equation and substituting,
f= 10cm
u=-30cm
We get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{10}-\dfrac{1}{-30} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{4}{30} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\dfrac{30}{4}=7.5cm \\
\end{align}$
Size of image AB= 7.5 -7.14 =0.36cm
So, the correct answer is “Option 1”.
Additional Information: A convex mirror or diverging mirror may be a curved mirror during which the reflective surface bulges towards the sunshine source. Convex mirrors reflect light outwards, therefore they're not wont to focus light. The image is smaller than the thing , but gets larger because the object approaches the mirror.
Virtual images are always formed by convex mirrors. Plane mirrors and convex mirrors will always produce an upright image if the thing is found in front of the focus.
Note: While using sign convention, note that we always place an object in front of the mirror hence the sign of the object is taken as negative. Since, the centre of curvature and focus lies behind the convex mirror, so sign of radius of curvature and focal distance are taken as positive just in case of convex mirror.
Formula used: Mirror equation,
$\dfrac{1}{u}+\dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete step by step answer:
For point A,

f= 10cm
Object distance AB = 5cm
u = -25cm
Now using mirror equation and substituting the value of f & u we get v,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{f}-\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{10}-\dfrac{1}{-25} \\
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{35}{250}=\dfrac{7}{50} \\
& v=\dfrac{50}{7}cm=7.14cm \\
& \\
\end{align}$
For point B,

Again applying mirror equation and substituting,
f= 10cm
u=-30cm
We get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{10}-\dfrac{1}{-30} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{4}{30} \\
& \Rightarrow v=\dfrac{30}{4}=7.5cm \\
\end{align}$
Size of image AB= 7.5 -7.14 =0.36cm
So, the correct answer is “Option 1”.
Additional Information: A convex mirror or diverging mirror may be a curved mirror during which the reflective surface bulges towards the sunshine source. Convex mirrors reflect light outwards, therefore they're not wont to focus light. The image is smaller than the thing , but gets larger because the object approaches the mirror.
Virtual images are always formed by convex mirrors. Plane mirrors and convex mirrors will always produce an upright image if the thing is found in front of the focus.
Note: While using sign convention, note that we always place an object in front of the mirror hence the sign of the object is taken as negative. Since, the centre of curvature and focus lies behind the convex mirror, so sign of radius of curvature and focal distance are taken as positive just in case of convex mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




