
A convex lens of focal length is $\dfrac{2}{3}$times \[R\]. Find the refractive index of the material.
Answer
469.2k+ views
Hint: We are going to find the refractive index of the material with the given focal length is $\dfrac{2}{3}$ times \[R\] .We need to discuss the convex lens and the formula used to find the focal length of the convex lens. A lens is a material having one of the surfaces curved. The convex lens containing a surface bulged on one side is called a simple convex lens. Refractive index is defined as the ratio between the velocity of light in a vacuum$(c)$ and the velocity of light in a given substance $(v)$. It is also the ratio between the sine of the angle of incidence $(\sin i)$ and the angle of refraction $(\sin r)$.
Formula used:
Using Len’s maker's formula, the focal length of a lens is given by
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {n - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right)$
Where,
$f$- focal length of a lens
$n$- refractive index of the material
${R_1},{R_2}$ - radii of curvature of the lens
Complete step by step solution:
From the given data, the focal length is $f = \dfrac{2}{3}R$.
For convex lens,
${R_1} = + R,{R_2} = - R$.
Applying these values in the above formula,
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {n - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right)$ , this formula becomes
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}R} \right)}} = \left( {n - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{{ - R}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{{2R}} = \left( {n - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{R} + \dfrac{1}{R}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{{2R}} = \left( {n - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{2}{R}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{{2R}} \times \dfrac{R}{2} = \left( {n - 1} \right)$,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{4} = \left( {n - 1} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow n = \left( {\dfrac{3}{4} + 1} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow n = \left( {\dfrac{7}{4}} \right)$
$\therefore n = 1.75$
From the above calculations, we found that the refractive index of the material $n = 1.75$ when the focal length of the convex lens is,
$f = \dfrac{2}{3}R$.
Note:
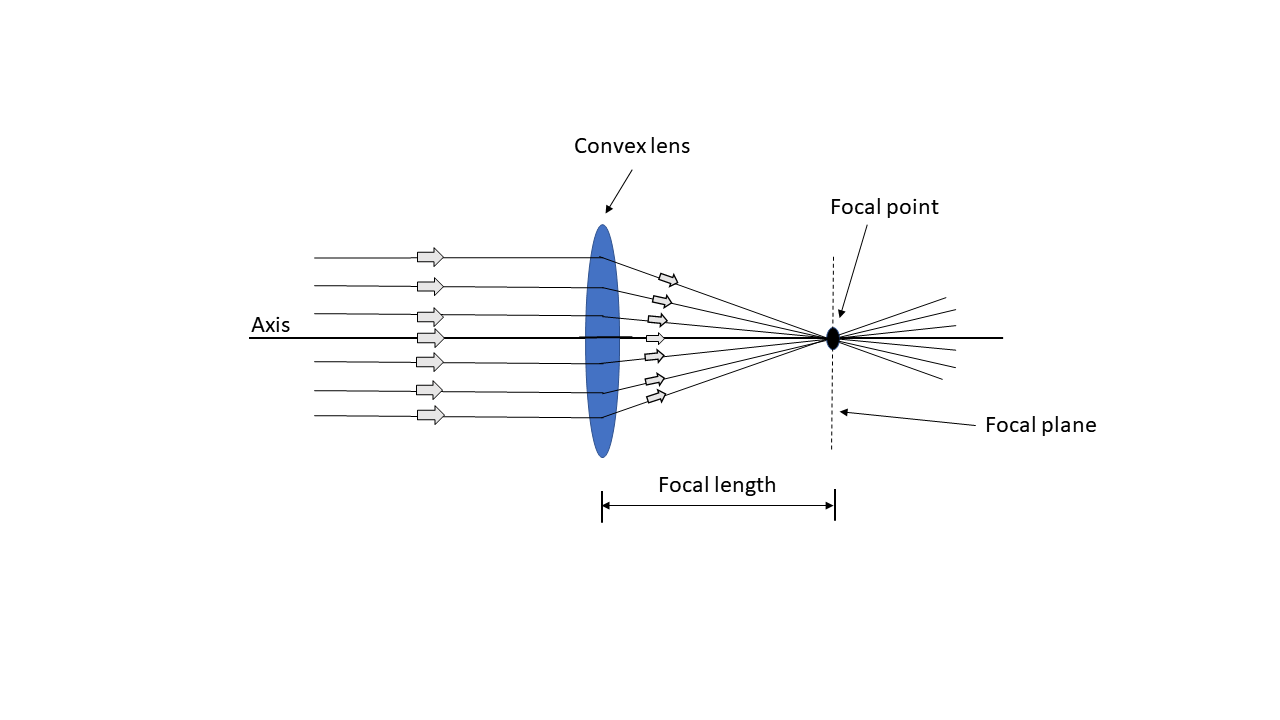
The collimated beam, when passing through the convex lens, is focused in a spot. The distance between the lens and the point focused by the converging beam is called focal length and that point is known as the focal point. The convex lenses are in cameras, microscopes, eyeglasses, projectors, etc. The Convex lens is mainly used for converging all incident rays to a particular point.

Formula used:
Using Len’s maker's formula, the focal length of a lens is given by
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {n - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right)$
Where,
$f$- focal length of a lens
$n$- refractive index of the material
${R_1},{R_2}$ - radii of curvature of the lens
Complete step by step solution:
From the given data, the focal length is $f = \dfrac{2}{3}R$.
For convex lens,
${R_1} = + R,{R_2} = - R$.
Applying these values in the above formula,
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {n - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right)$ , this formula becomes
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}R} \right)}} = \left( {n - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{R} - \dfrac{1}{{ - R}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{{2R}} = \left( {n - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{R} + \dfrac{1}{R}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{{2R}} = \left( {n - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{2}{R}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{{2R}} \times \dfrac{R}{2} = \left( {n - 1} \right)$,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{4} = \left( {n - 1} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow n = \left( {\dfrac{3}{4} + 1} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow n = \left( {\dfrac{7}{4}} \right)$
$\therefore n = 1.75$
From the above calculations, we found that the refractive index of the material $n = 1.75$ when the focal length of the convex lens is,
$f = \dfrac{2}{3}R$.
Note:
The collimated beam, when passing through the convex lens, is focused in a spot. The distance between the lens and the point focused by the converging beam is called focal length and that point is known as the focal point. The convex lenses are in cameras, microscopes, eyeglasses, projectors, etc. The Convex lens is mainly used for converging all incident rays to a particular point.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




